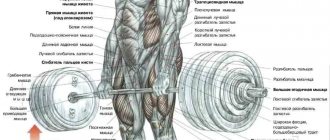
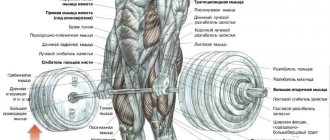
The deadlift is one of the key compound exercises that involves a large number of muscles. It simultaneously works the trapezius, lower back muscles, quadriceps and biceps femoris, posterior deltoids and even biceps. Due to the large number of working muscles, the deadlift causes a good anabolic response and stimulates the production of your own testosterone. It is this fact that makes the deadlift one of the most effective exercises you can perform in the gym.
Deadlifts place serious stress on the spine and knee joints. For this reason, it is contraindicated for many who have injuries. Deadlifting is also not recommended for beginners, since their muscles are not yet sufficiently prepared for high loads. The solution is to use alternative exercises that work the same muscle groups.
Unfortunately, it is unlikely that it will be possible to fully replace the deadlift ; it engages about a third of the body’s muscles, like almost no other exercise. So before you think about replacing the deadlift, weigh the pros and cons. Well, if more factors speak against it, we have found alternatives that provide a similar load on the same muscle groups that are involved in the work during the deadlift. Pay attention to technique - some exercises can put stress on the knee joints or spine, and if you have any injuries, it is better to avoid them in favor of other alternatives.
Romanian single leg deadlift
Working muscles: gluteal, hip adductors, hamstrings, quadriceps, trapezius, rhomboid, latissimus.
How to replace deadlifts? Romanian deadlift on one leg! The exercise helps to better coordinate the work of the muscles on the right and left sides of the body, which is much more difficult to do during a traditional exercise. Many beginners face this problem: when trying to lift weights, they often use stronger muscles. As a result, the exercise technique changes, the spine begins to experience overload, and the body composition becomes disproportionate. With the Romanian Single Leg Deadlift you won't have this problem.
Another benefit of the exercise is that it helps to work on muscle coordination and balance.
Technique
- Take dumbbells or weights in your hands. Stand up straight and move your left leg slightly behind your body.
- Take a breath. As you exhale, begin to move your left leg back, while simultaneously moving your body forward. When it becomes parallel to the floor, pause and stay in this position for 1-2 seconds.
- Slowly return to the starting position and repeat the same with the other leg.
Details
- During the exercise, your gaze is always directed in front of you, and your back remains straight.
- The exercise can be performed with dumbbells, kettlebells or a barbell.
- As you move your leg back, your heel should point toward the ceiling.
- The supporting foot must be in contact with the floor at all times.
- To develop a sense of balance, practice doing the exercise with a light weight.
Don't tear your belly button, it's not a solution
If you are a non-professional powerlifter, then figure out your 1MB (maximum weight for one repetition), and return to it from time to time. Add the above 5 kg only after WW1 has been successfully overcome.
At the same time, you don’t need to set yourself up for unsuccessful repetitions. If you didn’t succeed in some weight either the first or the second time, lose 5–10 kg and work with this weight as with WW1 for several weeks. At the same time, do not forget that you need to touch this 1MB extremely rarely, no more than 1-2 times a month (I repeat: if you are not a lifter). Maximum attention to the weight with which 4-6 repetitions are obtained in the approach.
Good morning exercise
Muscles worked: gluteals, hamstrings, lats.
Unlike the deadlift, this exercise involves the knees to a lesser extent and is easier for beginners to master. In addition, it works the back of the thigh better due to the increased range of motion. Finally, another advantage of the exercise is that it activates several muscle groups at once, which means it can be called basic. As a result, it causes a good anabolic response and increased testosterone secretion.
Technique
- Take a barbell and “sit” it on the trapezius, as if you were going to do squats with a barbell.
- In the starting position, the body should be straight, shoulders straightened, feet shoulder-width apart, and knees slightly bent.
- Bend forward with the barbell while keeping your back straight. At the same time, move your buttocks back.
- As soon as your body is parallel to the floor, return to the starting position by tensing your gluteal muscles.
Details
- Never look at the floor. The gaze is always directed in front of you.
- Don't chase weight. The working weight in this exercise should be lower than in the classic deadlift.
- Do not round your back, this can lead to spinal injury.
Squat rack
This partial distance row is a gem for the hips. Racks lift the barbell off the floor from safety pins or stops in the squat rack. This is the same strength-building movement as the deadlift, compressed into a smaller range of motion. Rack rows are a great solution for people who lack the mobility to perform a full range of motion row with safe form.
Place the barbell on the pins in the rack so that it is at knee level. As your feet touch the bar, flex your hips—pull your hips back—to a position that allows you to hold the bar with a straight back.
Have someone watch you or take a video to determine if your back is truly straight. If you can maintain a flat back in the down position, you have the ability to break out of this position.
Continue lowering the pins from one workout to the next until you reach the lowest point where you can keep your back straight. Continue training at each height until your mobility improves. Work out using sets of 3-8 repetitions.
Bent-over T-bar row
Working muscles: latissimus, rhomboid, teres major, posterior deltoid.
A good alternative for the deadlift would be the bent-over row, but we decided to replace it with an easier exercise in terms of technique. In addition, the T-bar row uses a parallel grip, which is the strongest. This allows you to work with a higher working weight and activate your back muscles more.
The T-bar row can replace the deadlift only in relation to the back muscles: the leg muscles practically do not work during the exercise.
Technique
- Take the handle of the bar in your hands. So that it ends up between your legs. The arms are barely bent, the bar is suspended.
- Make a slight arch in your lower back; otherwise, your back should remain straight. Bend your knees, but not too much. Look straight ahead.
- As you exhale, pull the bar towards you until it almost touches your abdominals.
- Smoothly lower the bar down and return to the starting position.
Details
- Watch your biceps: they should not take the load from your back.
- Smaller weight plates will not limit the range of motion, so it is better to gain weight from them.
- In the negative phase of the movement, try not to suddenly release the barbell down, but return to the starting position smoothly and without jerking.
Causes
There are several main reasons:
- Injuries
- Disproportions in muscle development
- Lack of necessary equipment
- Lack of knowledge of the correct technique
Injuries
Injuries will be the biggest limitation and, in some cases, will prevent you from performing even alternative exercises because they will cause pain.
Oddly enough, injuries that prevent you from deadlifting are often caused by the deadlift itself. Injuries while performing deadlifts are most often caused by trying to lift too much weight for a small number of repetitions. Typically, this occurs during "walkthroughs" when the athlete is trying to figure out how much weight he can lift in one repetition.
Classic bodybuilding does not imply the mandatory regular performance of “steps”, therefore, to avoid injuries, it is better not to do them at all. Regular lifting is the lot of powerlifters. In bodybuilding and fitness, you can work with moderate weights in the 6-12 rep range, over multiple sets.
This approach, combined with correct technique and mandatory warm-up, allows you to reduce the likelihood of injury to zero.
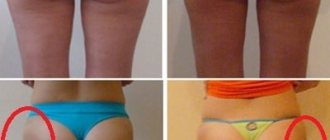
The deadlift primarily places stress on the rectus dorsi, gluteal muscles, and leg muscles. These muscles may respond differently to exercise in different people. For some, the development of these and other muscles occurs harmoniously, while for others, unaesthetic imbalances may occur.
In particular, direct intense load on the gluteal muscles sometimes (but not always) leads to their overdevelopment, which can negatively affect the appearance of the athlete. Therefore, if you think that the development of the gluteal muscles at this stage should be limited, then including deadlifts in your training will not be the best solution.
Of course, you don’t need any specific equipment for deadlifting. All you need is a barbell and plates. Well, there is definitely a barbell in every gym, regardless of its level of equipment. Otherwise, what kind of gym is this if it doesn’t even have a barbell?
Therefore, in this case, the lack of equipment should be understood as an insufficient number of pancakes in the gym to provide the working weight you need. And this may well be the case, because the deadlift is one of the most powerful exercises among all strength exercises, which means that even beginners can work in it with fairly large weights, not to mention experienced athletes.
Of course, in well-equipped modern halls it is difficult to imagine a situation with a shortage of pancakes, but in halls with a low level of equipment (or in home mini-halls) this may well become a stumbling block.
Performing deadlifts with a weight that is decent for you requires impeccable technique. This is not to say that this technique is too difficult to master, and anyone can master it, if desired. However, you still need to first learn this technique and then practice it so that it is “built into” your head.
Not everyone has the opportunity to study with an experienced mentor who could teach the technique and point out possible mistakes. Learning techniques from books and instructions is quite possible, but this option is much worse, since it is much more difficult to understand the correct technique and notice your mistakes yourself.
For this reason, some people simply refuse to do deadlifts for fear of possible injury.
It is impossible to definitively answer why exactly the lower back hurts. Maybe this is due to a violation of the technique itself, or maybe it is due to overload of the spinal muscles. And sometimes the appearance of unpleasant sensations is a signal of serious violations.
If a beginner has pain after deadlifting, this is quite natural, especially if he previously led a sedentary lifestyle. But it’s a completely different matter if the pain is sharp and acute.
During such squats, the back should be in a natural position, but if it deviates, the spine experiences severe stress.
You can learn the correct technique for squatting with weights only under the supervision of a professional trainer.
You can simply hang on the horizontal bar, or use a warming ointment. All this is only a temporary relief of symptoms, which does not eliminate the causes. It is important to identify the factors that triggered the pain and undergo an examination.
In some cases, the pain factor may be the intensity of the movements performed. Sudden jerks are more likely to cause a lot of trouble than to increase the effectiveness of your training.
A low or high bar is a direct road to back problems. Also, if you pull in your stomach too much during squats, your lower back will round. Taking a deep breath and using an athletic belt will help avoid incorrect execution.
Another reason may be the desire to experiment. Such attempts can be fraught with violation of the integrity of the intervertebral discs. In addition, discomfort may indicate the development of osteochondrosis and complications associated with it.
Also, excessive load can cause protrusion, during which the intervertebral disc moves beyond the spinal column, while the fibrous ring maintains its integrity. Protrusion causes pinching of nerves and blood vessels. A serious complication of the disease, if left untreated, is intervertebral hernia.
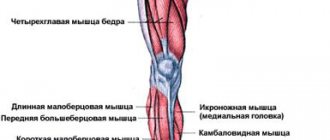
Leg bending in the simulator
Working muscles: muscles of the back of the thigh, calf.
This classic hamstring isolation exercise is a great complement to the T-bar row. Together they will create a load on almost the same complex of muscles as in the deadlift. The T-bar row will hit your back muscles, and leg curls will help work the back of your thighs. Only the gluteal and trapezius muscles will remain out of work.
Technique
- Lie on your stomach on the machine, place your legs behind the rollers.
- Take a breath, hold your breath. Raise your legs and exhale during the most difficult part of the exercise.
- Pause briefly at the point of maximum contraction of the hamstrings and slowly inhale to return to the starting position.
Details
- Do not lift your pelvis where the bench bends.
- By changing the position of the feet, you can shift the emphasis - work either the outer part of the muscles of the back of the thigh, or the inner. Heels together - the outer side works more, toes together - the inner side.
- The higher the range of motion, the better. Don't shorten it.
- If you pull your toes toward you during the exercise, your calves will receive additional stress.
From the author.
I tried to explain in more detail the deadlift technique and training system. But many questions will still arise. In practice, it can be difficult to achieve a complete combination of all elements without the special attention of the coach, understanding and effort of the athlete. All that remains is to wish you success in achieving better results, in which, perhaps, my experience will help.
Honored coach of the Russian Federation in powerlifting Askold Surovetsky
← Previous material
Next material →
Shrugs with dumbbells
Working muscles: trapezius, rhomboid.
Shrugs are a great isolation exercise for the trapezius. And although it is not as basic as the deadlift, shrugs can work this muscle group just as well.
Technique
- Take dumbbells in your hands so that your palms are turned towards your body. Drop your shoulders.
- Breathe. As you exhale, begin to raise your shoulders straight up.
- Pause at the top and slowly lower your shoulders to the starting position.
Details
- Shrugs can be performed with either dumbbells or a barbell.
- During the shrug exercise, the muscles of the arms and shoulders remain motionless.
- Traps love heavy weights, so the working weight in this exercise can be increased.
- In the negative phase of the movement, try not to let your shoulders go down, but return them to their original position smoothly and slowly.
deadlift
Prevention
Following simple rules will help avoid pain:
- correct execution technique. It must be carefully studied and practiced. Each approach should be carried out with the correct arch in the lower back. During the beginning of the movement, when the bar lifts off, it is especially important to monitor the correct execution;
- warm-up before starting classes;
- working on strengthening your back;
- correct weight. A barbell that is too heavy will do more harm than good;
- "No!" overload of the lower back;
- "Yes"! pull-ups. This is a good opportunity to stretch not only the muscles themselves, but also the spine.
Moderate physical exercise under the supervision of a specialist will help relieve the unpleasant symptom.
Emergency help
If your lower back hurts terribly during training, follow these rules:
- stop the load;
- Lie in a position that minimizes pain. Lie down until the pain goes away. If this does not help, classes should be cancelled;
- You can apply ice or a cold compress to the sore spot and wait for an ambulance. Thermal procedures are not permissible, as they will only aggravate the situation, increasing swelling and inflammation.
Do not self-medicate by prescribing medications to yourself, especially those administered parenterally.
In any matter, a competent approach to business is important. When playing sports, listen to the recommendations of professionals, and if you experience alarming pain, consult a doctor.
Diagnosis and treatment
If an athlete has back pain after deadlifting, it is necessary to consult a doctor and undergo a series of tests. Depending on the general condition of the patient and the nature of the pain, the patient may be prescribed the following procedures:
- MRI (it is especially important for those athletes who suspect a spinal injury to undergo it);
- X-ray;
- general urine and blood tests.
Additional studies may be prescribed to a person based on the results of the initial examination and basic diagnosis. Depending on the diagnosis, a person may be prescribed local treatment (compresses, ointments, pain-relieving injections), general medications that promote tissue restoration, as well as various physical therapy. treatments, including massage.
If there was a serious injury, the patient may be prescribed a temporary restriction of physical activity, and then exercise therapy. He will be able to return to normal sports activities only after complete recovery.
Sumo or classical (classical)?
- What is the difference between these two types of traction? Well, the answer is obvious: the position of the legs. Depending on the width of your legs, the height of the barbell changes. The wider the legs are spread, the lower the lifting height of the projectile. Those. By placing your feet wider, you simply make the task a little easier for yourself and reduce your range of motion.
- Typically, the classic deadlift is chosen by people with shorter legs and a longer torso. Still, the sumo style requires a certain flexibility and mobility in the hip and knee joints.
- With the sumo deadlift, all the hip adductors are more fully involved. The classic technique loads the back a little more.
- Classic requires parallel placement of the feet. Sometimes trainers advise turning them slightly to the sides. When doing sumo deadlifts, your goal is to rotate your feet 45 degrees outward.
Both deadlift variations are equally good. If you are in doubt about the choice, experiment with both options. Only then will you be able to figure out what is more convenient for you to do. The sumo deadlift has its pros and cons, just like the classic one, so the choice between them is a purely individual matter and depends on your personal comfort.