Science that studies the body
In this regard, the concepts of “fascia” and “myofascial chains” also appeared. The science that directly deals with the health of the human body is called kinesiology. From “kinesio” - movement, “logos” - to study. That is, she studies the patterns of body movement.
This may be applicable in sports, in the treatment of pathologies, massage therapists and chiropractors may be interested in this. There are not many kinesiologists, but more and more modern doctors - osteopaths, neurologists - are interested in this area.
Pronation and supination: what does it mean?
Let's look at some of the terms used by kinesiologists and their explanations. Rotation, pronation and supination are types of movement of the limbs and shoulder joints in kinesiology.
Pronation is the inward turning movement of the upper or lower limbs. This may include movement of the hand, forearm and humerus. As well as the foot, lower leg and femur.
Let's look at the example of a hand. If you extend your arm forward so that your thumb is on top, and then rotate it 90 degrees inward so that your palm becomes horizontal, this movement will be pronation. This type of rotation is performed by a group of muscles called pronators.
In the same way, supination is performed by muscles called supinators. Only in this case is the lateral edge turned outward, in the opposite direction.
Rules for choosing shoes for deformation
“Carriers” of neutral pronation have a wide choice of models, which cannot be said about people with identified deviations. If the disorder intensifies, when choosing shoes, pay attention to the following factors:
- additional source of depreciation;
- the force of the impact load during movement on the longitudinal part of the foot.
| Turn | Shoes | Features of sole cushioning | Advantages |
| Inadequate | Shock absorbing |
|
|
| Reinforced | Stabilizing |
|
|
It is important to know the peculiarities of pronation before choosing sports shoes; the mechanism is carried out while running.
Pronation of the foot
Let's take a closer look at what it is - pronation of the foot? You can also pronate your foot separately. In this case, it is necessary to turn it, lowering the medial part down (inward, towards the central axial line of the body). The muscles involved are the pronators of the lower extremities. Pronation of the foot involves the peroneus longus and brevis muscles.
Supination is the outward turning of the lateral part of the foot (outward, outward from the center line of the body) of the lower or upper extremities. The principle is the same as in pronation, only the movement is in the opposite direction. It is carried out by a group of muscles - supinators: long extensor pollicis and tibialis anterior.
What diseases can impaired supination lead to?
Increased hypersupination and especially hyperpronation are the cause of chronic pain in the legs and lower back, as well as regular injuries.
Discomfort of the cervical spine, headaches, malocclusion - may be a consequence of flattening of the foot as a result of increased load.
As a result of the deviation of the knee joint to the central axis of the body, the kneecap can move outward, resulting in abrasion of its cartilage.
Features of gait and shoes
Perhaps many have noticed how some people walk “clubfooted,” that is, they have weak arch supports and the foot falls inward. Or, conversely, a Chaplin-style gait indicates weakness of the pronators. It should be noted that these muscle groups are antagonists. Antagonists are groups that are opposite in their biomechanics, designed together to balance each other, keeping the limb in a central position.
Pronation and supination - this affects the upper limbs and is very different from the same movements of the lower limbs. This is due to the structure and mobility of articular and tendon structures. There are three ways to place your foot when walking or running:
- With normal pronation. It can be easily identified by the footprint of a foot in wet sand or a wet foot on paper or the floor. The imprint will be characteristic, curved outward. An imprint is not formed at the instep of the foot; it should be understood that this is normal pronation of the foot.
- With overpronation. In this case, the person becomes as if turning his foot inward; this is typical in the presence of flat feet. The imprint of such a foot is wide, almost not curved, the instep is either minimal or absent at all. In this case, the sole of the shoe will wear off from the inside (especially the heel). The foot, “piled” inwards, twists the remaining parts of the leg in a chain, creating rotation of the knee joint and greater trochanter of the femur. Which leads to wear and tear of the articular surfaces. Severe pronation of the foot is, in fact, flat feet.
- With hypopronation. This means weakness of the pronators and inversion of the foot. Also, the gait of people with hypopronation is special - they seem to throw their socks out, and the outer side of the sole of the shoe, especially the heel, wears off. At the same time, the knee joint also rotates, creating pathology, and the femur is also slightly everted.
People with pronation problems should consult with an orthopedic doctor or kinesiotherapist and choose the best shoe option for themselves. The sole should not be thin, the heel part will be reinforced and have a small heel. In case of hypopronation, doctors often recommend wearing special inserts and insoles - arch supports. This is done so that disorders from the foot do not rise up the muscle chains and do not cause arthritis and arthrosis of the joints due to compensatory rotation.
Overpronation
One of the most common types of pronation. Overpronation is a natural trait and the older you get, the more susceptible you are to a range of sports injuries.
Overpronation is excessive flattening or inward roll of the foot, reducing the longitudinal arch of the foot. Excessive pronation has a negative effect on shock absorption. The ligamentous apparatus is continuously in a tense, stretched position.
The running cycle begins with inner heel strike. The foot flexes inward more than the ideal 15%. The foot and ankle experience constant discomfort when stabilizing the body, which means shock absorption is less effective. The push-off from the ground in the final phase of the running step occurs mainly due to the biggest and second toe. They bear the main burden. Overpronation causes additional stress, muscle tension and dangerous side effects.
When performing a step, the ankle, knee and hip internally rotate medially. With overpronation, there is excessive inward rotation. This increases stress on the musculoskeletal system. Moving the foot too much causes calluses on the big toe and bunion area, as well as injuries such as runner's knee, medial tibial stress syndrome, plantar fasciitis, and inflammation of the Achilles (Achilles tendinitis).
A custom orthotic can help you eliminate some discomfort when running or walking. But we must not forget that only in a complex way can this problem be solved. You must understand that while pronation can influence certain injuries, it is not the only factor influencing their development.
Shoulder
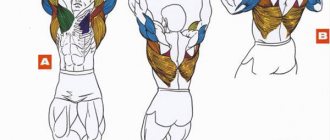
Pronation and supination are two types of movements that also affect the shoulder. It differs in biomechanics from other parts of the body and completely depends on the structure of the shoulder joint - one of the most complex in its biomechanics. It is produced by moving the shoulders inward (pronation) and moving the shoulders back (supination). The pronators and supinators of the shoulder girdle are designed to maintain posture, straight position of the upper back and are also opposite in their biomechanics (antagonists).
The following muscles work in pronation (inward rotation) of the shoulder: pectoralis major, teres major, latissimus dorsi and subscapularis.
The muscles involved in supination (outward rotation of the shoulder) are the infraspinatus and teres major.
How to diagnose foot deformity?
There are several diagnostic methods: orthopedic (more accurate) and a method of determining at home.
Diagnosis of foot deformities by orthopedic doctors
Podiatrists who specialize in correcting foot deformities use three main methods to clarify the situation:
- X-ray;
— podometry (diagnostic method using computer measurements);
- (analysis of the foot using sole prints).
Taking into account the results, the doctor will select corrective insoles and orthopedic shoes to correct deficiencies.
Diagnosis of foot deformities at home
In addition, you can determine the type of pronation at home. The most understandable and well-known is to wet your feet in the bathtub, or in any container of water, and then lower them onto paper. Now you need to examine the wet trail left behind. If the width of the print is almost equal to the width of the foot, and almost the entire surface of the foot has left its mark, this is flat feet. If there is a deflection, or “arch,” and its width is approximately the same as the width of the foot, pronation is normal. When the deflection is very steep, and most of the heel and toe pads are imprinted, this is hypopronation (clubfoot).
To detect deformation, they even use coins of various denominations, which are inserted under the arch of the foot. If a 10-kopeck coin does not pass, it means you have overpronation (flat feet). If it passes, they try to do the same with a ruble coin. The ruble passed even with a little effort - you have normal pronation. If a ruble, or even a two-ruble coin, passes freely, we can say that you have hypopronation.
Next method: ask someone to take a photo of your legs from behind, while standing straight and natural. Then evaluate the result from the photo.
They also observe their sensations while sitting on a chair and bending their foot to a right angle. Discomfort or pain may indicate flat feet.
You can analyze old shoes for wear. If the most abraded areas are on the inside, this is flat feet; if the most abrasion is on the outer part of the shoe, this is hypopronation. If the inner part is worse preserved, this indicates normal pronation of the foot.
Rotation
Rotation is another type of movement and it means “turning.” It is inherent not only to the limbs of the human body, but also to some constituent elements, for example, vertebrae. Pronation and supination can be considered incomplete rotation. The range of motion of the upper and lower extremities is very different, which is important to remember. Any rotation is designed to stabilize parts of the body during movement.
The rotator muscles (pronators and supinators) are small and unremarkable in the general relief of muscle mass. But athletes need to be told about them; the coach must convey to beginners the importance of antagonists for building body composition.
Use in bodybuilding
In bodybuilding, the use of pronation and supination is popular, this is important, for example, when lifting dumbbells. When working with free weights, an athlete can use different muscle groups. Pronators and supinators must be inflated evenly. Visually, these are the muscles of the forearm and lower leg. If you don’t do this, then the bodybuilder will have his arms spread out to the sides while walking, and his legs will “throw out” in a funny way.
The pronators and supinators of the shoulder, as antagonists, can either ruin posture or improve it. Therefore, a bodybuilder needs to pump up both the pectoral muscles and the back muscles. Sometimes an athlete’s shoulders seem to be turned forward, this indicates stretching of the rhomboid and infraspinatus muscles, while the pectoralis major, on the contrary, is severely spasmed. This can cause numbness in the fingers and pain in the attachment points of the pectoralis major muscle.
What is pronation with flat feet?
Anatomy defines the absence of a bend as flat feet. The disorder reduces the endurance of the calf muscles. The muscle, tissue, and entire apparatus suffers—pain appears in the legs, back, and hip bones. Manifestations are noticeable when:
- the outer surface turns inward;
- the sole goes out.
The presence of a defect is determined independently by assessing:
- sensations of discomfort in relation to the load;
- shoe wear.
To determine pain syndrome, it is recommended to perform a “rotation test”:
- Sit down.
- Place your legs parallel.
- Extend your foot as much as possible.
- Extend your thumb so that it faces the floor.
If the shoes wear out quickly, and after the test there are unpleasant sensations in the calf muscles, the possibility of flat feet cannot be ruled out. For further diagnosis, contact a medical facility. The doctor determines the degree of deformation taking into account the plantar slope and arch. The more severe the degree of flatfoot, the less the bend - the more profound the turn.
Raising the forearm with supination
Lifting dumbbells with supination is carried out with the hand turned outward. The supinators are trained: short supinator and biceps muscle (biceps). The biceps muscle becomes stronger when the elbow is bent to 90 degrees. We perform rotation of the forearm with supination while working with a screwdriver, for example, or unscrewing a tap.
Thus, the supinated biceps curl trains additional muscles and stabilizes the forearm, making it strong. This is especially important in arm wrestling.
The pronators include: pronator quadratus and pronator teres. They are much weaker than their antagonists. When a person finds it difficult to unscrew a bolt that is twisted crookedly, he uses more force and uses inward rotation of the shoulder (shoulder pronation). The brachioradialis muscle acts in this case as a pronator, although initially this function is not inherent to it. Initially, the brachioradialis muscle is a flexor of the forearm.
A harmonious body structure is the goal of muscle development, so it is necessary to take into account the role of pronation and supination for both professional athletes and beginners.
Treatment methods for foot supination
The need for therapy is determined by the pain syndrome. The treatment is based on a single goal - getting rid of discomfort. It is important to approach the problem systematically:
- Include daily 15-minute physical therapy exercises.
- Carry out preventive therapy - salt baths, acupressure at least three times a week.
| Method | Effect | Mode of application |
| Exercise therapy |
|
|
| Massage |
| |
| Baths |
|
In addition to the complex, special shoes are used. An orthopedic pair or insole with arch support will provide a cosmetic advantage and hide the external defect of the foot.