Have you ever wondered what is the best exercise to build chest muscles? You won't have to rack your brains over this question anymore! Here is our selection of the top 10 exercises for the pectoral muscles.
There are dozens of exercises for the chest muscles. There are at least 84 similar exercises listed in the Bodybuilding.com database alone, but you probably don't want to spend days trying every single chest exercise. We did the work for you and selected the most effective basic chest exercises, as well as isolation exercises.
Please note that this list does not include exercises that are too heavy. It contains only the best chest exercises for increasing muscle mass with little instructions and tips on how to perform them. You can include any of them in your chest training program or simply change one exercise for another whenever you want to try something new.
What muscles are involved?
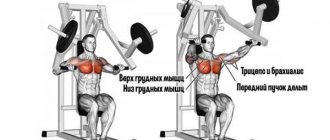
Let us immediately note that the main muscles involved are the pectoralis major and minor. These groups are the focus when working with block weight simulators. Hummers are the most popular, but there are other proven mechanisms. In addition to breasts, you can develop:
- shoulders (back, middle, front deltas);
- lateral triceps bundles;
- medium and long triceps bundles;
- serratus anterior abdominal muscle.
Important! The exercise is considered isolated and allows you to work out the pectoral muscles as much as possible. This should be taken into account when building your training program.
How to get into the starting position for the dumbbell overhead press
To get into the starting position for the overhead dumbbell press, find a helper or two or use the method described below. But if you intend to do a seated bench press with your back resting on the back of the bench, then first prepare the bench - set its back at an angle of 75-80 degrees and tilt its seat if it is adjustable.
Stand directly in front of the bench, with your feet hip-width apart. Each dumbbell should lie on the floor touching its corresponding foot. The dumbbell handles should be parallel to each other. Bend your legs and grab the dumbbells from the floor with a parallel grip and good form, just like a deadlift. Standing straight, hold the dumbbells so that the center of the back end of each dumbbell rests on the corresponding thigh, just above the knee.
If you are using dumbbells with raised ends or locks (likely collapsible dumbbells), then align just the inside of the bottom plate of each dumbbell with the outer bottom of the corresponding thigh. You can do this if the radius of the dumbbell plate is large enough so that the dumbbell sits vertically on your thigh when you sit down. But make sure the locks are securely in place. What could be more dangerous than a dumbbell that falls apart during an exercise?
Sit on a bench, rest your buttocks on the lower back of the bench if you are going to do bench presses while sitting on an incline bench. When you sit down, the dumbbells will be in a vertical position. The dumbbells should still remain on your thighs, just above your knees.
As soon as you sit on the bench, sharply lift your right knee up and at the same time powerfully pull the dumbbell with your right hand to throw it towards your right shoulder. Then do the same with your left knee and left arm to throw the second dumbbell to your left shoulder.
Once the dumbbells are at your shoulders, you have three options. You can stand up and do a standing press, or you can do a seated press, or you can do a seated press with your back against the back of a bench. If you choose the last option, then, without arching your lower back
, lean back to rest your back against the back of the bench. You will be in the starting position for the press.
After completing the dumbbell press, lower the dumbbells straight to the floor under control. Bring your knees together so as not to touch your legs with the dumbbells.
Before doing heavy overhead dumbbell presses, learn to get into the starting position. Over the course of a couple of workouts, do sets and reps with relatively light weights so you can learn the proper technique needed to lift dumbbells safely.
In addition, there is another possibility of performing any variant of the dumbbell press - be it standing, lying on a horizontal bench or on an incline: using chains of adjustable length, you can hang the dumbbells from the bar at the top. The dumbbells should hang at the point where your bottom position will be in the exercise. However, make sure that this design is reliable.
The picture shows a way in which you can pick up dumbbells from the floor and take the starting position.
Overhead press. Notice how the grip changes from parallel to pronated as you move.
Exercise technique
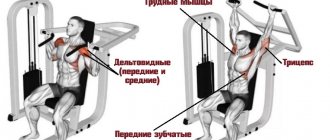
Make sure that the handles of the machine are adjusted to the level of your shoulders (or slightly lower). Sit up straight, press your back and neck against the back of the machine. The legs should be spread wider than the shoulders, and the feet and knees form a right angle. Use an overhand grip with your palms facing forward. Hands - approximately shoulder width apart. Procedure :
- Take a deep breath and begin to squeeze the handle away from you, trying not to exhale.
- You can exhale in one of two cases - when you have passed the point of highest tension or with your arms fully extended.
- The top point is the right moment for a short pause.
- Hold your breath.
- Proceed to smoothly, without jerking, return the handles to their original position.
- At the lowest point of the amplitude, do not take any breaks - immediately squeeze the handles according to the scheme described above.
On a note! The exercise differs in that each arm of the athlete receives a personal load. This leads to uniform pumping of muscle groups. You can get a similar effect by working with dumbbells. It’s just not recommended to change the amplitude in the simulator.
Varieties of seated press: correct technique and significant nuances
In gyms there are various modifications of devices for performing pressing movements. They can be either load-bearing or loadable. You can train in them at an angle, as well as do horizontal and vertical bench presses: it all depends on the design of the particular simulator.
All such simulators are characterized by a common algorithm of actions.
Before starting the class, you should warm up your upper body, paying special attention to your shoulder joints. Before the first approach, install a small weight: this will be a warm-up set.
V
Bench press in a special machine
Many gyms have press machines that allow you to move upward at an angle, as well as horizontal presses. They are used in complex training of the upper body.
Almost all such devices provide the ability to adjust the seat - you need to use it by adjusting the height to suit your height. Having settled down while sitting, press your body tightly against the back, straighten your shoulders and slightly lean your chest forward. Legs spread apart rest firmly on the floor.
Holding the handles with a comfortable grip, remove the weight and hold it with your hands (if there is a special pedal for bringing the weight to the starting position, this will make the task much easier). The shoulder blades are in a flattened state, the elbows are apart.
- Exhaling, with a powerful effort, squeeze the weight in front of you until your arms straighten, maintaining a slight bend in the elbow joints (“soft elbows”).
- They are fixed in this position for a couple of seconds: the target muscles are statically tense.
- As you inhale, maintaining tension in the muscles, slowly return the handles to their original position.
V
Do 12 times in 3-4 sets.
Video: Technique for performing seated bench presses in a machine
Hammer Seated Press
For performing the seated press, an ideal machine is called a “Hammer” in the sports community, after the manufacturer of such devices.
This lever type machine is simple and efficient, being operated by pushing out a lever to which a weight is attached. It was originally created to reduce the load on athletes’ joints during pressing movements.
A
The halls feature a variety of modifications of Hummers, allowing you to shift the working emphasis in the presses:
- A vertical press device that simulates similar movements with free weights. The deltoids receive the main load here.
- Angle press machine. It activates the pectoral muscles with an emphasis on its upper zone.
Before starting the lesson, the selected device must be adjusted to suit your height. The seat is installed so that the handles are placed at mid-chest level or slightly lower. The optimal weight is placed on the machine.
Having settled down on the seat, you need to press your back tightly against its back: there should not be a large distance between the exercise machine and your lower back. Feet rest on the floor.
Holding the handles of the Hummer, squeeze your shoulder blades together, spread your elbows to the sides and take a deep breath. With an optimal grip width, the forearm at the lowest point will be perpendicular to the body.
- With a powerful muscular effort, while exhaling, squeeze the weight in front of you, straightening your arms (the elbows remain “soft”, without “snapping” in the joints). Shoulders are pressed against the back, elbows pointing to the sides.
- At the top point you need to fixate for 1-2 seconds, focusing on the static contraction of the target muscles.
- While inhaling, slowly and smoothly lower the handles to their original position.
Do 12–15 repetitions in 3–4 approaches.
V
When practicing the Hummer, during the positive phase of the movement, you need to learn to resist the instinctive arching of your back. This is important, since with this technique the back muscles will take on a significant part of the load, and the spine will be subject to undesirable effects.
The lowering of the handles lasts longer than the pressing movement. Here you need to avoid sharply “throwing” your arms down, moving them under control and maintaining tension in the muscles.
V
The correct biomechanics of movement in this device implies a contracted position of the shoulder blades and a protruding chest at all points of the trajectory. There is no need to concentrate on pushing the weight out (similar to a barbell bench press). What is important here is a smooth and leisurely straightening of the arms; you should seem to be moving the weight, not pushing it.
Video: How to properly perform a bench press in a Hummer
Smith machine press to work the pectoral muscles
You can specifically work the target muscles without spending additional effort on the work of the stabilizer muscles in a Smith machine. As with other bench press machines, the Smith uses the same movements as in a free weight class, but in a more focused manner. This is due to the fact that the bar here goes strictly along the guides, the trajectory of its movement is set initially.
Press sitting in front of you at an angle in the Smith machine
First you need to set the desired angle of the bench and place it directly under the bar. It is advisable to determine the exact placement on an individual basis by performing several trial repetitions without weight. After this, the optimal weight is set.
After sitting down on a bench (the bar is in front), you need to fix the position of the body: your feet rest on the floor, your pelvis and back are pressed against the seat). The bar is taken with a straight closed grip with a wide stance of the hands, by turning it, remove it from the stoppers and lower it to approximately the level of the chin.
- As you exhale, squeeze the bar above yourself. The arms are not fully straightened, leaving a slight angle at the elbow joints.
- At the top point, pause for a second, concentrating on peak muscle contraction.
- As you inhale, lower the bar under control to its original position. There is no need to put it on your chest.
Perform 10–12 times in 3–4 approaches.
V
During movements, you should not arch your lower back - this will overload the spine and change the emphasis of the load.
Video: Press sitting in a Smith machine in front of you - pumping up the chest and shoulder muscles
Smith machine overhead press
Before you begin this exercise, you need to thoroughly warm up your shoulder joints, since they have serious work ahead of them: the overhead press is more dangerous than other similar movements.
In the Smith machine, the bar is placed in the top position, so that it can be comfortably grasped with straightened arms. A weight is placed on it. A bench with a vertical backrest is placed under the bar (if it is not available, a regular gymnastics bench will do). You should position yourself on it so that the bar is positioned exactly above your head. The abdominal muscles are statically tense, the feet rest firmly on the floor. Raising your hands, grab the bar with a grip wider than your shoulders and remove it from the stoppers.
- Inhaling, in a controlled movement, bring the barbell behind your head to approximately the middle of your head or slightly lower. In the lower position, an angle of 90 degrees should form between the joints of the shoulder and elbow. This is an average indicator; the level of lowering of the bar is determined by the flexibility of the athlete’s joints. It's important not to overdo it here.
- There is a second pause at the bottom.
- As you exhale, push the bar up with a powerful movement, avoiding “snapping” in the elbow joints.
Do 8-10 times in 3 sets.
V
To make launching the projectile more comfortable, it is permissible to tilt your head forward slightly, without allowing your back to lift off the back of the bench. The bar must move strictly along a vertical trajectory without deviation to the sides.
It is not recommended to work with heavy weights in this exercise: this increases the risk of injury to the shoulder joints.
Video: Correct technique for performing seated overhead presses in a Smith machine
Are there any alternatives?
It is important to understand that we are talking about the “finishing” type of strength exercises. The seated press is performed at the end of the workout to focus attention on poorly developed muscle groups. The bench press is more popular, but it is not suitable for bodybuilders who have suffered a back injury. Thus, the bench press and seated press are interchangeable, but it all depends on the presence/absence of injuries. You can also achieve a similar effect by pressing dumbbells.
This is not a basic exercise. The seated press is an imitation. You lift the usual pancakes, only they are secured in blocks. This exercise will not seriously increase muscle mass, but you will get the desired relief.
Using a barbell on a Smith machine
Hand presses in the exercise machine from behind the head are a rather complex and traumatic exercise, and therefore require careful warming up of the joints. The bar in the machine is installed in the upper position, but the equipment should be comfortable for a classic grip. A bench with a vertical back is installed under the weighted bar. It is important to position yourself on the gymnastic apparatus so that the bar is directly above your head.
The abdominal muscles must be kept static, and the feet should rest firmly on the floor. The projectile is removed from the stoppers with a controlled movement, while the bar is retracted approximately to the middle of the head. You can lower it lower, but it is important to ensure that a 90-degree angle is formed between the joint of the shoulders and elbow. The indicator is average, since everything is determined by the athlete’s flexibility indicators. In the lower position, a pause is necessary, and then with a powerful movement the bar is pushed up.
The trajectory of the barbell's movement should be strictly vertical, and your back should not leave the bench. It is important to choose small weights, since weight increases the risk of injury when sitting on a chest press.
Workout table
| Curling arms with weight | 12 times, 3–4 sets |
| Vertical presses | 12–15 times, 3–4 sets |
| Smith machine presses | 10–12 times, 3–4 sets |
| Barbell on a Smith machine | 8–10 times, 3 sets |
Let's consider the benefits
So, why not dumbbells or a “standing” version? The exercise has a number of advantages that allow you to confidently introduce the seated press into your training complex. These are the benefits :
- Effectively working the pectoral muscles with minimal stress on the back.
- Platen racks are useful when dealing with injuries.
- The isolating type allows you to maximally work specific muscle bundles.
- The technique is quite simple.
- The risk of injury is reduced to a minimum.
- The trajectory of movement of the handles is rigidly fixed.
Chest press in a block machine
Train in lever trainers – developing and honing the shape of bulky pectoral muscles. Differs from the barbell press in the degree of isolation. Having taken a specific position, work is performed in the simulator along a given trajectory. The load is concentrated as much as possible on the muscle group. There are no stabilizing muscles that perform other functions. Tip: it is recommended to perform the exercise after the basic exercises for maximum muscle development. Pros:
- Stabilizers do not work.
- It is possible to work out each side of the body separately, to give symmetry to paired muscle groups.
- The exercise is safe to perform as it reduces the risk of injury. You need to work in the simulator with the correct technique and not chase huge weights.
To apply the load on the chest, you need to monitor the position of your elbows relative to each other during execution.
Technical advice from professionals
It is important to take into account the following detail : mainly the anterior muscle bundle is worked out. The triceps is involved as an extensor, the serratus anterior and pectoralis minor muscles are responsible for shifting the shoulder blades. Fitness trainers recommend paying attention to the following details:
- the maximum load is obtained only in one case - when the elbows move along the trajectory of a small arc;
- Having reached the end point of the amplitude, do not forget to move your hands in the direction of the conditional center of the body;
- the shoulder blades should move to the sides when performing the exercise;
- contractions of two muscle bundles - the serratus anterior and pectoralis minor - will help make the body static;
- try to turn off the stabilizer muscles - this is how you can work the target group;
- Do not move your elbows too far behind your back;
- Make sure that the pectoral muscles do not relax at all.
A guarantee of no injuries is to hold your breath at the start. The spine is extended, which leads to an anatomically correct location of the joints. According to statistics, strength increases by 20% with breathing holds.
“To increase the intensity, I do a full stretch—lowering the weight as much as possible. The arms at the elbows should straighten completely, and at the final point of the amplitude I rest for no more than a second. Partial reps at the end of a set are another secret to my success.” (Dorian Yates)
Useful tips
- You should not take a long break in the starting position between each new repetition, since during the maximum approach of the handles, the chest muscles become very tense. It should be spent on performing the exercise, and not in vain. Stopping can greatly relax the muscles, so the athlete will have to strain again to move the weight. However, in some cases, this technique is used to stimulate muscle growth.
- It is important to hold your breath as this helps keep your body straight. Experts have calculated that muscle strength increases by 10% when holding your breath.
- If the weight is too heavy, you can try pressing your feet harder into the floor, but do not lift your back and lower back from the back of the machine.
- To work the muscles from different angles, you can use another type of grip, when your palms face each other.
When returning to the starting position, it is important to watch your elbows - they should not go beyond the level of your back, as you can injure your shoulder.
Typical beginner mistakes
Let's look at the typical mistakes of novice bodybuilders when doing chest presses in block weight machines. Most of the “jambs” have already been voiced, so let’s summarize :
- elbows pushed too far back;
- improper breathing;
- pauses between repetitions;
- sudden jerks;
- pushing out the weight with the body (this should be done with the pectoral muscles);
- incorrect height adjustment of handles;
- legs brought together or straightened at the knees.
Dumbbell press
Dumbbells can be used for any of the three main variations of the overhead press: standing, sitting, and sitting with your back against the back of the bench. Dumbbells allow you to hold your hands parallel to each other with either a pronated grip or a mixed grip. During each repetition, you can change the position of the hands directly along the movement, if it is more convenient for you. Try different hand positions and find the one that allows you to make the most powerful and comfortable movement. You may find that it works best for you to keep your hands parallel to each other at shoulder level, and then rotate your hands into a pronated position as you move through the upper half of the range.
When doing dumbbell overhead presses, be sure to hold the dumbbells above your shoulders. Don't let them "drift" to the sides and drop too far down in the bottom position.
Dumbbells can be pressed simultaneously or alternately, i.e. her hand straightens at the moment when the other goes down. Or, you can raise and lower one hand while the other hand waits its turn at your shoulder. However, this technique results in asymmetrical loading and a tendency to lean laterally. If you have a bad back, it is safer to squeeze both dumbbells at the same time. If you don’t want to lift two dumbbells at the same time, then try doing a dumbbell press with one hand.
The one-arm dumbbell press can be done while sitting or standing. Using both hands, grab a dumbbell and bring it to your right shoulder. Holding the dumbbell in your right hand, grab something strong and stable with your left hand. Holding the support in this way with your left hand, perform a dumbbell press with your right hand, moving the weight along the trajectory that seems most powerful and comfortable to you. Then grab the support with your right hand and perform the exercise with your left hand. By holding onto the support with your free hand, you will be able to perform the exercise more technically and reduce the tendency to lean back.
The dumbbell press forces you to control your balance more than the barbell press and is a great workout for the shoulders, upper back and triceps. It also puts more stress on your core muscles if you do it while standing. But probably its most important advantage is that it allows you to find the position of your hands and the trajectory of movement that suits you ideally. The barbell limits your freedom in choosing the position of your hands, because you are forced to grip the bar with a pronated grip.
The disadvantage of dumbbells is that they make it more difficult to take the starting position and maintain balance during the exercise. It is much easier and safer to perform the barbell press inside a power rack with the restraints set at the correct height.
One-arm dumbbell press.
Bench press VS seated press: the agony of choice
Probably, many athletes were tormented by the torment of choosing between two types of chest press - sitting and lying. The question comes down to this: Can you lift the same amount of weight doing a seated chest press as you can doing a bench press? The answer is: sitting, you live more. But don't rush to conclusions. The bench press has its advantages and disadvantages. Let's start with the pros:
- Synchronized hand movement.
- Increased strength as you lift heavier weights.
- Working with free weights, which leads to activation of stabilizer muscles.
Among the disadvantages, we note the dangerous position of the shoulder joints, the high level of injury risk with incorrect technique and the need to constantly search for a partner for backup. The simulator successfully solves these problems. Meanwhile, the bench press remains the foundational powerlifting exercise and produces maximum muscle growth. And the seated press pumps certain bundles, that is, it carries an additional load, and not the main one.
The free weight bench press is a more accurate measure of your strength compared to a machine. Since the weight of the barbell with weights can vary significantly from the weight of the loads in the simulator.
Summarize . You shouldn’t give up the barbell in favor of a block weight machine. With the guidance of a good trainer, you will eliminate the possibility of injury under the barbell while lying down and quickly build muscle mass. And exercise machines like the Hummer will help strengthen individual bundles. Combine these exercises in a general program - and you will be happy.
What are the features?
The main advantage of the exercise is the ability to lift heavy weights, as is the case with the barbell press. In addition, the amplitude of arm movement and the overall effectiveness of the exercise increases.
The downside is that the stabilizing muscles responsible for holding the instrument in weight are switched off (as is the case with a barbell or dumbbells). Consequently, the basic component of the exercise is reduced, and muscle training takes on an isolating character. The seated press on a machine is an ideal option when you need to “finish off” the muscles already worked in the basic exercise, or in the absence of a partner.
Many athletes are too focused on the classic bench press, devoting all their time to working the chest. But it's not right. To increase the effectiveness of classes, the program should be as diverse as possible. This is required not only to improve overall results, but also to eliminate psychological fatigue from going to the gym.
Obsession with the same exercises sooner or later ends in injury and stops the growth process. It's easy to explain:
- monotony of exercise leads to muscle addiction. Muscle fibers simply stop accepting the same exercises. The muscles receive a load, but grow less actively;
- the occurrence of injuries is explained by the athlete’s excessive self-confidence when the exercise is done through pain. This is a grave mistake. Whatever muscle group you are pumping, training through pain is prohibited.