Powerlifting programs from famous coaches and athletes. All training programs are functional and effective, but depending on the physical characteristics of each person, not every lifting program may be right for you.
Choose and try to find exactly the powerlifting program that will give you the greatest increase in triathlon. If you are interested in the bench press, then see bench press programs here.
You can find many different powerlifting programs in books.
Powerlifting programs
Powerlifting programs from famous coaches and athletes. All training programs are functional and effective, but depending on the physical characteristics of each person, not every lifting program may be right for you.
Choose and try to find exactly the powerlifting program that will give you the greatest increase in triathlon. If you are interested in the bench press, then see bench press programs here.
You can find many different powerlifting programs in books.
Sheiko B.I. cycles in Excel
Very conveniently designed powerlifting programs by Boris Ivanovich Sheiko, you just plug in your performance in the exercises and all the weights are recalculated for you.
Self-calculating cycles by Dmitry Golovinsky in Excel
Dmitry Golovinsky - MSM WPC/AWPC of Ukraine, record holder and world champion in powerlifting and bench press, national category judge.
Here are self-calculating powerlifting cycles for athletes of various levels of preparedness from beginners and advanced athletes to intermediate athletes. You will find a detailed description of cycles and their use on Dmitry’s website.
Here are some more programs and loops in Excel
List of the best programs
I advise you to definitely read an excerpt from the book “Body of Tips on Explosive Training.”
Train according to the program, but don't be afraid of workarounds
You need a program designed to help you achieve your training goals. The difference is that each program has its own strengths and weaknesses. Time and experience are the best teachers. Find out how you can tailor the program to suit you. For beginners, I would advise using proven powerlifting training programs. They are not as effective as custom-made ones, but they are much better than those that you can come up with without experience. That's why they are described at the beginning - they serve as a starting point.
At intermediate and advanced levels, you need to think of your program like driving a car on the highway. You must go in the right direction, no matter who tells you what. The difference is that you need to read the signs. On any long journey there are slowdowns, stops, and detours. As travelers, we expect this, but we still get upset when we come across them. It's part of the game. There are things that can ruin the training process. Things may not go as planned and you may find a workaround. In fact, if you find yourself running ahead of schedule and everything is going smoothly, be on guard.
Get your ass off!
You read about the dynamic and maximum effort method. The problem is that you started training 6 months ago and you look like a stick. However, you feel that this is the best way to train strength and you have heard many others say the same thing. You read all the articles, but missed the point.
Yes, you can use these techniques, but only when they are inserted into your program based on your weaknesses.
What is your weakness? Hips? Triceps? Or maybe the whole body is just weak? A beginner does not need to start with advanced training methods. He needs to build a strong foundation with basic movements.
It's not easy to overcome
Are you worried that progress is not too fast? You know, I've never seen anyone worry about progressing too quickly. There are those who can gain strength just by looking at the weights. These guys can train once a week and they all grow like weeds. But it's not me, and I'm willing to bet it's not you.
Work to get results. The road is never easy and it can take several years to gain a few pounds. This is not easy, even for those who progress quickly. Sooner or later this happens to everyone. If you can't handle this, get out of the room.
With fanatical faith anything is possible
If you want to achieve results, you must have fanatical faith in your own ability to succeed. The best example, I think, is Matt Krozaleski.
Just a few weeks before the Arnold Classic, Matt noticed that his knee was hurting. The condition worsened.
“I think tomorrow will be better,” he said Monday.
"It's really swollen," he said Tuesday.
On Wednesday he said: “Guys, I can’t get out of my chair. My knee hurts so much that I can't touch it. I have no idea what happened."
On Thursday it was even worse: “I can’t walk without crutches. The knee does not bend. The pain is unbearable."
On Friday he was beside himself: “I went to the doctors, but they don’t know what happened.” Arnold Classic is in two weeks. He growled that this wasn't what he was "busting his ass for." “I'm going to convince myself that I'm getting better and the knee is healing,” he said.
At the tournament he squatted 440 kg, despite the fact that two weeks ago he was on crutches. Such is the power of faith.
You can download this and other books here.
Videos on powerlifting training programs
Source: ZhimLezha.ru
This is interesting: Heart training: techniques, exercises, practical recommendations, pulse for heart training, types of cardiac hypertrophy and what an untrained heart leads to
Powerlifting Principles
The key goal of powerlifting training is to gradually increase the weight lifted to the maximum possible, while there is no emphasis on developing endurance. Also, the athlete does not strive to gain weight or gain relief.
But for the effect to be truly impressive, you need to strive for results by observing the following principles:
- Variability of training. This means that the intensity of training should alternate. For example, after a high-intensity workout, there is a low-intensity workout with light weight, and then again with a heavy weight and high-intensity workout. This is necessary so that the muscles have time to recover.
- Do not increase the weight unplanned, even if it seems that the current one is easy to lift. It is important to strictly follow the selected training program. The working weight should remain at the same level for at least two weeks. This will allow the muscles to maintain and increase their strength.
- No need for forced repetitions. Forced repetitions are those very last presses that are done through force. Since powerlifting doesn't require endurance and the weight used is so heavy, forced reps not only won't help, but can also lead to injury. There is no point in doing them.
- No additional exercises and strict adherence to the program.
Powerlifting - strength training program
The main feature that distinguishes powerlifting from other related sports is the absolute priority of developing strength indicators over other functional capabilities of the human body. Accordingly, the main goal facing any powerlifter is to lift the maximum possible weight in one repetition in one of the 3 classic weightlifting basic exercises (remember, these include the bench press, squats and deadlifts). Once upon a time, the list of competitive disciplines also included the military standing barbell press, but a large number of injuries among competing athletes led to the removal of this exercise from the list for competitions.
Lifting maximum weight in powerlifting requires an athlete to work on developing their strength. Drawing up training programs for a powerlifter has its own specifics, which distinguishes it from training programs for other strength sports.
This material will discuss how to create a training program to obtain the greatest results in the development of strength and power indicators, which training program is best suited for powerlifting, the basic principles of training for strength development, issues of periodization and diet and recovery.
Powerlifting - what is it, its differences
Powerlifting or powerlifting is a sport. Athletes competing in powerlifting competitions set their main goal to overcome the resistance of the maximum weight for the athlete. Raising maximum weights occurs in three exercises; the competitive results of weightlifters of the same weight category are compared with each other and assessed in total based on the weights taken in all 3 exercises.
Bodybuilding is aimed primarily at developing muscle mass, relief and body proportions, and does not require high functionality, while powerlifting is focused on constantly increasing strength results.
Powerlifters do not need to develop endurance, unlike track and field athletes, as well as athletes competing in the CrossFit discipline.
Basic Training Principles for Strength Development
Powerlifting training is exclusively strength-based. Which means a periodic but regular increase in the intensity of training and an increase in the volume of the total load produced in the form of weights lifted by the athlete.
In practice, the training regimen looks like this: Powerlifters work on one or two multi-joint competition movements each workout, in 4-6 sets, with a low number of repetitions (2-5 repetitions).
This is another difference from bodybuilding, in which athletes most often work out only one or two muscle groups in one workout, performing 3-4 working approaches for an average number of repetitions (8-15).
Creating a powerlifting training program
Training programs for powerlifting should be compiled by experienced athletes who understand the specifics of approaches to strength training, and also understand the need for an individual approach to the selection of a training program, depending on his personal strength qualities, experience, as well as the anatomy and physiology of the athlete.
Every novice athlete who decides to engage in power lifting is recommended to first master the basics of the correct technique for performing the classic three basic exercises; it would not be a bad idea to visit any good powerlifting section/school. Work with a personal mentor at the initial stage of training, who will explain the main principles of powerlifting and help you begin targeted, effective training as quickly as possible.
The “golden three” of powerlifting are the squat, bench press and deadlift. These are classic basic exercises. Without their implementation, it is impossible to achieve significant development of strength and impressive muscle volumes.
In addition, a powerlifter's program should have a place for auxiliary exercises designed to work on weak points when performing exercises that limit overall performance. Such movements include hyperextension, wide-grip pull-ups, leg press in a machine, bending over with a barbell, as well as dips, etc.
A powerlifter needs more rest time between sets than a bodybuilder. If in bodybuilding it averages 1-2 minutes, then in powerlifting, due to the specifics of the heavy load, you will need up to 5 minutes of rest or more before performing the next approach.
Number of workouts per week: since heavy loads require quite a lot of time for muscle recovery, it is recommended to stop at 3 (maximum 4) visits to the gym per week.
Periodization of loads in powerlifting
Training in powerlifting involves a regular progression of loads, but it will not be possible to constantly linearly increase the weights on the bar from session to session, because such a technique will certainly cause the athlete a phenomenon called overtraining syndrome and can lead to a loss of desire to train at all. To prevent this, it is necessary to use the principle of load periodization.
The principle comes down to alternating loads, namely, heavy exercises are replaced by fairly light ones, and then light ones are replaced by workouts with a medium load.
This periodization of loads can be applied both within one week and over the course of a month, i.e. microcycles and mesocycles are used.
In practice it looks like this:
- first week (heavy) – the athlete performs a bench press with a weight of 100 kg in 5 sets of 5 repetitions,
- second week (easy) – 60 kg bench press in 3 sets of 8 repetitions,
- third week (medium) – 80 kg bench press in 4 sets of 6 repetitions,
As already noted, the training program used in powerlifting is tailored to each athlete individually. An experienced trainer leaves it based on your personal characteristics, experience and the results of the “pass” (read about it below).
It is most common to create such programs for a 3-month period, since their preparation for longer periods will lead to the body becoming accustomed to the load and slowing down the rate of your progress. Therefore, after training for three months, it is necessary to re-do the drilling and make changes to the training plan.
Most strength training programs in powerlifting are designed for 3 workouts per week. In the program, there is always a bench workout between the squat day and the deadlift day. Since the legs are heavily involved in both squats and deadlifts, they should be given more time to recover, so a bench press is always placed between the squat and deadlift. Sometimes, on one training day, 2 basic exercises are performed, but in this case, one of them is performed with large weights, and the other with small ones.
Walking in powerlifting
“Passing” in powerlifting is the definition of the maximum weight in each of the three competitive lifts that an athlete can lift. Competently drawing up a training program requires mandatory drilling. A feature of training programs in powerlifting is the use of a percentage of one repetition maximum (1 RM) that the athlete lifts.
Based on this principle, 3 types of training are distinguished: light, medium and heavy, in which work is performed with various weights of weights (in light training, the load is 50% of 1 rep.M., in medium - 65%, and in heavy - 90% ).
It is possible to perform powerlifting exercises on all muscle groups in one day, but it is necessary to take a long break between approaches. For example, first perform a squat, then a barbell press, and finally a deadlift, but a prerequisite for progress is a thorough warm-up and warming up of the muscles before each super-heavy approach.
It is necessary to carry out penetration by gradually increasing the weight on the bar between approaches, initially it increases by 10 - 20 kg, in the last approaches up to 2-3 kg.
The walk involves doing it with a partner. Since the goal is to find the maximum weight, the last set should be accompanied by muscle failure and the inability to lift the weight on your own. At this moment you will need a partner, otherwise you will simply be crushed during the bench press or squat.
Examples of Powerlifting Training Programs
Examples of training programs based on the principle of periodization on a weekly cycle, with three workouts per week:
Training program 1
First day:
| Exercise | Approaches | Repetitions |
| 1. Bench press (80% of 1 R.M.) | 5 | 5 |
| 2. Squats with a barbell on the shoulders (60% of 1 R.M.) | 5 | 5 |
| 3. French bench press with a horizontal barbell. bench | 3-4 | 8 |
Second day:
| Exercise | Approaches | Repetitions |
| 1. Deadlift (80% of 1 rep.m.) | 5 | 5 |
| 2. Hyperextension | 3-4 | 10-12 |
| 3. Standing biceps curl | 3-4 | 8-10 |
The third day:
| Exercise | Approaches | Repetitions |
| 1. Bench press (60% of 1 R.M.) | 5 | 5 |
| 2. Squats with a barbell on the shoulders (80% of 1 R.M.) | 3-4 | 10-12 |
| 3. Swing dumbbells to the sides (or bending over/in front of you) | 3-4 | 10 |
As can be seen from the given lesson plans, the working weights depend on the results of driving with maximum weights. This is only a general method of execution; a specific cycle is compiled with the help of an experienced trainer, especially in relation to novice athletes.
Training program 2
Day 1 (pectoral muscles):
| Exercise | Approaches | Repetitions |
| 1. Squats with a barbell on the shoulders (60% of 1 R.M.) | 5 | 5 |
| 1. Bench press (75% of 1 R.M.) | 5 | 5 |
| 3. Standing barbell press (military press) | 5 | 8-10 |
Day 2 (back):
| Exercise | Approaches | Repetitions |
| 1. Deadlift (75% of 1 rep.m.) | 5 | 5 |
| 2. Shrugs with a barbell | 5 | 16-20 |
| 3. Close grip barbell press | 5 | 8-10 |
Day 3 (quadriceps and calves):
| Exercise | Approaches | Repetitions |
| 1. Squats with a barbell on the shoulders (75% of 1 R.M.) | 5 | 5 |
| 2. Calf raises | 3 | 18-20 |
| 3. Barbell row to the chin | 4 | 8-10 |
The duration of this training program should not be longer than 3 months. Training takes place three times a week, with the first week the load being 75% of your repeated maximum, which was determined using walking. The second 7 days the work is performed at 80%, and then the load increases by 2.5% with each subsequent week. As already mentioned, after completing the 3-month cycle, this program must be changed by performing the penetration again.
Training program 3
Day 1:
| Exercise | Approaches | Repetitions |
| 1. Squats with a barbell on the shoulders (75-85% of 1 R.M.) | 5 | 5 |
| 2. Bench press (65-75% of 1 R.M.) | 5 | 16-20 |
Day 2:
| Exercise | Approaches | Repetitions |
| 1. Deadlift (75-80% of 1 rep.m.) | 3-4 | 5 |
| 2. Bent-over barbell row | 3 | 6-8 |
Day 3:
| Exercise | Approaches | Repetitions |
| 1. Squats with a barbell on the shoulders (55-65% of 1 R.M.) | 5 | 5 |
| 2. Bench press (75-85% of 1 R.M.) | 5 | 5 |
| 3. Close grip barbell press | 3-4 | 8-10 |
Classes also take place three times a week. This training program is well suited for beginners in powerlifting. If after performing heavy basic movements there is still strength left, then after them you can add one or two isolating ones to work individual muscles, but you can completely do without using them.
How to Avoid Injuries in Powerlifting
When starting powerlifting classes, do not try to learn the technique of performing heavy, complex movements on your own; seek help from a coach or an experienced athlete; this will reduce your time and also reduce the risk of injury tenfold.
With the correct movement technique, the likelihood of injury (sprains, bruises, as well as ruptures of muscles, ligaments and tendons) is minimized.
Strength increases gradually, do not chase the weights on the bar, do everything according to plan and in a timely manner.
To support your lower back and spine when deadlifting and squatting, use a weightlifting belt. To protect your knees, you can use elastic bandages, bandages or special knee pads.
Powerlifter training program - Pavel Badyrov:
Share: Source: power-body.ru
What is powerlifting
Powerlifting is a strength sport, the essence of which is to develop the athlete’s strength, and the result is lifting the maximum possible weight. Thus, the achievements of a powerlifter are measured in the number of kilograms lifted.
Unlike regular bodybuilding, powerlifting does not involve the pursuit of beautiful body lines.
An athlete's qualifications are determined by performing basic multi-joint exercises. Performance is assessed according to three parameters:
- correct execution technique;
- total weight taken;
- number of repetitions.
Dmitry Golovinsky - biography of the Ukrainian powerlifter
Dmitry Golovinsky is a popular Ukrainian powerlifter, coach, record holder in Ukraine and the world. The athlete was able to bench press a barbell weighing 302.5 kg without using a bench shirt.
Dmitry was born in 1988 on June 29. Received a diploma from a higher state university. He started playing sports at the age of 14. At the age of 17, he began to be interested in powerlifting, especially the bench press. He is a simple, modest person, so he did not chase records, especially competing in competitions. I devoted more experience to the sport itself, but was in no hurry to participate in competitions.
This choice was made correctly, since Dmitry Golovinsky emerged as a strong athlete who devoted himself headlong to the bench press. Mentor Dmitry Kurochkin, who helps him draw up a training plan. The coach helped him become the world and Ukrainian champion in this movement.
Bench press – 302.5 kg
Such strong strength indicators made him a Master of Sports of international class in various alternative federations. In 2014, he bench pressed his first 300 kg at the GPA Championships, and then 302.5 kg. Thus, Golovinsky is the strongest bench presser in Ukraine.
Careful planning and preparation for competitions is Dmitry’s labor-intensive and favorite part. He also likes to participate in discussions on social networks, where he firmly defends his opinions. Helps beginners for free. Repeatedly competed with Kirill Sarychev. He developed a special training method for strength sports - “LMS”.
Squats 330 kg
The man does not hesitate to talk about steroids to beginners. Explains all the consequences of taking pharmacology.
Strength indicators:
- Squats – 270 kg (in the gym 330-340 kg in bandages);
- Bench press – 302.5 kg (Ukrainian record);
- Deadlift – 270 kg (in the gym 300-320).
Dmitry focused on other exercises, which significantly improved his triathlon total. On the Internet you can see how he can easily handle a weight of 330 kg in squats, which is an excellent result. At this rate, the amount of 1000 kg without the use of overalls is very close to being realized.
Anthropometric data:
- Weight – 135 kg;
- Height – 185 cm;
- Bench press – 302.5 kg.
He does bench presses at every workout, but also performs other exercises from powerlifting. Also, standing barbell presses with heavy weights, different grips during the press. Uses additional exercises. When the week is intense, do paired workouts three times. In some ways this is similar to a weightlifting program. Reduces the volume and number of training sessions before competitions.
Dmitry's biceps record is 100 kg
To restore muscles, the total training load is not very large. Additional exercises focus on the triceps and pectoral muscles.
He does not consume sports nutrition. Rarely buys Riboxin and vitamins. It’s not clear about pharmacology, but there was talk that the athlete uses growth hormone, inulin and other steroids.
The athlete actively tries himself in arm wrestling. He showed pretty good results at the Ukrainian Championship, where he took second place. By the way, Dmitry looks a little like the vocalist of the Rammstein group Till Lindemann.
Liked? Tell your friends:
Source: x-power-club.com
This is interesting: Pilates for beginners - Pilates basics, scientific research and training scheme
Daily and nutritional regimen in powerlifting
To develop muscle strength, it is important to devote a lot of time to muscle growth and recovery. As you know, muscles recover effectively during sleep and rest. Therefore, an athlete’s sleep should be complete and amount to at least eight hours.
Huge strong muscles also require special nutrition. Therefore, when creating a powerlifting program, coaches advise taking into account the following points:
- Eat only natural products, excluding synthetic semi-finished products.
- Avoid constant consumption of unhealthy drinks and overly sweet foods. This results in elevated insulin levels, which is not desirable for a powerlifter.
- You need to eat every two or three hours. It is this food intake schedule that will ensure maximum muscle mass gain in the shortest possible time without increased formation of fat in the body.
- You need to eat enough protein at every meal. This can be lean meat, as well as eggs, cottage cheese, cheese, legumes, milk, protein supplements.
- Combine the consumption of plant and animal proteins throughout the day.
- Enrich every meal with raw vegetables. This helps speed up metabolism, eliminate toxins and improve overall performance, which ultimately leads to increased strength.
- Consume fast carbohydrates only after training.
- Avoid trans fats.
- Eat healthy fats such as virgin vegetable oils, red fish, and nuts. You can also add fatty acid supplements to your diet.
By following all these rules, you will indirectly affect your strength performance.
Powerlifting training programs
The main goal that is set for every athlete involved in powerlifting is to lift the maximum weight in one of the basic exercises - bench press, squat, deadlift. Previously, this list consisted of four exercises. The large number of injuries that athletes received led to the exclusion of the standing barbell press from competitions. To lift weights in powerlifting, an athlete needs to develop strength.
Drawing up a training program for a powerlifter can only be done by an experienced athlete who fully understands the essence and ultimate goal of the entire process. Particular attention is paid to the individual abilities of the athlete, which include: strength, experience, anatomical and physical indicators. Beginners are recommended to start training on their own after visiting any powerlifting section. At the initial stage, you should find a mentor who can help with understanding the basics of powerlifting and the technique of performing basic exercises.
Performing powerlifting moves
The term “lift” refers to the maximum possible weight that an athlete can lift. It is a must for anyone who wants to practice this discipline. This is due to the peculiarity of the program, which consists in drawing up a training process based on a certain percentage of the weight lifted by the athlete. There are three types of training - light, medium, heavy. The first is to lift weights from 50, the second - from 65, and the third - from 90% of the weight that the athlete lifts.
In one day you can perform drilling on all muscle groups at once. The main thing is to take a long break between approaches. You can do a squat first, then a bench press, and then a deadlift. Of course, before each difficult approach you need to warm up and warm up well. It is best to work on the penetration with someone in pairs. This is necessary to correctly find the maximum liftable weight. The projectile in the final approach should be so heavy that it cannot be lifted. At the moment of failure, you will need the help of a partner who will back up the athlete. Otherwise, there is a risk of injury when pressing or squatting. The passage is carried out according to the principle from largest to smallest. At first, the step between approaches should vary from 10 to 20, and in the last attempts - from 2 to 3 kilograms.
Powerlifting training
The training program is developed by an experienced specialist who takes into account the results obtained during the excavation and individual capabilities. The total duration of each training plan is a maximum of three months. This limitation is due to the body getting used to it and the lack of any progress. After 90 days, you need to perform the excavation again and change the program.
Most of the training developed to increase strength in powerlifting involves training three times a week. The training process is designed in such a way that between the day of performing squats and deadlifts, there is always a bench press session in the schedule. This step is explained by the high load on the legs when performing deadlifts and squats. Therefore, this muscle group needs more time to recover, which is what makes a bench press day possible. When two basic exercises are performed at once in one workout, then one is performed with light weight, and the other with heavy weight.
All of these principles together make up a powerlifting training program.
No. 1 Training program
First day:
- Heavy Press
- Light squats
- If you still have some strength left, you can do a French press or dips.
Second day:
- Deadlift
- If there is strength left, then we do hyperextensions and biceps curls + hammers.
The third day:
- Light press
- Squats are heavy
- If there is strength left, then we work on the deltas - swings in an incline, to the sides, in front of us.
Training weights will depend on the results of your progress, that is, on the maximum performance. The number of repetitions and method of execution will depend on the cycle you use (the Russian and Verkhoshansky cycles are very famous in powerlifting). Professionals know how to use these cycles, but for beginners, we recommend contacting a trainer who will guide you in the right direction.
No. 2 Training program
Day 1 – chest:
- Light squats - 5 sets of 5 reps with 60% of the maximum weight;
- Bench press – 5×5 with 70-100%;
- Military press – 5×10.
Day 2 – back:
- Deadlift – 5×5 with 70-100%;
- Shrugs – 5×20;
- Close-grip triceps press – 5X10.
Day 3 – legs:
- Squat – 5×5 with 70-100%;
- Calf raises – 4×20;
- Barbell row to the chin – 4×10.
The duration of this training cycle should not exceed 3 months. Train 3 times a week, in the first 7 days work with 75% of your maximum, which you set on the tunnel. Next week work with 80%, and then increase the working weight by 2.5% each week. After the end of the program, it needs to be replaced, or started over again, doing the penetration again.
No. 3 Training program
Day 1:
- Heavy squat - 5x5 - 75-85%;
- Light bench press – 5×5 – 65-70%.
Day 2:
- Deadlift – 3×5 – 75-80%;
- Bent-over barbell row – 3×6-8.
Day 3
:
- Light squat 3×5 – 55-70%;
- Press heavy 5×5 – 75-85%;
- Close grip press 3x8-10.
Classes 3 times a week. The use of this powerlifting training program is recommended for beginner athletes. If you have the desire and strength, then you can add a couple of isolated exercises for individual muscle groups to the basic exercises, but practice shows that this set is enough for a beginner.
Video “Pavel Badyrov’s training program”
Video “Educational program on training programs”
Source: builderbody.ru
No. 3 Training program
- Heavy squat - 5x5 - 75-85%;
- Light bench press – 5×5 – 65-70%.
- Deadlift – 3×5 – 75-80%;
- Bent-over barbell row – 3×6-8.
- Light squat 3×5 – 55-70%;
- Press heavy 5×5 – 75-85%;
- Close grip press 3x8-10.
Classes 3 times a week. The use of this powerlifting training program is recommended for beginner athletes. If you have the desire and strength, then you can add a couple of isolated exercises for individual muscle groups to the basic exercises, but practice shows that this set is enough for a beginner.
Source
Powerlifting Exercises
Exercises in powerlifting do not differ in variety. The most important thing is a gradual increase in weight and very clear and competent adherence to technique. The technique must be honed to perfection, because the work is carried out with a lot of weight, and violations in the execution of exercises can lead to serious injuries.
Squats with a barbell on your shoulders, how to do it correctly
This exercise is a basic exercise for lifters. It engages the muscles of the entire body, but mostly the legs, buttocks, core and abs.
- Grasp the bar with both hands, bring your shoulder blades together, place the bar on your middle trapezius and rear deltoids. Stand under the barbell, distributing your weight evenly on both legs. Remove the barbell from the bar and take two steps back with your feet approximately shoulder-width apart or slightly wider. This will be the starting position.
- As you inhale, bending your knees, we squat. We keep the back straight, without bending, only the natural lordosis in the lower back remains. We direct our gaze straight ahead. We concentrate on the tension in the leg muscles. The body leans forward slightly, the knees do not go beyond the line of the toes. The legs stand firmly on the entire foot.
- At the exit, we straighten our legs and stand in the starting position.
- Repeat the required number of times.
A variation of the exercise is the front squat. The technique is the same, only we place the barbell on the upper part of the chest and deltas. In this case, the emphasis is on working the quadriceps.
Video: Squats with a barbell on the shoulders - strength training
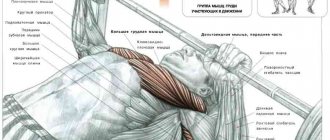
Close grip bench press
The exercise targets the shoulders, forearms and trapezius.
- We lie down on the bench, grab the barbell with an overhand grip, placing our hands slightly narrower than our shoulders (at a distance of about 20–30 centimeters from each other).
- We remove the barbell from the bar and smoothly lower it to the chest.
- Slowly raise the barbell up as you exhale, fully straightening your arms.
- As you inhale, lower the barbell to your chest again.
- Repeat as many times as necessary.
Bent-overs with a barbell on your shoulders
This exercise perfectly works the back muscles, gluteus maximus, spinal extensor muscles, and abdominal muscles.
- We stand straight, legs slightly wider than shoulders, slightly bent to the knees, toes slightly turned away from each other.
- We take a barbell and place it on the upper trapezius and rear deltoids.
- As you inhale, moving your pelvis back, bend down with the barbell. Movement occurs only in the hip joints. Ideally, you should bend over at a 90-degree angle until your torso is parallel to the floor.
- We return to the starting position as we exhale.
- Repeat as many times as necessary.
This exercise can be quite traumatic; beginners are advised to exclude it or perform it with an empty bar.
Video: Forward Bends with a Barbell on the Shoulders
Deadlift
A classic exercise for bodybuilding and powerlifting. It is a basic exercise and works muscles such as:
- spinal extensors;
- latissimus dorsi muscles;
- upper back muscles;
- buttocks;
- thigh muscles;
- quadriceps;
- muscles of the forearms.
- Starting position: feet shoulder-width apart, parallel to each other, toes on the bar of the barbell lying on the floor. We grab the bar with an overhand grip, with our wrists slightly wider than shoulder-width apart, our arms perpendicular to the floor, and our shoulders positioned directly above the bar.
- As you exhale, we lift the barbell smoothly and evenly, the bar sliding along the legs. Raising the barbell above the knees, straighten the torso as much as possible and bring the shoulder blades together, concentrating on working the back muscles.
- Moving the pelvis back, we gradually lower ourselves to the starting position, also sliding the bar along the legs.
- Once the pancakes touch the floor, repeat the required number of times.