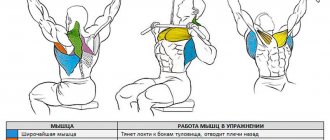
Straight arm vertical block rows are aimed at developing the latissimus and teres major muscles. In static conditions, it “pumps up” the triceps too. But as the main movement it is used for the back muscles. The exercise is used by both bodybuilders and representatives of other sports disciplines. In particular, it is common for strength training of swimmers.
Execution technique
Initial position
- You need to attach a straight and wide handle to a vertical block;
- Stand straight at the machine, stretch your arms straight up;
- Place your palms on the handle;
- Move your shoulders away from your ears, lower your shoulder blades, tighten your stomach;
- Take a step back and lean forward slightly.
Movement
- By tensing your back and triceps muscles, lower the handle towards your hips;
- Bring it back slowly and in a controlled manner;
- Repeat as many times as necessary;
- When returning the machine to its original state, try to raise your shoulders sharply towards your ears.
bodymaster: Lat Pulldown
Attention
- The back tilt is achieved by flexing the hip joints. It does not increase as you “sag” forward;
- You shouldn’t swing your arms like a pendulum either;
- The movement is performed exclusively in the shoulder joints, and not in the hip joints and not due to the work of the body.
Pull the block down with straight arms[edit | edit code]
Characteristics
:
Pulling the block down with straight arms
- Assistance exercise focusing on stabilizing muscles
- Isolating one joint when pulling a block down with straight arms
- Traction movement
- Closed kinetic chain
- Using weights
- For intermediate and advanced levels
This exercise is aimed at working the stabilizing muscles of the trunk, in particular the abdominal muscles, serratus anterior and lower trapezius muscles. The quality of the exercise in this case is more important than the magnitude of the load.
Pulling the block down with straight arms
Inclusion in the training program
There is one problem with numerous block pulls “with variations”. Not all of them help build muscle size and mass. Many are completely useless in this regard and offer nothing to those looking to gain muscle mass and get in shape. The straight arm row will help shape your silhouette and correct your posture a little, but it is not intended for those who have problems gaining mass.
Everything is quite simple. This exercise is included third or fourth in a program that already has any variation of vertical rows (pull-ups, regular or with weight, or a simple heavy vertical row), and horizontal rows to the waist. The classic deadlift is an exercise option for developing the back only because doing it literally forces you to engage the latissimus muscles in a static manner, and the significant weight helps to load them decently.
The straight arm row is not intended to correct the deadlift, and does not have any additional effect on it. It shapes aesthetics for the most part. This exercise is also called a standing pullover; biomechanically it is identical to a regular pullover. You can add movement to your training plan if you have problems with posture.
The exercise is performed in 4-5 working sets with medium to light weights, and can be included in the plan as a finishing movement. For most bodybuilders, it makes sense to do it on back and biceps day, but for those who have obvious postural problems due to improper bench press technique or shoulder injuries, it can also be done on chest day.
Basic errors during execution
Common mistakes:
- Stooping (curvature of the spine).
- Lifting the buttocks from the seat.
- Full extension of the forearms at the top point.
- Redistributing the load on the biceps of the arms, rather than the body.
- Too much weight or a large number of approaches, which will make it difficult to perform the exercise correctly.
If you don't straighten your back when performing overhead pull-downs, you may get injured.
Consequences of incorrect execution:
- injuries;
- pain in the body, resulting from the accumulation of lactic acid;
- ineffectiveness of working out the spinal muscles and hypertrophy of the arms, not the back.
To speed up the elimination of lactic acid after exercise, you can do a relaxing massage or take a warm bath.
Read also: What is more caloric, lavash or bread?
Almost all bodybuilders include overhead pull-downs in their basic training routine. In addition, this simple strength exercise is widely used by beginners. The main thing in forming a beautiful figure is to adhere to systematicity and the correct technique.
What muscles work
The exercise works the lats, teres major as movers, as well as the shoulder and triceps muscles in static positions. Movement is not energetically expensive and does not require large calorie expenditure. You can include it in a training plan for weight loss only if the athlete has already completed a regular block lift or deadlift.
During operation it is necessary to statically
The movement is not recommended for those who have problems with control of the projectile and a shoulder injury; it is possible that the arms “shoot” upward and re-injury.
A simple test - if you cannot move your forearm behind your ear while standing, you should not perform this movement as an auxiliary or main one until moving your hand behind your ear becomes available to you throughout the entire depth of the amplitude.
When to Use the Straight Arm Reach
Perform straight-arm pull-ups before deadlifts or other back exercises to prepare your lats for the force and increase muscle growth in that area. Because the straight-arm lat pulldown provides an intense stretch for the lats in the top (starting) position, this exercise is also useful early in a workout to improve back and shoulder mobility.
Try doing the exercise at the end of your workout for several sets of 10-15 reps with short rest periods in between (30-45 seconds). This will greatly improve blood flow to the area, which itself is a mechanism for muscle growth.
Purpose of the exercise
In bodybuilding they usually say that this movement gives a characteristic “shoulder turn” and helps give the body a V-shape. In reality, the purpose of the exercise depends on the body type and the purpose of the training. While for some people this exercise is a good way to “lift” the chest by engaging the lats more, for others it is purely a rehabilitative movement for the rotator cuff.
Movement is included in training in different ways. If a light, “pump” back workout is planned, this may be the first exercise in the cycle; if something heavier is planned, with a deadlift, this may be one of the final exercises.
Recommendations and possible errors
Basic recommendations and elimination of main mistakes for effective execution of the exercise:
- The most common mistake is rounding the back. Most gym goers accept it. In some athletes, the rounding occurs so strongly that it creates compression of the vertebrae in the thoracic and cervical region;
- To avoid rounding your back, push your chest forward and keep your neck straight;
- Bend your knees, this is important for fixing the body. Straight legs, especially if heavy weights are used, will place excessive stress on the joint;
- The back must be kept straight, but the lower back should not be arched excessively. Try to keep the curves of the spine in a natural position;
- Learn to pull with your back, not your arms. The neuromuscular connection plays a key role in this exercise. Many athletes focus on their arms, which reduces the load on the lats;
- To pull a weight with your back, imagine that you are not pulling on the handles, but by moving your elbows as far back as possible. At the same time, relax your hands slightly so that they hold the handle;
- Always bring your shoulder blades together at the top point; without this, you will not be able to perform the movement to its full amplitude;
- When returning to the starting position, move your shoulders forward a little, this will create an additional stretch. But you should not hunch your whole back, this is a mistake;
- Start pulling the weight when placing on the bench only when your feet are resting on the platforms. Often athletes first pull the cable and only then place their feet on the supports. This is a serious mistake that can easily lead to injury.
It's a HORIZONTAL BLOCK PULL, baby!
Types of overhead pull-downs and execution techniques
Initially, all types of deadlifts are divided into two categories - with the position behind the head and in front of you. Pulling the upper block to the chest is considered more anatomically correct, since in this position all the levers have a natural position and the chances of getting injured are reduced to almost zero. To properly do lat pull-downs behind your head, you need high flexibility in the shoulder joints and good stretching of the pectoral muscles. Most gym goers don't have this because it requires regular chest stretching and shoulder mobility work. It follows that for most people, bringing the handle to the chest is more suitable than pulling the block behind the head.
Other ways to diversify the load come down to adjusting the grip width and using different handles.
Wide grip lat row
This is a classic version of traction with a vertical block. It is considered optimal for evenly distributing the load across all muscles, with the main emphasis on the latissimus. The most important point that affects the effectiveness of the exercise is not even the movement itself, but the adoption of the correct position.
Extremely important:
- Adjust the fixation rollers so that your feet are firmly on the floor with a right angle at the knees;
- Take a place on the bench so that in the starting position the handle is at the level of the conventional vertical line that runs along the spine;
- Take a position in which the body is in an upright position with a straight back. In the process of pulling the block towards you, the body will lean back slightly so that the handle moves exactly towards the front delts.
If all conditions are met, traction will be safe and effective in almost all cases.
Technique:
- Sit in the machine, take the wide handle with a straight grip closer to the edges;
- Inhale and begin to pull the handle, keeping your back straight. While lowering the weight, lean back slightly so as not to change the trajectory of the handle of the upper block.
- Lower the handle at least to the level of the bottom of your chin. Although it is considered correct to pull the handle with a light touch to the clavicular area;
- As you exhale, return the weight to the starting position at a slower pace, controlling each part of the movement.
Reverse Grip Lat Pulldown
It is generally accepted that reverse-grip lat pulldowns load the biceps much better, although from a biomechanical point of view this is not the case. The biceps takes on a little more load, but in return the load is “given” from the latissimus muscles. This makes the movement less beneficial for the target area, which is the back. At the same time, the load on the biceps will not be enough to use this variation to pump up your arms.
In fact, the lat pulldown with a reverse close grip is considered an optional exercise and serves as a way to add variety to the training process. The movement is best suited for back/biceps splits, in which case the exercise will target two muscles worked per session.
Technique:
- Grab the handle with a reverse grip (narrow or medium, wide is not suitable for this technique). Tilt your body back in the starting position, an angle of 30-45 degrees;
- Start pulling the handle down, trying to lower it to the bottom of your pecs;
- At a slower pace, return to the starting position.
Parallel grip lat row
This option is more applicable and has some advantages even over the classical technique. The exercise better loads the deltoid muscles, especially the posterior head. The grip can be used medium or narrow, depending on the chosen handle.
Technique:
- Sit down in the exercise machine, take the handle so that your palms are directed towards each other. Lean your body back at an angle of 45 degrees, keeping your back straight;
- Start pulling the handle down, trying to bring it to your chest as close as possible (up to a light touch);
- Return the weight to the starting position at a slower pace.
Pull-down of the upper block behind the head
If you do decide to perform lat pulldowns, there are key features to consider for proper body position. Basically they come down to the main rules:
- In the initial position, the body must be moved slightly forward. The handle should be at the level of a conventional line that can be drawn from the spine and neck upward;
- Unlike the classic or reverse versions, the body must be in a straight position all the time. Any rocking forward or backward is excluded; this is a gross mistake that leads to the risk of injury to the cervical spine;
- To avoid hitting yourself on the back of the head with the handle, when lowering the projectile you need to move your head forward a little. It is forbidden to lower your head too low and “peck” it at the floor. It is enough to bend your neck at an angle of 10-15 degrees so that the handle falls behind your neck without interference and correctly.
In other nuances, the technique of moving behind the head is similar to the classic pull-down of a vertical block in front of you. This option does not provide any pronounced advantages. It loads the posterior bundles a little better, but given the risks and difficulties, it is not recommended as a priority.
Exercise technique:
- Grab the handle of the cable trainer and move away from it at a distance of approximately one to two meters. Your hands should be positioned on the handle of the machine wider than shoulder width (see photo).
- Move your body back at an angle of 30° and extend your arms forward. If you can’t immediately stretch your arms forward, to make the task easier, take another half step back until you reach the correct position. After this (but not before!) start the exercise.
- Perform a pull-down, keeping your arms straight so that they are as close to your body as possible. This movement should be performed while exhaling. Try to hold your hands in this position for a few seconds to feel the muscles as much as possible.
- As you inhale, smoothly raise your arms to the starting position.
Standing one-arm lat pulldown
Muscles working in one-arm row while standing in the lower block: 1 - deltoid; 2 - trapezoidal; 3 - pectoralis major (clavicular part); 4 - biceps Inventory
: training apparatus.
Core muscles
: anterior, middle part of the deltoid muscles, clavicular part of the pectoralis major muscle.
Additional muscles
: short head of biceps, trapezius muscle.
Level of training
: intermediate, advanced, professional.
When performing this exercise, many muscles are involved - trapezius, deltoid, etc. The load is largely directed at the middle bundle of the deltoid muscle.
Step 1
. Legs slightly apart. Grasp the handle of the machine, keeping your hand near your hip.
Step 2
. Inhale and move your arm to the side to a position above horizontal.
Step 3
. As you exhale, return to the starting position. Returning to the starting position should occur smoothly, do not suddenly release the handle.
How to gain weight?
Each athlete chooses his own weight for his physical shape. But for progress to occur, the load must be constantly increased. To avoid spinal injuries, this should be done smoothly. The optimal solution would be a block simulator in increments of 1.5-2 kg. For the load to be effective, the weight must be such that the athlete can do 6-8 repetitions of 4-5 approaches.
Remember that in any variation of the execution, the pull-down of the lower block is an isolating exercise, and you should not get carried away with heavy weights. The main thing here is to work well on your technique. To increase the load, you can, for example, reduce the rest time between approaches.
Why do you need a tiny pocket on jeans? Everyone knows that there is a tiny pocket on jeans, but few have thought about why it might be needed. Interestingly, it was originally a place for storage.
11 Weird Signs That You're Good in Bed Do you also want to believe that you please your romantic partner in bed? At least you don't want to blush and apologize.
9 Famous Women Who Have Fallen in Love with Women Showing interest in people other than the opposite sex is not unusual. You are unlikely to be able to surprise or shock anyone if you admit it.
13 signs that you have the best husband Husbands are truly great people. What a pity that good spouses don't grow on trees. If your significant other does these 13 things, then you can s.
20 photos of cats taken at the right moment Cats are amazing creatures, and perhaps everyone knows this. They are also incredibly photogenic and always know how to be in the right place at the right time.
These 10 little things a man always notices in a woman Do you think your man doesn’t understand anything about female psychology? This is wrong. Not a single little thing can be hidden from the gaze of a partner who loves you. And here are 10 things.
Exercise options
It is important to understand that the pull to the belt on the block can only vary in the choice of handle and grip. The movement itself remains unchanged - it involves pulling the handle towards the body. Athletes often confuse seated rows with a pendulum exercise or a rowing exercise, where the body moves forward and backward. This is a significant mistake that increases the risk of injury. Also, rocking the body puts a lot of stress on the joints and increases compression of the vertebrae while sitting. The pull-down in the lower block is performed without swinging or with minimal deviation, about 10 degrees.
With wide handle
In terms of loading the target area, wide grip rows are most beneficial as they involve less arm involvement.
But this option shortens the amplitude, so it should not be considered as the only one. The long handle and wide grip are ideal for alternating with the classic version or other techniques, but on different days. It is also worth considering that with a wide grip, the handle should not be brought to the lower abdomen. With this technique, the shoulders will be overloaded, which will make the movement ineffective and traumatic. In this version, it is anatomically correct to pull it to the middle of the abdomen, between the solar plexus and the navel. In this position, the elbows will be pulled back as far as possible.
With rope handle
This is a very effective option that is more suitable for advanced athletes.
It provides pumping not only for the lats, but also for the arms and forearms. Also, with this option, the abdominal muscles are more actively loaded. In terms of the amount of muscle fiber recruitment, the rope option is the most effective. But without perfect technical execution, it will be less effective.
Technique:
- Sit on a bench and grasp the ends of the rope handle in your hands. The back is straight, the knees are bent;
- Start pulling the weight towards your waist;
- At the point of maximum tension, spread your shoulder blades to the sides, and also additionally stretch the rope handles to the sides;
To the chin with a rope handle
This is an alternative option that focuses on developing the upper back, as well as the arms and shoulders.
It is an independent exercise and can be performed together with classic deadlifts in one workout. Technique:
- Place yourself on a bench and grasp the edges of the handle so that the pears on the edges are directed upward;
- Pull your hands towards your neck;
- At the top point, spread your arms in different directions as far as possible.
The exercise creates increased stress on the shoulders, so you should approach it only after a thorough warm-up.
Horizontal block thrust target
The horizontal pull-down is an athletic exercise that allows you to achieve the following goals:
- Increased strength and endurance of the back muscles. The lat pulldown in the simulator is a complete basic exercise. During its execution, movement occurs in 2 paired joints (elbow and shoulder). A convenient location on the machine bench relieves stress from the lower back and allows you to use large working weights.
- Rehabilitation and recovery. Sports activities using a horizontal block isolate the upper body. In contrast to bent over rows of barbells or dumbbells, the load on the lumbar spine is significantly reduced. When exercising with a block simulator, it becomes possible to better control the weight of the weight and concentrate on muscle contraction. This makes it possible to continue training even with minor sprains and injuries.
- Giving depth and definition to the back muscles . Due to the hormonal characteristics of the female body, it is impossible to build large muscle volumes in girls without the use of special means. Therefore, building the depth of the muscles of the back of the body is one of the few ways to create the appearance of a harmoniously developed and strong back.
Horizontal block row to the abdomen - working muscles
When performing horizontal block rows, the following large and small muscle groups are involved in the work:
| Name | What role do they play? |
| Latissimus dorsi muscle | These paired muscles bear the main load. The latissimus dorsi muscles are responsible for abducting the arm beyond the plane of the body and bringing it to the sides. |
| Rhomboid muscles | Internal back muscles. Located in the upper third of the body. This paired muscle group is shaped like a diamond and is located under the trapezius muscles. The main task of this group is to bring the shoulder blades together. |
| Trapezius muscles | They belong to the group of postural muscles. They are responsible for maintaining the correct position of the spine and for the correct location of the shoulder joint. The trapezius is located symmetrically along the spine. |
| Rear delts | Participate in abduction of the arm beyond the line of the body and transverse adduction of the shoulder. The arm is also bent at the elbow joint. |
| Teres major muscles of the back | Paired muscles located above the latissimus in the upper back. Responsible for moving the chest up and forward. They have a postural nature and help to form correct and healthy posture. |
| Long back extensors | The muscles are located in the lower back and are located symmetrically along the spine. |
To effectively train all of these muscle groups, girls need to follow a number of recommendations:
- To engage the muscles responsible for the correct position of the spine and posture, it is necessary to bring the shoulder blades together as fully as possible and move the elbows back. In this case, the trapezius and rhomboid muscles of the back receive sufficient incentives to grow and strengthen.
- All athletic movements in the gym must be performed smoothly. This is especially true for training with block simulators and horizontal rows in particular.
- Watch the position of your legs. The lower limbs should be securely fixed and slightly bent at the knee joint. Straight legs will cause excessive tension in the hamstrings. In this case, performing the exercise will become uncomfortable. Excessively bent lower limbs will interfere with the movement of the machine handle.
- Body rocking. Girls should not resort to this technique. Thanks to swinging, it becomes possible to operate with large working weights. This is not required to build a harmoniously developed back.
- Elbow position. The practitioner's hands should move along the body. They should not be moved to the sides when pulling a horizontal block. This will reduce the effectiveness of the exercise.
The horizontal block row requires compliance with the rules of technique for performing the exercise. Rocking the body or rounding the thoracic spine can lead to injury. Such disorders prevent the back muscles from performing their functions. The load is transferred to other muscles (extensors and biceps).
How to choose a working weight
If the weights in the machine are incorrectly installed, it will be very difficult to perform the movement correctly. Moreover, the overall injury rate will increase significantly. Incorrect selection of weight is one of the most common and main mistakes in seated block rows.
Weight is always selected individually, based on strength capabilities. Beginners are advised to do a minimum “walkthrough” in order to determine their one-repetition maximum. Then, with an understanding of the one-repetition maximum, it will be possible to more competently select the weight as a percentage. For deadlifts, it is optimal to choose a weight in the range from 60 to 80% of 1RM.
To work in the 8-12 repetition mode, it is recommended to take the weight no more than 60-70% of 1 RM. With a weight of 80% of 1RM you should work in the 5-8 repetition mode. Setting the weight below 60% is recommended only for high-repetition techniques, when working for 15-20 repetitions per set.
It is also worth considering that one of the criteria for correctly selected weight should be the ability to bring the shoulder blades together at the peak point and not swing the body.
Vertical block row for the head
The advantage of this exercise is to develop the width of the back muscles. This exercise prepares your back muscles for pull-ups and free weight exercises.
What muscles work
- Latissimus dorsi muscles.
- Teres major muscle.
- Biceps brachii.
- Shoulder muscles.
- Brachioradialis muscles.
- Lower part of the trapezoid.
- Rhomboid muscle.
Exercise technique
- Grab the wide handle with a wide grip from above, lower your pelvis onto the seat, straighten your arms above your head, lock your hips under the bolsters.
- Lean your body forward slightly, keeping your back straight.
- As you exhale, move the handle behind your head without touching the cervical vertebrae. Do not lower the handle below your neck. Bring your elbows towards your body by bringing your shoulder blades together, working concentratedly with your back muscles.
- Lock the muscles at the lowest point with maximum contraction.
- As you inhale, slowly straighten your arms above your head.
- Repeat the movement.
Pull in different directions
Traction can be performed in several main directions:
- To the lower abdomen. With this option, the back muscles are included in the work. The main emphasis of the load shifts towards the bottom of the lats. Also, a significant part of the load falls on the posterior bundle of deltoid muscles. This occurs due to the greater range of motion of the elbow. The hand goes further beyond the line of the body. At the same time, the rear delta contracts and stretches more intensely.
- To the chest. The deadlift engages the muscles of the entire back of the body. The main load is distributed between the large round muscles and the top of the latissimus. Depending on the selected grip width and type of handle, both the rhomboid and trapezius muscles can be involved in the work. The rear delts work to a lesser extent.
- To the head. This version of the exercise is performed sitting or standing in a crossover. All muscles of the upper back are involved. The pull of the horizontal block to the head allows the shoulder joint to perform external rotation. This strengthens the internal rotator cuff.
Romanian deadlift
Another lat pulldown movement that many women love is the Romanian lat pulldown while standing with your back to the crossover.
The pulley cable passes between the legs, the handle is held in straight, lowered hands. As in the classic version with a barbell or dumbbells, here the load is aimed at the gluteal muscles, hamstrings and lower back.
Unlike a barbell, the center of gravity of the weight is shifted back (behind the back).
This feature allows you to achieve unusual sensations in the target muscles. This can provide an additional incentive for their growth.