Introduction
It is known that movement is the most important stimulator of the vital functions of the human body. With a lack of movement, a weakening of physiological functions is usually observed, the tone and vital activity of the body decreases. Physical exercises activate physiological processes and help restore impaired functions of the human body. Therefore, physical exercises are a means of nonspecific prevention of a number of functional disorders and diseases, and therapeutic exercises should be considered as a method of rehabilitation therapy.
Physical training affects all muscle groups, joints, ligaments, which are strengthened, increasing muscle volume, elasticity, strength and speed of contraction. Increased muscle activity forces the heart, lungs and other organs and systems of our body to work with additional load, which increases a person’s functionality and his resistance to adverse environmental influences. Regular exercise has a particular effect on the musculoskeletal system and muscles. Physical activity produces heat in the muscles, which the body responds to by sweating. During exercise, blood circulation increases: blood brings oxygen and nutrients to the muscles, which decompose throughout life, releasing energy. When muscles move, reserve capillaries additionally open and the amount of circulating blood increases significantly, which leads to improved metabolism.
When muscles are inactive, their nutrition, volume and strength decrease, their elasticity and tone decrease, they become weak and sluggish. Restrictions on movement (physical inactivity) and a passive lifestyle lead to various prepathological and pathological changes in the human body. For example, American doctors, after incapacitating volunteers by applying high plaster and following a normal diet, made sure that after 40 days they began to atrophy muscles and accumulate fat. At the same time, the reactivity of the cardiovascular system increased and basal metabolism decreased. However, over the next 4 weeks, when the subjects began to actively engage in physical exercise (with the same diet), the above-mentioned phenomena were eliminated, the muscles became stronger and hypertrophied. Thus, physical activity led to the restoration of both functional and structural relationships. Physical activity has a diverse effect on the human body and increases its resistance to negative environmental influences. For example, physically fit people tolerate a lack of oxygen better than unfit people. There is a high ability to work when the body temperature rises above 38°C during physical activity. It has been established that physically active radiologists have less impact of penetrating radiation on blood morphology. In animal experiments, it was possible to show that systematic muscle training slows down the development of malignant tumors.
In the human body’s response to physical activity, the first place is taken by the influence of the cerebral cortex on the regulation of the functions of the main systems: changes in the cardiorespiratory system, gas exchange, metabolism, etc. Exercises contribute to the functional restructuring of all parts of the musculoskeletal system, cardiovascular and other systems, and improve tissue metabolism. Under the influence of moderate physical activity, cardiac output, hemoglobin and red blood cell content increase, and the phagocytic function of the blood increases. Improves the function and structure of the internal organs themselves, improves chemical treatment and promotes intestinal nutrition. The joint activity of muscles and internal organs is regulated by the nervous system, the function of which is also improved through systematic training.
Physical exercises help accelerate regeneration processes, saturate the blood with oxygen, plastic (building materials), which speeds up recovery. In diseases, the general tone decreases, and the state of inhibition in the cerebral cortex increases. Physical exercise increases overall tone and stimulates the body's defenses. For this reason, therapeutic exercises are widely used in the practice of hospitals, clinics, sanatoriums, physical therapy clinics, etc. However, during an exacerbation of the disease, at high temperatures and other conditions, physical exercises cannot be performed.
Physical activity, in addition to normalizing the reactions of the cardiovascular, respiratory and other systems, restores the adaptability of a recovering person to climatic factors, increases a person’s resistance to various diseases, stress, etc. This happens faster if gymnastic exercises, sports games, hardening procedures, etc. are used. In many diseases, properly dosed physical activity slows down the development of the disease process and promotes a more rapid recovery of impaired functions. Thus, under the influence of physical activity, the structure and activity of all human organs and systems improves, performance increases, and well-being improves.
Legal foundations of sports in the Russian Federation
The main law regulating sports in Russia is Federal Law No. 329-FZ “On Physical Culture and Sports in the Russian Federation”.
According to this law. Sport is a sphere of socio-cultural activity as a set of sports, developed in the form of competitions and special practices of preparing a person for them.
A sport is a part of sport recognized in accordance with the requirements of this Federal Law as a separate sphere of public relations, for which appropriate rules are established, approved in the manner established by this Federal Law, the training environment, the sports equipment used (except for protective equipment) and equipment.
Sports and disciplines recognized in the Russian Federation in accordance with the established procedure are included in the All-Russian Sports Register. The procedure for recognizing sports, sports disciplines and including them in the All-Russian Sports Register, the procedure for its maintenance is determined by the Government of the Russian Federation.
As of March 28, 2008, the All-Russian Register of Sports included 159 sports.
Sports, depending on the participation of athletes in sports, are divided into:
- Sports activities
- Martial arts
- Other sports
Depending on their inclusion in the Olympic Games programs, sports are divided into:
Olympic sports:
- summer.
- winter.
Non-Olympic sports
There are other classifications of sports.
The law provides for the creation of:
- Russian Olympic Committee,
- Russian Paralympic Committee,
- All-Russian, regional and local sports federations,
- Physical education and sports organizations,
- Sports clubs.
Within each sport, sports disciplines are distinguished - parts of the sport that have distinctive features and include one or more types of sports competition programs.
Physical training of blood circulation
Physical exercises improve a person’s posture; they characterize not only the shape of the body, but also the functions of the motor system. The development of good posture is associated with increased joint mobility, especially in the intervertebral joints. No less important is the formation of the nervous and muscular apparatus of the body - the ability of muscles to relax, tense and stretch. Good development of the back muscles is an important prerequisite for the formation of correct posture and has a positive effect on the respiratory and circulatory system. Physical exercises have the greatest impact on the formation of posture in primary and secondary school age (up to 14-15 years). During physical activity, muscle strength increases, and physical activity improves the training of the lower extremities, especially the arches of the foot.
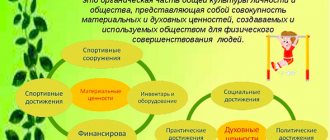
Social significance of sport
Sport as a type of social activity includes competitive activity itself, special preparation for it (training process), certain attitudes, norms, achievements, as well as certain values that arise in the process of this activity. The meaning of sport is universal, determined by the structure of modern society and its many functions. Moreover, the functions of sport are not limited only to competitive actions, victories and defeats, but include other socially significant goals.
Sport is a faithful companion in the fulfilling life of a modern successful person. Formation, grace, a sculpted body, a confident appearance - this harmony in a person deserves respect. People of athletic build who lead an active lifestyle achieve success everywhere: at work, in communicating with children, friends, and new acquaintances. And all this is thanks to his physical attractiveness, which is known to attract others, as well as the healthy energy with which they are charged during training.
Even if at one time a person did not pay due attention to his body, it is never too late to start doing something that will bring him tremendous pleasure, both from the process and from the result obtained. The main thing is the right attitude and the desire to get closer to the ideal. It is necessary to tune in to sports as an integral part of life. It won't be that easy at first—it takes time for your body to develop this habit. But over time, sports will become a primary need.
Sport is an active lifestyle, a release of unnecessary energy, accumulated fatigue from everyday life, a fight for oneself and a manifestation of willpower. A person not only trains his body, he strengthens his character. Some modern sports, such as fitness, bodybuilding, powerlifting, allow you to bring your figure closer to ideal. Of course, ideal is a rather subjective concept. But not a single person has yet ruled out physical attraction from him. Each of us experiences pleasant sensations from contemplating a beautiful figure. Our emotions are the true determining factors of our entire lives. If you begin to purposefully engage in one sport, the need for physical activity it develops will inspire a person to live a life where beauty and health, character will be irreplaceable components.
Improving the functioning of the respiratory system
Under the influence of exercises at rest, breathing movements become less frequent (6-8 times per minute) and deeper, which helps to renew the pulmonary air. Studies have shown that athletes breathe less than untrained people. It is known that the most important indicator of respiratory health is lung capacity. This indicator also depends on innate data, and not just on various learning conditions, one of which is physical education. Athletes are often physically gifted people with lung volumes of up to 7 liters or more. Lung capacity is especially high in athletes who row, swim or ski. Athletes' lung capacity is usually 25-30% higher than it should be. The minute volume of the respiratory tract in trained people is slightly less than in untrained people.
Professional sports
Nowadays, when the leisure culture is highly developed, sports and watching them have become a popular entertainment for spectators and a professional activity for athletes. High-level professional athletes earn large fees and income from advertising various products and become celebrities - sometimes exclusively among fans, sometimes among the majority of the population.
To regulate what happens in professional sports, general and highly specialized organizations and associations are created that unite athletes, coaches, judges, and sometimes fans. The fact that sport has become a business and a source of wealth greatly influences the nature of the competition. Sports rules change frequently due to entertainment requirements or the convenience of refereeing.
Increased functionality of the circulatory system
Under the influence of training, which is closely related to respiratory function, circulatory function also changes. Increased muscle activity leads to hypertrophy of the heart muscle - an increase in its mass, thickening of muscle fibers and functional changes. In athletes, an increase in heart size is observed on x-rays and often when determining the boundaries of the heart by heartbeat. In trained people, the heart weighs up to 400-500 g, and in untrained people - only 200-300 g. Experiments have proven that under the influence of movement, the intensity of oxidative processes in the heart muscle increases and its working potential increases. The amount of hemoglobin and energy-rich phosphorus compounds increases. At the same time, the athlete's heart works more efficiently and consumes less energy per unit volume of blood than the heart of an untrained person. As the mass of the heart muscle increases, its circulatory network changes. Exercise increases the number of capillaries in the heart. In order to judge circulatory function, it is important to take into account data on cardiac function and basic hemodynamic parameters (heart rate and blood pressure). For athletes at rest - from 50 to 60 beats per minute. This is especially true for long-distance runners, cyclists, skiers and swimmers. During exercise, a number of electrographic parameters change, which is a sign of good oxygen supply to the heart muscle. Blood pressure in the range of 100-110 mm indicates changes in the vascular channels that create conditions for the efficient functioning of the heart, since blood enters the vessels with reduced resistance.
History of sports
The development and changes of sport throughout human history can tell a lot about both social changes in society in general and the essence of sport in particular. Many examples of cave art discovered to date contain images of ritual ceremonial scenes. Although the activities depicted in these images cannot be attributed exclusively to the modern concept of sports, it can still be concluded that activities and rituals reminiscent of sports activities existed even then. These images, located in France, Africa and Australia, were taken 30,000 years ago.
There are objects and buildings that indicate that activities that fit the modern definition of sport existed in China as early as 4000 BC. Apparently, gymnastics was a popular sport in ancient China. Images and objects in the tombs of the pharaohs also indicate that various sports were developed several thousand years ago, among which are swimming and fishing. On the territory of Ancient Persia, sports such as polo and competitions of mounted knights on spears originated. There were already many sports in Ancient Greece. The most developed were various types of wrestling, running, discus throwing, and chariot competitions. Judging by this list, military culture and military art in Ancient Greece (and not only) were directly related to sports. The Olympic Games were also held here every four years, in a small village in the Peloponnese called Olympia.
From the times of Ancient Greece to the present day, the history of sports can be easily traced. Over time, the sport became more organized and regulated. New types and subtypes of sports appeared and were formed, the rules were clarified, and the sport acquired traditions and supporters. The Industrial Revolution and mass production led to the fact that more and more people had free time, which led to the mass nature of sports - more and more people wanted and were able to make sports a part of their lives, playing sports directly or devoting their leisure time to playing sports. These trends have been further developed with the advent of mass media and global communications. The sport became professional, which further increased its popularity.
Modern post-industrial society, relying on resources such as information and knowledge, using the possibilities of individual contacts of people using Internet technologies, is actively developing intellectual sports such as poker and multiplayer online games.
The influence of physical activity on human motor functions
Under the influence of rational engine tension, a number of progressive changes occur in the bone and skeletal support. The obvious effect of training is reflected in the increase in muscle strength. The muscles of a trained person have the ability to perform not only one effort, but also long-term work. Under the influence of movement, the ability of the muscles to relax improves, at the same time the ability of the muscles to create tension increases, and the difference between the created tension and relaxation increases.
Improvement in muscle function is closely related to improvement in the neural regulation of motor activity. Muscles, measured by their electrical activity, are excited by centrifugal impulses from the central nervous system, which cause muscle contraction and tension. At the same time, muscle function is a stimulus for receptors, from which centripetal impulses enter the central nervous system and transmit current information about the movement itself. The most important effect of improving the muscular system under the influence of movement is an increase in muscle sensation.
Sports in Russia
Sports in Russia are one of the most popular activities among Russians. They go in for sports professionally and amateurly. Amateur sports are closely related to the concept of physical education. Both directions are being developed and promoted in Russia, but not as actively as required for progress and modern achievements. Many Russian children attend various sports clubs. Mass sports competitions are held, for example, “Cross of Nations” and “Russian Ski Track”. Summer and winter rural sports games, similar to the sports days of the former USSR, are held among residents of villages and hamlets. And all this happens, as a rule, in capitals, regional centers, less often in districts, and children from villages and collective farms have long been forgotten. Although a good half of the Soviet athletes were from village boys and girls, who later became champions of the USSR, Europe and the world. They have pleased us many times with Olympic medals of various denominations.
Many Russian sports schools occupy leading positions in the world, which is confirmed by high achievements at the most prestigious sports competitions, such as the Olympic Games, World and European Championships in various sports. Many Russian athletes are “stars” of world sports. The regulation of the sports sector in the Russian Federation is carried out by the Federal Agency for Physical Culture and Sports of Russia (Rossport). Also in Russia there is a tradition of empathy for participants in sports competitions. The most popular among fans are team and individual winter and summer sports: football, hockey, basketball, biathlon, cross-country skiing, athletics, swimming, tennis and others.
As of 2008, there were 2,687 stadiums in Russia with stands for 1,500 seats or more, 3,762 swimming pools, and 123,200 flat sports facilities. In 2008, the number of people involved in sports sections and groups was 22.6 million people, including 8.1 million women. In 2011, at the XXV World Winter Universiade, the Russian team took first place in the team competition.
The effect of physical activity on the nervous system
The training process improves strength, balance, and mobility of key neural processes. As a result, conditioned reflexes are established faster and more successfully. Most trained people belong to a strong and mobile type of nervous system. Under the influence of movement, nervous processes improve, which helps a person to more successfully tune in to the upcoming activity. Mobilization of all strengths and capabilities is especially successful among qualified athletes. This adjustment of the body manifests itself in relation to various functions of the body - breathing, blood circulation, metabolism. Changes in the functional state of the brain, musculoskeletal system and all organs in general during training are associated with increased tissue instability.
Changes in the activity of the endocrine glands during training play an important role. There is especially a lot of data on changes in adrenal function during training. Adrenaline and corticoid hormones are very important for human performance. The activity of the endocrine glands regulates the functioning of the nervous system and determines the normal functioning of all organs and systems. Hormones affect the nervous system, tone it and increase its functionality.
The stress doctrine is of interest when it comes to assessing the consequences of physical activity and the development of resistance to harmful factors. At the right dosage, exercise increases the body's resistance to cold, certain toxins, certain infections, and even penetrating radiation in smaller quantities - compared to people who have not been trained.
Sports concept
Sport (English Sport, an abbreviation from the original English disport - “game”, “entertainment”) is an activity of people organized according to certain rules, which consists of comparing their physical and intellectual abilities, as well as preparation for this activity and interpersonal communication. relationships that arise in its process.
Sport is a special type of physical and intellectual activity performed for the purpose of competition, as well as targeted preparation for them through warm-up, training combined with rest, the desire to gradually improve physical health, increase the level of intelligence, receive moral satisfaction, the pursuit of excellence, and personal improvement. , group and absolute records, fame, improvement of one’s own physical capabilities and skills.
Sport is an integral part of physical culture. This is the actual competitive activity and preparation for it. It clearly manifests the desire to win, achieve high results, mobilize the physical, mental and moral qualities of a person. Mass sports give millions of people the opportunity to improve their physical and motor abilities, improve their health and extend their creative longevity.
High performance sport is the only model of activity in which, among outstanding record holders, the functioning of almost all body systems can manifest itself within the zone of absolute physical and practical limits of a healthy person. The goal of elite sport is to achieve the highest possible athletic results or victories at major sporting events.
Complex for physical exercises
The starting point is your feet together. Walk, step by step - left, right, step by step. Speed is average. The movements may be accompanied by striking the palms to the music.
Starting position - feet shoulder-width apart. Place your hands on the belt or at your sides and follow your body as it rotates. Start turning your body left and right, and then return to the starting position. Do 2 sets, 8 times each, without rushing.
Starting position: feet shoulder-width apart, arms down. Arms extended upward, standing on toes. Return to the starting position. Perform 2 sets 8 times. Then stretch your arms forward. Also do 2 sets 8 times.
Starting position: stand. For “one” you sit down, for “two” you get up. Hands forward. Perform the exercise in 2 approaches - 8 times each.
The starting point is your feet together. Lunge forward, mandatory support from hand to hand. Adjust your foot, rotate it in the opposite direction (180°) and repeat the same with the other leg. Perform 2 sets of 8 times with each leg.
The starting position is on your stomach. Bend your legs, tighten your body, lift your shin with your hands and stretch it. Return to the starting position. Perform 1-2 sets 3 times.
Starting position - support for knees and arms (elbows are possible). Stretch your legs one by one. Perform 1-2 sets 6-8 times. Repeat the exercise for each leg the indicated number of times.
For boys. Starting position: rest on your knees or legs (difficult option) and on your hands. Push-ups on the floor. Do 1-2 approaches - as much as you can.
For girls. Starting position: sitting, palms together at chest height. Press into your palms, stretch your arms. Perform 1-2 sets 6-8 times.
For boys. Starting position - sitting on the floor, legs extended forward. For “one time” - slightly raise your body, bending your knees. On “two” return to the starting position. Perform 1-2 sets 5-8 times.
For girls. The starting position is on her side. The legs are as comfortable as possible. One hand forward, the other behind the head. Raise your body with a small amplitude and return to the starting position. Do 1-2 approaches, 5-6 times on each side.
Starting position: sit, one leg straight, the other bent. Hold the bent leg in this position for 1-3 seconds. Return to the starting position. Repeat the procedure once for each leg.
Starting position: sitting, legs together, extended forward. The arrows reach the legs and remain in this position for 1-3 seconds. Return to the starting position. Connect your legs by bending your knees and spreading them apart. Elbows rest on your knees, lean forward slightly and remain in this position for 1-3 seconds. Repeat several times.
Starting position - standing, right hand on the belt, left extended forward, right leg forward, on the toes. On “one” we simultaneously put our foot back and put our hand behind our back, on “two” we return to the starting position. Slowly continue 2 sets of 8 times in each direction.
The starting position is the main frame. With “one” raising of the shoulders up, the arms drop freely, with “two” - the shoulders down. Do the exercise 10 times.
Starting position: standing, legs as wide as possible, knees slightly bent. Immediately” - a slight bend forward, the back is straight. At “two,” the elbows go as far back as possible, bending the arms. Perform 2 sets 3-5 times.
Starting position - standing, one leg extended forward, bent at the knee, the other back, hand resting on the bent knee, back straight, the other freely lowered. We start with the arm bent as far back as possible and at the same time raise the shoulder. Perform 2 sets 3-5 times.
Starting position: stand with your hands clasped above your head. For “one time” - we move our hands forward to the chest, the back is round, the legs can be slightly bent at the knees. On “two” you return to the starting position. Perform 2 sets 5-10 times.
The starting position is on your stomach. For “one” we take out the left leg with our right hand, for “two” we change the leg and arm. Perform 5 times in each direction.
Starting position: sitting, head on knees, legs bent. For “one time” - lean against the floor with your hands, take your body back, legs in a suspended position, bend your knee, but not completely. On “two” we return to the starting position. Do 2-3 sets, repetitions - as much strength as is sufficient.
Bend forward with a round back and stand in this position for 10 seconds or hang your hands on a barbell.
Sport as a school for developing moral and psychological qualities
In the process of playing sports, numerous connections arise between people, which are manifested in the transfer of knowledge, experience, and skills. Sport is organically included in a holistic, well-functioning socio-pedagogical system and is one of the most effective factors in personal development, especially in childhood and adolescence. When mastering a new type of activity—sports—the circle of participants in the pedagogical process expands significantly. Sports specialists pass on relevant knowledge and skills to their students, thereby shaping the athlete’s personality.
Elite sport develops such important qualities as honesty, a sense of duty, respect for an opponent, pride in belonging to a particular team, and others. So, in some sports, such as tennis, there are unspoken codes of honor for the athlete. And such a seemingly aggressive sport as professional boxing contributes to the development of certain moral qualities in athletes. This is stated in an interview with the absolute world champion in all versions of boxing, Konstantin Dzyu (2003). To the question of a correspondent of the weekly “Arguments and Facts”: “Who do you see in the ring, an enemy or an opponent?”, he replied: “I only see an opponent, because I know what pain is, I went through it.”