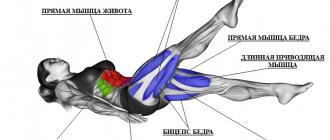
Regardless of gender, age and preferences in exercise, everyone wants beautiful and sculpted abs. It is a mistake to believe that beautiful abs can be achieved solely with the help of exercise machines and special devices. It is the lifting of the torso that is the basis of abdominal training. In addition, in this exercise you can increase the load for mass gain, or vice versa - make sure that the relief improves and the waist becomes thinner. Let's take a closer look at the variations, anatomy and technique of lifting the body on the floor below.
Benefits of exercise
- This is the best and most comfortable exercise for the abdominal muscles.
- Using a technique that involves lifting the body, you can create a six-pack, making your muscles thicker, or reduce your waist size, making your stomach flat and sculpted.
- Technically, the exercise is safe if you strictly follow the instructions and carefully work with weights if necessary.
- The exercise can be performed solo, since it completely affects the rectus abdominis muscle, and not just one part of it. You can add other exercises to the lifts if you wish - to work the abs more deeply, but this is not necessary.
- Lifting can improve your posture by strengthening the spinal stabilizer muscles and prepare you for challenging compound exercises that require trained abdominal muscles, such as deadlifts and squats.
- The exercise perfectly warms up the whole body, for example, at home you can start your workout with it.
Why, when and how many times to train the abdominal muscles
Many athletes do not want to devote enough time to training their abdominal muscles, arguing with a popular phrase among beginners: “The abs are involved in all exercises, so there is no point in training them separately.” Yes, indeed, I partly agree with them. The abdominal muscles are indeed loaded in almost all strength exercises, because they are part of the core muscles, which are responsible for stabilizing our body. But this does not mean that this load is enough to increase the strength and endurance of the press.
Why pump up your abs?
There are many positive factors from strong pumped up abs:
- Beautiful aesthetic appearance . Many people dream of being the owner of beautiful and sculpted abs, and those who deny this are most likely lying;
- Correct posture and healthy spine . With a weak press, the load on the intervertebral discs increases, which in turn can lead to problems with the lumbar spine;
- Normalization of the gastrointestinal tract . With active training on the abdominal muscles, the digestion of nutrients is noticeably improved, constipation and bloating are prevented;
- Strength indicators . As mentioned above, the abdominal muscles are involved in all strength exercises. The logic is simple: strong abdominal muscles = increased strength in squats, deadlifts, presses, dips, etc.;
- Benefits during childbirth. Refers to cute and beautiful girls. Strong abdominal muscles help ease the birth process.
When
At the beginning of the training, it is better to perform a couple of light sets of abdominal exercises to warm up the body, but it is advisable to perform full strength abdominal exercises at the end of the workout, when they are already fully warmed up and slightly tired.
I would like to remind you that abdominal training should be given the same attention as the chest or leg muscles.
Training frequency
There is a lot of controversy among athletes regarding the frequency of training. Some believe that the abdominal muscles are incredibly resilient and therefore need to be trained daily, while others, on the contrary, are sure that the abdominal muscles, like other muscle groups, need recovery and rest.
I train my abs 1-2 times a week with weights at the end of my workout. The workout consists of 2-3 exercises, for example:
- lifting the body while lying on an inclined bench;
- raising the legs while resting on the elbows;
- plank
I perform the exercises with additional weight in the form of a barbell or leg weights. But this does not mean that this training option is suitable for you. All people are individual, so you need to experiment and find your own training method.
Technique for lifting the body from a supine position
- Take a lying position and bend your knees. If necessary, secure your feet to make it easier to lift your body. To simplify the load, you can hold your hands in front of you or on your chest; if you are more prepared, it is better to place your palms behind your head.
- As you exhale, gradually lifting each part of your spine from the floor, lift your torso up. Keep your back round by contracting your abdominal muscles. This is also important for reducing stress on the spine. Do not straighten your back under any circumstances.
- As you inhale, slowly return each section of the spine gradually to the floor, relaxing the abdominal muscles only while lying on your back.
Options for advanced
- To complicate the load, you can use additional weights - a dumbbell or weighted disk, which are placed on the chest.
- You can also use a kettlebell or medicine ball, which is held in your hands at your sides, including the kettlebell, and raised above your head when your torso reaches a vertical position. You can also use dumbbells, pushing them above your head, as in the example with a kettlebell.
- Without additional equipment at home, you can use fitness bands that are attached at a certain distance behind the athlete. Holding the edges of the tape with your hands, when lifting the body, the tape will stretch, creating the necessary resistance.
- Another option is to perform an exercise in a crossover, similar to the previous option, only instead of a tape there is a lower block cable. It is better to choose ropes as a handle.
Option for rehabilitation and strengthening of the transverse muscle
It was previously mentioned that with proper and concentrated lifting of the torso, you can strengthen the transverse muscle, which affects the correct position of the lower back and stabilization of the spine when performing basic exercises, such as squats with a barbell.
- The technique remains the same, but there is one nuance: lifting the body is done as slowly as possible, feeling how the vertebrae are lifted off the floor one by one, and vice versa. Due to this method, the deep layers of the abdominal cavity, which do not work during dynamic performance, are maximally connected.
- You can hold your hands either in front of you or behind your head. The feet can be fixed, but the ideal option is for the legs to be unfixed and straightened. Then the torso will rise solely due to the abdominal muscles, and not with the help of the legs.
What to pay attention to
The nuances are as follows:
- We hold the weight between the back of the head and neck if we use weights.
- We rise as we exhale, we descend as we inhale.
- You can place the weight on your chest - it will be easier and safer.
- If the leg bolsters leave bruises (for girls), add a piece of foam rubber.
- You can do full or partial bends.
Body lifts on a Roman chair can be done in any yard where there are 2 adjacent pipes of different levels parallel to the ground (sit on one, secure your legs under the second).
How to implement it into training
- Regardless of the training set or methodology - be it a split program, circuit training or interval training - it is best to perform body lifts at the end of the workout .
- The exercise can be supplemented with other abdominal techniques , for example, focusing on the upper or lower part of the rectus muscle, or the oblique abdominal muscles.
- to fatigue your abs in leg workouts that involve working with free weights at the end.
- If the workout is performed with your own weight, for example at home, then in the warm-up you can perform a torso lift , which will further warm up the body.
- You need to perform the exercise until you feel a burning sensation - this is the main criterion for correctly selected load.
- In order to burn fat and reduce waist size, perform the exercise within 15-30 repetitions, depending on the equipment and physical training.
- In order to create cubes , the abdominal muscles need to be built up. To do this, the load should be increased with the help of additional equipment to such an extent that the number of lifts does not exceed 12 times. For muscle growth, the range of lifts varies between 8-12 repetitions.
Recommendations on how to lose belly fat faster?
- Exercise more than 200 minutes a week and walk at least 10 thousand steps a day.
- Focus on healthy and effective nutrition (fruits, vegetables).
- Sleep 7-8 hours and always recover after training or physical activity.
- Avoid psychological stress. Visit friends or new acquaintances more often. Visit new places.
- Visit parks and forests more often. Those places where the air is the cleanest.
By following all the recommendations above, you will definitely increase the effectiveness of the exercise of lifting your torso from a lying position, improve your health and feel your best!
Overview of Disc Degeneration Diseases
The intervertebral disc is a cartilaginous connection of the vertebral bodies that stabilizes them and the spine as a whole. The disc also facilitates multiplanar movements and helps absorb stress on the spine. The disc consists of three parts: the outer layer is the fibrous ring, in the center is the nucleus pulposus and 2 hyaline cartilages - the end plates (64). The ring, consisting of an inner and outer component, contains multiple layers of collagen fibers consisting mainly of type I and type II collagens (39). The ring resists outward pressure, known as circumferential stress, during axial compression and stabilizes the spinal joints during movement (138). In addition, the ring serves as a container for the inner core, which has a gel-like structure consisting of a mixture of chondrocytes, collagen, elastin, and glycoproteins (130). Glycoproteins resist compressive stress due to the glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) they contain (114). GAGs are long chains of polysaccharides that attract and bind water, creating osmotic pressure. The core functions as a “water cushion,” helping the vertebrae cushion under axial load and distribute pressure evenly across adjacent endplates (111). The end plates contain predominantly type II collagen (55), are less than 1 mm thick, and their fibers extend into the disc (138). In addition to preventing protrusion of the nucleus into the adjacent vertebra, endplates also help absorb hydrostatic pressure caused by spinal loading (26, 81) and allow for the diffusion of nutrients (131).
Degenerative disc disease is a multifactorial process involving genetic, mechanical, biological, and environmental factors (59). The first general signs of degeneration often appear between 11 and 16 years of age. Approximately 20% of adolescents have mild disc degeneration (79). Mild signs of degeneration (formation of small clefts and granular changes in the nucleus) are observed at the age of 2 years (21). The disease tends to progress with age and by age 70, signs of degeneration are observed in most discs (79). Age-related degeneration includes a decrease in the content of glycoproteins and collagen (114), a five-fold decrease in the charge density (mechano-electrochemical force value) of GAGs in the nucleus (60) and a two-fold decrease in the level of hydration when comparing discs of young and 80-year-old people (129), which reduces the height of the disc and its ability to withstand loads (8, 22). Men have more severe disc degeneration than women due to greater trunk strength, increased lever arms, greater external loads, and distance for nutrient diffusion (79).
Intervertebral disc degeneration can manifest itself in the annulus, nucleus, and endplates (7). Age, apoptosis, and glycoprotein abnormalities may contribute to degeneration (71). With disc degeneration, localized endplate cartilage defects appear, the nucleus becomes more consolidated and fibrotic, and the number of annulus layers decreases (119). This results in decreased disc height, decreased spinal biomechanics and load-bearing capacity (99), and, in some cases, can lead to spinal stenosis, the most severe degree of disc degeneration that causes compression of the contents of the spinal canal, particularly the neural structures ( 93). Endplate calcification also contributes to disc degeneration by reducing nutrient diffusion, leading to changes in pH balance and increasing nuclear inflammation (34). Although there is a clear association between spinal degenerative changes and increased incidence of low back pain (LBP) (65), many people remain asymptomatic (19, 20, 139).
Nutrition
Even with the correct implementation of the complexes under consideration, achieving the desired result is quite difficult.
This is due to the fact that even with careful muscle training, they can be hidden under subcutaneous fat. Therefore, we note the following nuances of the training:
- Particular attention should be paid to nutrition. It should be low-calorie and fat-free. When creating a diet, remember to burn fat to reduce the amount of subcutaneous fat.
- In addition to the complexes themselves, you should do cardio training, which will burn subcutaneous fat. It is recommended to do running and other workouts immediately before the complexes themselves.
If you don’t pay attention to burning fat, then all the work on working out your abs will not bring the desired result.
When to expect the effect
It is impossible to answer exactly the question of when to expect the effect of training to pump up the abs, because it all depends on how much time you spend on sports. Those who devote 15 minutes to their abs daily notice the first real results after 2-3 weeks of regular training. And if you spend all of half an hour a week on your abs, then the results will not appear earlier than in a few months.
The trunk crunch is a simple and easy exercise that can be easily done at home in no more than half an hour. Therefore, with persistence, results may not be long in coming.
Raising the body is one of the simple, but at the same time effective exercises that helps to quickly tighten the muscles in the abdominal area and protect the back and spine from injury.
The abdominal complex is included in their programs by people who dream of not only improving their relief, but also increasing endurance and strength. But you need to start with a small load, allowing the body to prepare for more serious loads. Before training, consult a doctor to exclude contraindications.
Why are they needed?
The abdominal press brings invaluable benefits to experienced athletes and beginners.
This exercise, and there are several options for performing it, performs several functions at once:
- relieves stress from the spine in the basic complex;
- a strong press can take on part of the weight of the barbell and it is advisable to strengthen the press until the weight of the barbell reaches its maximum;
- helps relieve back pain caused by muscle spasms;
- aesthetically looks more beautiful than a round belly.
Those who choose strength training pump up their abs specifically to protect themselves from injuries resulting from hypertonicity of the back muscles. For runners, toned abs help achieve core stability while running and efficient lower extremity function.
Bodybuilders work out their abs for beauty, and those who dream of losing weight work them out, thinking that it will help, but this is their mistake. It is enough to simply tone the transverse and rectus muscles.
General recommendations
Please pay attention to the following nuances:
- When using additional weights, the weight should be kept just below the back of the head. You can also keep the weight on your chest, this will make it easier and reduce the risk of injury.
- Rise up while exhaling, and lower while inhaling.
- (Tip for girls) If the footrests leave bruises on your ankles, you can use something soft, such as a fitness mat.
- The body lifts do not have to be performed at maximum amplitude. Many professionals do them in partial amplitude.
Body sit-ups are an effective and accessible exercise for everyone that can be done without leaving home.
Contraindications and possible harm
The abdominal press, like many other exercises, has a number of contraindications for use. Before starting any workout, you should definitely consult a doctor.
You can’t pump up your abs if a person has problems:
- with the work of the heart and blood vessels;
- with the function of the respiratory system;
- with kidneys;
- with the spine;
- with the functions of the stomach and gall bladder.
Also, you should not include pumping the abdominal muscles in your training if a person has been diagnosed with rheumatism or is experiencing an acute period of diseases of organs localized in the peritoneal area.
Circle 1
"Book"
Technique:
- We sit on the mat, bring our legs together, bend our knees slightly. We rest our hands on the floor;
- straighten your legs without touching the floor. We tilt the body back;
- then we bend our legs again, pulling our knees to our chest. At this time, the chest moves towards the knees.
We do the exercise for 30 seconds.
Photo: istockphoto.com
"Bike"
Technique:
- We lie on the mat. We press our lower back and lift our legs off the floor. We pull our socks towards ourselves;
- We perform rotational movements with our legs, simulating riding a bicycle.
We do the exercise for 30 seconds.
Crunches
Technique:
- We lie on the mat. Legs bent at the knees, arms extended parallel to the floor;
- Raise your body without lifting your lower back from the floor. With straight arms we reach for our knees.
We do the exercise for 30 seconds.
Repeat the circle two more times!
Photo: istockphoto.com