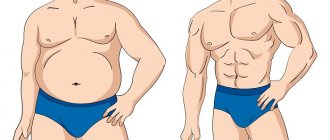
People all over the world differ from each other in appearance. Some are thin, others have toned, athletic figures, and some have wide bones. And very often these indicators do not depend on going to the gym or dieting. Belonging to one type or another is genetically inherent in people.
The predisposition to gain excess weight, to burn all the sweets you eat, or to actively develop muscles is built on the speed of metabolism. It is the metabolism and skeletal structure that determines which somatotype a person belongs to.
What is a somatotype
Somatotype means the type of structure of the human body, characterized by the characteristics of skeletal parameters, muscle development and the amount of subcutaneous fat. Also in the determination, the genetically determined metabolic rate plays a role, which affects the main external indicators of the body. the founder of such a definition system was W. Sheldon. He developed three concepts on which the entire theory of somatotypes rests.
There are three main categories: ectomorph (rectangular body type), mesomorph (triangular body type) and endomorph (square body type).
This classification is based on concepts taken from their embryology, and the names have a common root with the names of the germ layers: endoderm, mesoderm and ectoderm. The scientist W. Sheldon identified seventeen parameters according to which the main somatotypes were distinguished.
Fully or partially limited products
A diet for an ectomorph when gaining muscle mass excludes:
- Fresh wheat bread, pastries, cookies, waffles, puff pastry products, pastries, cakes, semolina, pancakes, dumplings, dumplings.
- Fatty pork, goose, duck, sausages, canned food, smoked meats, animal fats, fast food products, products containing food additives, semi-finished products.
- Sugar, honey, condensed milk, chocolate, ice cream, jam, dried fruits (raisins, figs, prunes, dried apricots, dates), jams, candies, sweet desserts.
- Caffeinated drinks, alcohol.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| red radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 20 |
| black radish | 1,9 | 0,2 | 6,7 | 35 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Fruits | ||||
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| raisin | 2,9 | 0,6 | 66,0 | 264 |
Snacks | ||||
| potato chips | 5,5 | 30,0 | 53,0 | 520 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| white rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
| pancakes | 6,3 | 7,3 | 51,4 | 294 |
Bakery products | ||||
| buns | 7,2 | 6,2 | 51,0 | 317 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jam | 0,3 | 0,1 | 56,0 | 238 |
| candies | 4,3 | 19,8 | 67,5 | 453 |
| pastry cream | 0,2 | 26,0 | 16,5 | 300 |
| cookie | 7,5 | 11,8 | 74,9 | 417 |
| dough | 7,9 | 1,4 | 50,6 | 234 |
| halva | 11,6 | 29,7 | 54,0 | 523 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Cakes | ||||
| cake | 4,4 | 23,4 | 45,2 | 407 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk 3.6% | 2,8 | 3,6 | 4,7 | 62 |
| milk 4.5% | 3,1 | 4,5 | 4,7 | 72 |
| cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,7 | 205 |
| sour cream 25% (classic) | 2,6 | 25,0 | 2,5 | 248 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cheese | 24,1 | 29,5 | 0,3 | 363 |
| cottage cheese 18% (fat) | 14,0 | 18,0 | 2,8 | 232 |
Meat products | ||||
| fatty pork | 11,4 | 49,3 | 0,0 | 489 |
| pork liver | 18,8 | 3,6 | 0,0 | 108 |
| pork kidneys | 13,0 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 80 |
| pork fat | 1,4 | 92,8 | 0,0 | 841 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
| beef liver | 17,4 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 98 |
| beef kidneys | 12,5 | 1,8 | 0,0 | 66 |
| beef brains | 9,5 | 9,5 | 0,0 | 124 |
| bacon | 23,0 | 45,0 | 0,0 | 500 |
Sausages | ||||
| smoked sausage | 16,2 | 44,6 | 0,0 | 466 |
| smoked sausage | 9,9 | 63,2 | 0,3 | 608 |
| sausages | 10,1 | 31,6 | 1,9 | 332 |
| sausages | 12,3 | 25,3 | 0,0 | 277 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| salted fish | 19,2 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 190 |
| Red caviar | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
| cod (liver in oil) | 4,2 | 65,7 | 1,2 | 613 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| creamy margarine | 0,5 | 82,0 | 0,0 | 745 |
| vegetable-fat spread | 0,0 | 40,0 | 0,0 | 360 |
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| instant coffee dry | 15,0 | 3,5 | 0,0 | 94 |
| Pepsi | 0,0 | 0,0 | 8,7 | 38 |
| sprite | 0,1 | 0,0 | 7,0 | 29 |
| black tea | 20,0 | 5,1 | 6,9 | 152 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
External differences
Although somatotypes differ from each other in a number of parameters, each representative has its own advantages and disadvantages. There is no absolutely ideal or losing body type. It is not difficult to understand which of them a person belongs to, and disadvantages can easily be turned into advantages.
- An ectomorph is distinguished by tall stature and thinness, low muscle mass and insignificant reserves of subcutaneous fat. Due to thinness, with optimal physical activity, muscle relief is clearly visible. The limbs are mostly thin and long, which ensures their owner is tall. Intensive metabolism does not allow him to gain body fat, but also does not contribute to the rapid development of muscles. To achieve a good result, they need to exercise according to a special training program with an emphasis on basic exercises.
- Mesomorphs have an athletic figure. They have average height and generally average indicators in terms of the ratio of body fat and muscle mass, average limb length, and an optimally balanced metabolism, allowing them to train effectively. This metabolism allows you to relatively quickly get rid of excess fat and build high-quality muscle mass. This is the ideal body type for bodybuilding. Their body is very defined and, with a responsible approach to training, develops evenly and balanced.
- The endomorph has a stocky figure. He may be full and not very tall. Along with an increased amount of subcutaneous fat, he has greater muscle mass. The limbs are short and quite dense. The strength and endurance indicators of representatives of this somatotype are very high. They have a slow metabolism, which prevents them from losing weight effectively. However, this is a positive point in maintaining muscle mass at the proper level.
Recommendations for diet and menu planning
- Focus on total calories. It's okay if sometimes there is a slight imbalance in nutrients, but the total calorie content should always be approximately the same.
- Keep your fast food consumption to a minimum. For ectomorphs, it is quite acceptable to regularly consume your favorite “junk” food in small quantities. However, it is better to find a healthier alternative to this. Burgers, pizza and baked goods can be made at home using healthy ingredients.
- Drink more water. This is necessary for normal hydration and maintaining water-salt balance. A person needs to consume at least 1 liter of water per 30 kg of body weight.
- Don't overeat. You should feel slightly hungry every 2-3 hours, then you can easily eat the required amount of food. If you eat your fill every time, you won’t be able to fit in 6-8 meals.
- Do fasting days. This will improve the functioning of the entire gastrointestinal tract. Try fasting once every two weeks, consuming only water or kefir, and see the results.
Recipes for healthy eating
Salmon steak in a frying pan
- 21.9 g Protein
- 19.1 g Fat
- 0.9 g Carbohydrates
- 221 kcal
15-20 min.
- #bell pepper
- #second course
- #greenery
- #salmon
- #dinner
- #roasting
- #chilli
- #tomato
- #vegetable oil
- #onion
- #fish
- #spices
- #dinner
- #garlic
Other recipes
Ways to determine your somatotype
How to understand what type a particular person belongs to? There are several ways to find out. You can be guided by faster evaluation methods, or use precise formulas that will require a more in-depth study of the issue. The second category of methods for determining somatotype requires more information and time for calculations.
The methods below range from simple to more complex.
1) Visual assessment method
Anyone can use this method. The information necessary to determine the type of body structure is knowledge of all the external characteristics inherent in an ectomorph, mesomorph and endomorph.
When looking at a particular individual, a well-read person can easily understand and identify belonging to one of the three body types.
2) Wrist measurement
This is a fairly old method, the reliability of which many experts today doubt. This definition is based on the measurement of a person's wrist. At the same time, a girth of 17.5 cm in length was initially considered the norm. A smaller wrist girth indicated that its owner was a thin-boned ectomorph. Mesomorphs will have a wrist circumference of up to 20 cm, while those with more impressive figures are endomorphs.
An even more old-fashioned way of determining the relationship between wrist size and somatotype will be effective if there are no measuring instruments at hand. You need to clasp your wrist with your middle and thumb fingers.
If the thumb overlaps the middle finger, then the person is an ectomorph. If the fingers only touch, then the owner of such a wrist is a mesomorph. And if the fingertips do not reach each other, then this is a clear sign of belonging to the endomorphic type.
3) Height to weight measurements
For this, different techniques are used. The simplest and most approximate way would be to subtract 110 from the height indicator in centimeters if the height does not exceed 170 centimeters. The resulting difference will approximately correspond to the ideal weight. Depending on the difference between this figure and the body weight, you can find out what type a person’s weight is close to.
A more complex method involves age-based calculations. The formula allows you to calculate your ideal weight, which is equal to: 50 + 0.75x(height in cm – 150) + (age in years – 20) / 4.
4) Using tables
You can also use the method of determining your body type using a table. To do this, you need to know your weight, height and age and, using the values indicated in the diagram, identify your belonging to one or another somatotype.
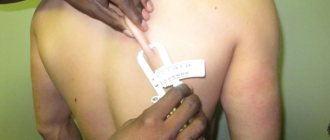
5) Calculations using formulas
The most accurate approach is considered to be the use of formulas that include several variables, including limb girths, body mass index, and measurement of skin folds. These formulas, derived by anthropologists, are named after their researchers.
So, among the most famous are the somatotyping of Heath-Carter, Chernorutsky, Chtetsov.
6) Analysis of human inclinations
An additional way to clarify knowledge about a particular somatotype would be to study the tendency to be overweight and the body’s reaction to different types of stress. Thus, the tendencies of an ectomorph include a low ability to gain weight, fat and muscle.
There are special calculators that allow you to find out what somatotype a person belongs to. Some measured parameters are taken as a basis, for example, hand and hip girths, height, weight.
Authorized Products
The diet for an ectomorph when gaining muscle mass includes:
- Chicken eggs in any form.
- Chicken, turkey, lean red meat (veal, beef), rabbit meat.
- Sea/river fish (tuna, herring, perch, hake, sardines, pike, salmon, trout, cod), seafood (mussels, shrimp, crabs, squids).
- Grain bread/without yeast, bread with bran, grain bread.
- Wholemeal pasta, cereals (oatmeal, wheat, buckwheat), white rice.
- Soups with low-fat broth, cabbage soup, borscht.
- Low-fat dairy/fermented milk products (yogurt, kefir, milk, cottage cheese, fermented baked milk), hard cheeses.
- Legumes (beans, chickpeas, peas, lentils), soybeans and soy-based products (tofu cheese, milk).
- Nuts, seeds, bran, seaweed, sesame and flax seeds.
- Non-starchy vegetables (carrots, onions, cucumbers, tomatoes, sweet peppers, cabbage, zucchini), garden herbs.
- Unrefined virgin vegetable oils (corn, olive, sesame, flaxseed), fish oil, butter.
- Unsweetened fruits/berries (red/black currants, apples, citrus fruits).
- Herbal tea, freshly prepared juices from apples, oranges, pomegranates, plums, purified still water, rosehip infusion, green tea with lemon.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| greenery | 2,6 | 0,4 | 5,2 | 36 |
| eggplant | 1,2 | 0,1 | 4,5 | 24 |
| beans | 6,0 | 0,1 | 8,5 | 57 |
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| broccoli | 3,0 | 0,4 | 5,2 | 28 |
| boiled cauliflower | 1,8 | 0,3 | 4,0 | 29 |
| watercress | 2,3 | 0,1 | 1,3 | 11 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| salad pepper | 1,3 | 0,0 | 5,3 | 27 |
| salad | 1,2 | 0,3 | 1,3 | 12 |
| beet | 1,5 | 0,1 | 8,8 | 40 |
| celery | 0,9 | 0,1 | 2,1 | 12 |
| soybeans | 34,9 | 17,3 | 17,3 | 381 |
| asparagus | 1,9 | 0,1 | 3,1 | 20 |
| tomatoes | 0,6 | 0,2 | 4,2 | 20 |
| Jerusalem artichoke | 2,1 | 0,1 | 12,8 | 61 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
| dill | 2,5 | 0,5 | 6,3 | 38 |
| beans | 7,8 | 0,5 | 21,5 | 123 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
| lentils | 24,0 | 1,5 | 42,7 | 284 |
Fruits | ||||
| avocado | 2,0 | 20,0 | 7,4 | 208 |
| oranges | 0,9 | 0,2 | 8,1 | 36 |
| pomegranate | 0,9 | 0,0 | 13,9 | 52 |
| grapefruit | 0,7 | 0,2 | 6,5 | 29 |
| pears | 0,4 | 0,3 | 10,9 | 42 |
| kiwi | 1,0 | 0,6 | 10,3 | 48 |
| lemons | 0,9 | 0,1 | 3,0 | 16 |
| mango | 0,5 | 0,3 | 11,5 | 67 |
| tangerines | 0,8 | 0,2 | 7,5 | 33 |
| nectarine | 0,9 | 0,2 | 11,8 | 48 |
| peaches | 0,9 | 0,1 | 11,3 | 46 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
| baked sweet and sour apples | 0,5 | 0,5 | 12,3 | 59 |
Berries | ||||
| gooseberry | 0,7 | 0,2 | 12,0 | 43 |
| Red currants | 0,6 | 0,2 | 7,7 | 43 |
| black currant | 1,0 | 0,4 | 7,3 | 44 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| nuts | 15,0 | 40,0 | 20,0 | 500 |
| cashew | 25,7 | 54,1 | 13,2 | 643 |
| sesame | 19,4 | 48,7 | 12,2 | 565 |
| flax seeds | 18,3 | 42,2 | 28,9 | 534 |
| fenugreek seeds | 23,0 | 6,4 | 58,3 | 323 |
| sunflower seeds | 20,7 | 52,9 | 3,4 | 578 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| oat groats | 12,3 | 6,1 | 59,5 | 342 |
| cereals | 11,9 | 7,2 | 69,3 | 366 |
| wheat bran | 15,1 | 3,8 | 53,6 | 296 |
| millet cereal | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
Bakery products | ||||
| whole grain bread | 10,1 | 2,3 | 57,1 | 295 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
Dairy | ||||
| skim milk | 2,0 | 0,1 | 4,8 | 31 |
| natural yogurt 2% | 4,3 | 2,0 | 6,2 | 60 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese 0.6% (low fat) | 18,0 | 0,6 | 1,8 | 88 |
| curd tofu | 8,1 | 4,2 | 0,6 | 73 |
Meat products | ||||
| beef | 18,9 | 19,4 | 0,0 | 187 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| boiled chicken fillet | 30,4 | 3,5 | 0,0 | 153 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Eggs | ||||
| hard-boiled chicken eggs | 12,9 | 11,6 | 0,8 | 160 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| boiled fish | 17,3 | 5,0 | 0,0 | 116 |
| squid | 21,2 | 2,8 | 2,0 | 122 |
| salmon | 19,8 | 6,3 | 0,0 | 142 |
| mussels | 9,1 | 1,5 | 0,0 | 50 |
| seaweed | 0,8 | 5,1 | 0,0 | 49 |
| herring | 16,3 | 10,7 | — | 161 |
| zander | 19,2 | 0,7 | — | 84 |
| cod | 17,7 | 0,7 | — | 78 |
| tuna | 23,0 | 1,0 | — | 101 |
| trout | 19,2 | 2,1 | — | 97 |
| hake | 16,6 | 2,2 | 0,0 | 86 |
| pike | 18,4 | 0,8 | — | 82 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
| linseed oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| olive oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| sunflower oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| instant chicory | 0,1 | 0,0 | 2,8 | 11 |
| green tea | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Why is this information needed?
Understanding your somatotype is a very important step. It has been proven that body type influences the development of an individual training program and diet.
The difference in somatotypes shows how differently representatives of these three physiological categories should train and eat, and what goals they should achieve.
In order to choose the optimal frequency and program of physical activity for yourself and create the right menu, you need to study your somatotype.
Many people who are prone to obesity dream of an ideal figure. Often they do not understand that nature has endowed them not only with a special metabolism, but also with a skeleton of a certain width.
Therefore, endomorphs, in particular women, must realize the impossibility of transforming a massive skeleton into a thin doe , no matter how much effort it costs them. This knowledge will help them come to terms with some of the characteristics of their body and turn imaginary shortcomings into advantages. After all, as you know, curvy shapes and a rounded silhouette are very feminine and seductive in the eyes of the opposite sex. By following a diet and moderate exercise, you can make your body truly beautiful, regardless of your figure type.
The same goes for ectomorphs who suffer from lack of muscle mass. But knowing the characteristics of his body, a naturally thin person can achieve good results in sports and create an elegant, sculpted body. And excess weight and shortness of breath definitely do not threaten him.
The luckiest of all seems to be the mesomorph, because thanks to moderate indicators of mass, volume, metabolism and general abilities, he best adapts to stress and diet. However, he should not become arrogant and lazy, because the risk of gaining excess weight and losing muscle is still present.
Ectomorph training
People with an ectomorphic body type should not exercise for too long, so as not to lose more energy than they have in reserve. Long-term training leads to the destruction of muscle protein, so you need to train for 40-60 minutes. You should perform split training, 2-3 exercises (basic and isolating) per muscle group.
A set of exercises for an ectomorph for a week
Day 1 (legs, shoulders)
- Squats with a barbell 4x8-10.
- Leg press 4x8-10.
- Seated leg extension 4x8-10.
- Sitting shin 4x15-20.
- Smith front press 4x8-10.
- Barbell row to the chin 4x8-10.
Day 2 (chest, triceps)
- Bench press at an angle of 4x8-10.
- Dumbbell press horizontally 4x8-10.
- Dumbbell fly 4x8-10.
- French press with dumbbells 4x8-10.
- Extension of the upper block with edges 4x8-10.
Day 3 (hamstrings, rear deltoids)
- Deadlift 4x8-10.
- Hyperextension 4x8-10.
- Leg curls in the 4x8-10 machine.
- Shin in a standing simulator 4x15-20.
- Wiring in the simulator for the rear delta 4x8-10.
Day 4 (back, biceps)
- Wide grip pull-ups 4x8-10.
- Lever rod 4x8-10.
- Dumbbell row to the waist in support 4x8-10.
- Wide grip barbell curl.
- Alternating lifting of dumbbells with supination.
Lack of body weight with normal nutrition
It also happens that the client’s diet is quite high in calories, he has no problems with appetite and eating disorders, but at the same time his weight is below normal. Then you should look for the cause in your health condition.
Here is a list of diseases that can potentially lead to underweight:
- hyperthyroidism and other problems in the production of thyroid hormones;
- type 2 diabetes mellitus (in some cases, instead of weight gain, it leads to rapid weight loss);
- severe stress and prolonged depression, when the nervous system is depressed;
- tuberculosis;
- long-term infectious and inflammatory diseases;
- celiac disease (celiac enteropathy or severe gluten intolerance);
- oncological diseases;
- chronic intestinal infections;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, including insufficient enzymatic activity of the pancreas and underdigestion of food;
- helminthiasis (in other words, worms).
However, without appropriate tests and examinations, it is impossible to say exactly what could have caused the loss of weight and appetite. Therefore, advise your clients to go through the following:
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland and consultation with an endocrinologist.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs and consultation with a gastroenterologist.
- Fluorography or x-ray of the lungs and consultation with a family doctor or TB specialist.
- Take a general and biochemical blood test, as well as blood tests for thyroid hormones, gluten tolerance, and worms.
- Make a tumor marker.
- Kaprogram and analysis for intestinal dysbiosis.
- Electroencephalogram and consultation with a neurologist.
- Consultation with a psychologist or psychiatrist.
If certain diseases are identified, the client will have to begin treatment for them. Otherwise, without eliminating the cause of weight loss, gaining additional kilograms can be very difficult. And, nevertheless, people with underweight need to adjust their diet in any case.
Body types and their features
- An ectomorph is always skinny, who doesn’t get fat from eating pizza, but her jeans are always hanging on her butt. It is difficult for ectomorphs to gain weight, but they lose weight instantly.
- Mesomorph - loses weight easily and quickly gains weight, but more often than others, he neglects himself. “Just think, I gained a couple of kilos. When I want, I’ll quickly throw them off.” Those who are mesomorphs, I think, have recognized themselves.
- Endomorph - capable of gaining weight just from sniffing a bun??? We'll pump up our butt, we'll gain mass, it's easy. But losing fat is oh so difficult. And endomorphs get fat instantly???.
This method of determining body type is unlikely to be suitable for those who are determined to build impressive muscle mass or completely lose weight. To choose the right strategy, we need to accurately determine our somatotype. A measuring tape will help here.