The flexor tendons can be damaged by a deep cut (a serious cut can also damage surrounding structures such as nerves and blood vessels). In many cases, damage that appears simple when viewed from the outside turns out to be more complex when viewed from the inside. A serious cut that injures the tendon will mean that bending the finger(s) will be impossible.
Flexor tendon injuries are a traumatic condition classified by the zone of injury (zone 1 distal to the flexor digitorum superficialis insertion, zone 2 from the flexor digitorum superficialis to the distal palmar crease, zone 3 to the palm, zone 4 to the carpal tunnel, zone 5 to the carpal tunnel). wrist to forearm).
Damage zones
- The basic concepts in restoration are the same for different zones.
- The location of the injury directly affects the healing potential.
Tendons that may be affected include:
- Flexor pollicis longus (flexion of the tip of the thumb).
- Flexor digitorum profundus (finger flexion).
- Flexor digitorum superficialis (flexion of the middle joint of each finger).
- Flexor carpi ulnaris.
- Flexor carpi radialis.
Pronation and supination anatomy. Supination, pronation and VPN exercises
Supination, pronation and VPN exercises
If you carefully study the anatomy of muscles and especially the functions they perform, you can learn a lot of interesting and practically useful things.
In this article, we'll delve deeper into the muscles that control the shoulder joint. There is no doubt that the shoulder joints are extremely important in everyday life. In essence, this is the place from which hands grow, with all the ensuing consequences
When doing fitness, remembering the condition of your shoulder joints is one of the signs of caring about your health and a manifestation of an elementary training culture.
What is supination and pronation?
To clearly understand what we are talking about here, you should understand these terms - supination and pronation. They are often found in books and articles on training.
Supination is an outward rotational movement of a limb or part of it. For example, if there is supination of the hand, bent at the elbow at an angle of 90 degrees, then the hand turns from a palm down position to a palm up position. In the figure this is indicated by number 1.
And it is not so important how the arm is bent at the elbow. Rotation in the direction indicated by arrow 1 is always supination.
Pronation is the opposite of supination, a rotational movement that occurs inward. If you hold a handful of coins in your palm and then decide to pour them out, you need pronation.
The use of the terms pronation and supination in relation to the hand is more or less clear. They are especially popular on bodybuilding forums when it comes to training the biceps and forearms.
What about shoulder pronation and supination?
We hear about this much less often. And completely in vain. In this picture, the athlete performs supination of the shoulder joints.
And on this pronation.
What is VPN?
VPN stands for shoulder external rotation. That is, shoulder supination.VPN exercises are exercises that develop the muscles that rotate the shoulder outward (shoulder supinators).
Why is this necessary?
At the beginning of the article, I drew your attention to the study of muscles and their functions. We read about the muscles that control the shoulder joints:
Shoulder pronation: 1) subscapularis, 2) pectoralis major, 3) anterior deltoid, 4) latissimus dorsi, 5) teres major. Shoulder supination: 1) infraspinatus, 2) teres minor, 3) posterior deltoid. muscles
If you look at the drawing carefully, a lot will become clear. A – front view, B – rear view.
Note! The pronators of the humerus are the two largest muscles in the body - the pectoralis major and the latissimus dorsi! And also the anterior deltoid. During training, everyone does nothing but develop these muscles in every possible way. What happens?
It turns out the following. From strength training, muscles shorten and become noticeably stronger and increase in volume. Have you noticed how funny the arms of massive bodybuilders diverge to the sides? One of the reasons for this is the penetrating effect of the pumped pectoral and latissimus muscles.
The shoulder joint gradually more and more comes into a state of slight, but still noticeable pronation. This is not a completely natural position, and the shoulder joint should bear the main load in a neutral position, and not in a supinated or pronated position.
If we constantly do nothing but pump up the pronators of the shoulders, we create all the prerequisites for distorting the normal geometry of our own shoulder joints. From here it’s not far to injury. Especially when performing bench presses, bent-over rows, and pull-ups. Once! And a sharp pain in the shoulder!
What to do?
1. Include in your training exercises that develop shoulder supinators. This is VPN exercise. They develop mainly the muscles lying on the back of the shoulder blades - supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor.
I will tell and demonstrate them in one of the upcoming articles.
2. Practice stretching the most powerful pronators of the shoulders - the chest and latissimus muscles. I will also write a separate post about them.
Completing these points during training will take 5-7 minutes. But what health benefits!
When building your exercise sets, keep all of the above in mind. And when you use other people's programs, at least superficially analyze them for the purpose of this article.
Be healthy!
Wrist bending technique
Flexion is an antagonistic movement to extension with dumbbells or a barbell. Involves mainly flexor muscles. It is recommended to perform the exercise at a slow and controlled pace, this will increase its effectiveness.
Technique:
- Sit on the edge of a bench or chair, legs bent at right angles. Place your hands on your knees so that your hands hang in the air.
- While sitting, try to lean on your legs and round your back, this will help relax the remaining muscles and concentrate tension on the target area.
- Bend your wrists as much as possible.
- After a short pause, slowly return the weight to the starting position, then lower your hands slightly below parallel to the floor. This will create additional stretch and increase the efficiency of the movement.
Pronation and supination of the foot. What is the difference between pronation and supination?
Biomechanics defines supination and pronation as rotating movements of any limbs that occur as a result of the work of special muscle groups with similar names - supinators and pronators. Essentially, these two concepts are opposites: supination is responsible for turning the legs and arms outward, and pronation, on the contrary, controls rotation inward. By studying the influence of the characteristics of foot placement while running, it is possible to adjust the training process so that it does not harm health.
Pronation of the foot, as well as supination, helps to properly distribute the load when jogging, when the impact force falls on the foot during contact with the hard surface of the ground. Thus, the pronators help the athlete maintain balance both when pushing and when landing. This action of the feet can be compared to the action of car springs, when the suspension spring softens shocks and shocks when driving on an uneven road.
There are various pathologies that disrupt the basic functions of the musculoskeletal system. As a result, an additional increased load is created on absolutely all the muscles of the legs, which is why a person begins to suffer from pain in the knees and joints, as well as from sprained legs and pinched Achilles tendons. The risk of serious injury in this case is very high.
How the foot moves during movement can be traced by paying attention to the so-called “step cycle”, which takes into account two phases: transfer and support. During a step, all leg muscles work, including instep and pronator muscles - it is their level of training that affects the degree of fatigue from exertion. To better understand the differences in foot placement, it is worth taking a closer look at the main types of pronation:
Neutral
The position of the feet is symmetrical - this position is considered correct. During movement, contact with the surface occurs with the outer heel, and the foot itself turns inward quite a bit, a maximum of 13-16%. The arch of the foot is neutral, which allows you to distribute the load evenly over the entire surface during the push. Only this type of pronation can provide a sufficient level of natural shock absorption, so that when jogging, the main force of the impact will be concentrated in the front of the foot.
Overpronation
Violations in the position of the foot in this case are associated with turning it inward - this affects the level of depreciation, reducing it. Load absorption occurs partially, so if shoes are chosen incorrectly, as well as in the absence of special insoles, at the end of the day or after a hard workout, painful sensations may appear in the legs. Push-off during overpronation occurs mainly through the thumb and index finger. In this case, balance can be difficult to maintain, and stability also suffers. It is also worth paying attention to the protection of the ankles; if pronation is impaired, they are more susceptible to dislocations.
Underpronation
In this case, pushing off the ground occurs thanks to the outer side of the foot. Just like in the previous case, natural depreciation is not enough here, so you will have to compensate for it in alternative ways. The main load falls on the little toe; this placement of the foot can soon cause serious pathologies - clubfoot, various deformities, calluses and tendon damage.
What muscles work
During the exercise, almost all the muscles in the wrists and forearms are used. The main burden falls on:
- Flexor carpi radialis.
- Palmaris longus muscle.
- Superficial finger flexors.
- Elbow flexors and wrist extensors.
- Flexor pollicis longus.
- Extensors of the little finger.
- Extensor radialis brevis.
- Finger extensors.
- Extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis.
Pronation and supination of the elbow joint. Introduction to the concept
From an anatomical point of view, pronation and supination are rotational movements of the limbs controlled by special purpose muscle groups. And the science that studies the work of muscle groups in the human body is biomechanics, which appeared relatively recently - in the 70s of the last century.
This medical field studies a number of important problems that arise in the human body during movement. The data obtained as a result of research is of great help to athletes and patients with impaired motor function.
Science that studies the body
In this regard, the concepts of “fascia” and “myofascial chains” also appeared. The science that directly deals with the health of the human body is called kinesiology. From “kinesio” - movement, “logos” - to study. That is, she studies the patterns of body movement.
This may be applicable in sports, in the treatment of pathologies, massage therapists and chiropractors may be interested in this. There are not many kinesiologists, but more and more modern doctors - osteopaths, neurologists - are interested in this area.
Supination in shoes. What is an arch support?
They mean a certain part of the insole, which performs the function of supporting the longitudinal arch of the foot. Typically, arch supports are used in special orthopedic shoes.
about arch supports
The instep support is an orthopedic medical product. therefore, it must be selected individually for each person after consultation with an orthopedic doctor, who will outline the selection criteria. Wearing shoes with arch supports is prescribed for flat feet or for its prevention, and sometimes after severe injuries to the lower leg or foot. The underframes themselves can be made of various materials that have shock-absorbing properties: leather, plastic, rubber or cork. Most often, when people talk about arch supports, they mean children's shoes. Indeed, during the formation of a baby’s foot, various deformations often occur. And the main role of the instep support in this case is to support the muscles and direct them towards proper development. If the child’s foot is developing normally and the doctor does not give recommendations for wearing special orthopedic shoes, then an instep support on the insole is not needed, since it will only interfere with the natural development of the muscles. You cannot prescribe insoles with arch supports for your baby on your own.
how to choose shoes with arch support
When buying orthopedic shoes for your child, keep in mind that they cannot be used for growth. The fact is that the function of the instep support is to support the inner zone of the foot. but if the shoes are not the right size, then the guide will be out of place. in this case, it will not only not be able to fulfill its positive role in the formation of a child’s foot, but on the contrary, it will do harm. Please also note that the arch support used to prevent flat feet should not be too hard and high, because in this case the arch of the foot will constantly rest on the support, and the muscles that support it in tone will begin to weaken. This, in turn, will lead to the formation of longitudinal flat feet. Orthopedic shoes must hold the foot tightly and firmly, that is, have lacing or tight fasteners. A rigid heel counter that secures the heel is also important. Currently, manufacturers of preventive footwear prefer to use anatomical insoles. At the same time, they do not try to make a rigid, clearly visible instep support. Anatomical fit is achieved by making indentations for the heels and linings for the outer and inner arches of the foot. As a result, the foot is correctly positioned in the shoe, and thanks to this, flat feet are prevented. Flat feet is a serious disease. People suffering from it cannot stand for a long time, travel long distances on foot, and constantly feel pain in their legs. Therefore, try to prevent its development as early as possible, and if it does occur, give preference to shoes with arch supports.
5 basic exercises from Gennady Kvikviniya[edit | edit code]
Gennady Kvikvinia is a world and European champion in arm wrestling. Performs in the category up to 110 kg. Weight at the time of writing this material is 130 kg country - Georgia Gennady Kvikvinia
“When you just come to arm wrestling, you need to devote at least three years. in order to achieve good results in setting up technique and achieving minimum strength indicators. You need to have strong willpower to get through this stage of targeted training. Having performed in competitions, we can already see our strengths and weaknesses. After identifying your strengths, you need to continue adding strength to these movements without stopping. In three years, it is unlikely that you will be able to strengthen everything you want and become a universal armwrestler. Once you have mastered your strong movement, you can spend more time on the weaker aspects of your wrestling. Then at the next competitions, when your opponents see your struggle, where there are no weaknesses, when you have a strong hand, fingers, tension, biceps, your opponents will simply get lost. They will have nothing to oppose you. I have all the tournaments, from the beginning of my performances to the last start, in the recording and in my memory, I constantly review everything, draw conclusions and analyze myself based on the materials. I always need to know how effectively I am using this or that technique. Not everyone becomes a champion right away, I started with regional tournaments and so reached the World Championship, where I became a champion. My credo is to always be in good shape. The goal is not to fight with one specific opponent, but to be stronger than yourself and everyone. If I only focused on one person, I would never win a single tournament. Only with the attitude of being stronger than everyone else was I able to achieve results. I respect all my opponents, whether he is stronger or weaker, my attitude towards him is always friendly.
In the case when an opponent surpasses me in strength, I never get angry with him or with myself. Those emotions that arise during a fight. “It’s an adrenaline rush, it adds strength.”
Sparring[edit | edit code]
According to Gennady, sparring is the basis of armwrestling. Namely, developing and honing your signature movements. Whether a beginner or an experienced armwrestler, wrestling should be present in any case.
Table wrestling outside of competition (training wrestling) serves as a good simulator for developing technique and endurance in arm wrestling. Gennady also noted the fact that he spar with opponents who are weaker than him. This way he can work in all the movements he deems necessary. This happens due to the fact that the opponent creates pressure, but the partner does not have the strength to stop Gennady’s movements. If there is a training partner next to you. who is superior to you in strength, then the procedure will be as follows: the opponent must give you corners, while not attacking, but taking only a defensive position, and you, in turn, make an attacking movement. Since Gennady is generally superior to his sparring partners, with one armwrestler it is not possible to work out all the movements to the smallest detail. IN
On average, the number of sparring partners in Gennady’s training is 3-5. According to Gennady, sparring at the table is the final exercise of his training.
Curved bar biceps curls[edit | edit code]
In his arsenal of curved bar biceps curls, Gennady Kvikvinia performs two versions of this exercise. The first is standing biceps curls, the movement is performed in full amplitude. The second is biceps curls, sitting on the “Scott Bench”, the movement is performed with a short amplitude. There is a nuance in the first option; it lies in the fact that the movement is carried out together with the elbows. That is, the elbows are not statically fixed, but at the top point they should go slightly forward and upward along with the bar. As for weight, Gennady starts with 15 kg for 10 repetitions. The weight increase interval is as follows: 15 kg - 25 kg - 30 kg - 35 kg - 45 kg - 55 kg - 80 kg - 10 repetitions, 90 kg - 100 kg - 7 repetitions. Rest between sets for 1 minute. Next comes work on the “Scott Bench”. Here the interval for increasing working weights is as follows: 15 kg - 35 kg - 90 kg for 7 repetitions. The amplitude is incomplete.
Stretch[edit | edit code]
In this exercise, the brachioradialis muscle is included in the work. Having warmed up a little with a weight of 15 kg, Gennady begins to randomly lift the weight without a clear interval. Smoothly reaches the maximum weight on the block. Often, when Gennady is preparing for competitions and his form is close to peak, there is not always enough weight on the block. When the block is fully loaded, Gennady performs the movement to failure.
Grif[edit | edit code]
Many athletes note the great finger strength that Gennady Kvikvinia possesses. When Gennady went to show that secret movement with which you can get the key to the strength of your fingers, our team assumed that it would be something supernatural. But when we approached the apparatus and Gennady demonstrated the exercise, we were surprised. Simple standing Olympic bar lift. The maximum weight with which it was possible to work with this projectile was 130 kg. The entire exercise consists of 8 approaches. Each approach is 10-15 repetitions. The last approach is performed to failure.
Handle on straps[edit | edit code]
Gennady Kvikvinia's favorite exercise. Even when going on business trips, Gennady takes his pen with him. It is worth noting that many arm wrestlers love this exercise for its effectiveness. Also starts: 15 kg - Gennady’s basic warm-up weight. Then it gradually reaches its maximum weight. As for the number of approaches, it is from 8 to 10. The number of repetitions is 10-15.
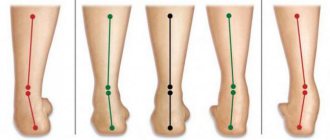
Pronation and supination
The mechanism of pronation and supination is the natural shock absorber of the foot.
- Pronation – translated from Latin – to bend forward.
- Supination – also from Latin – to throw back.
During the landing phase, pronation occurs, that is, the arch of the foot tilts. At the same time, the arch of the foot straightens, absorbs the impact and is “charged” for repulsion.
During the push-off phase, supination occurs. The arch of the foot begins to return to its original position and helps push off more effectively.
This is how the depreciation process occurs in the absence of deviations. On
If the feet work this way, then everything is fine. You don’t need to invent anything, bother with insoles and special sneakers. Unfortunately, this doesn't happen often. Most beginning runners have ligaments, joints and muscles that are not designed for running, some even for walking. Why? It's simple: a sedentary lifestyle, sedentary work, all movements by transport. The need to move on foot has become far from paramount and the body has relegated this function to the background. This can be easily corrected with training, but first you need to take care of injury prevention.
The most important
Pronation helps smooth out the impact of landing, protecting the knees and hip joints from injury. Overpronation occurs in 75% of runners; underpronation is very rare. The main causes of overpronation are: weakness of the foot muscles, longitudinal flat feet, weakness of the thigh muscles.
The most accurate method for determining overpronation is a running video test. If overpronation is detected, constant strengthening of the muscles that perform a stabilizing function is necessary. You should pay attention to the selection of sneakers with protection against overpronation. Severe flat feet require custom insoles.
Hip supination
Hip adduction
Hip abduction
Hip extension
Hip flexion
Muscles that produce movements in the hip joint
BIOMECHANICS OF THE MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMB
The muscles of the lower limb produce movements in the hip, knee, ankle and foot joints.
According to three mutually perpendicular axes of rotation passing through the center of the hip joint, the following movements can be made in this joint with the thigh with the pelvis fixed, and with it the entire leg:
1) flexion and extension, i.e. movement forward and backward;
2) abduction and adduction;
3) pronation and supination;
4) circular motion (circumduction).
When securing the hip or the entire leg, the muscles produce movements of the pelvis: forward, backward, sideways and turns to the right and left. To carry out these movements, there are six functional muscle groups in the hip joint.
The muscles that produce flexion of the thigh in the hip joint include the muscles that cross the transverse axis of this joint and are located in front of it. These include:
1) iliopsoas;
2) tailoring;
3) tensor fasciae lata muscle,
1) 4) comb;
4) rectus femoris muscle.
Muscles that also cross the transverse axis of the hip joint, but are located posterior to it, take part in hip extension. These muscles go both from the pelvis to the thigh and from the pelvis to the lower leg. These include:
1) gluteus maximus;
2) biceps femoris muscle;
3) semitendinosus:
4) semimembranous;
5) adductor magnus
The hip abductor muscles cross the sagittal axis of the hip joint and are located on its lateral side. They are attached mainly to the greater trochanter. These muscles include:
1) gluteus medius;
2) gluteus minimus;
3) pear-shaped;
4) internal obturator;
5) twins;
6) tensor muscle of the fascia lata.
Adduction of the hip is carried out by muscles that cross the sagittal axis of the hip joint and are located medial to it. These include:
1) comb;
2) thin;
3) long adductor;
4) short adductor;
5) adductor magnus.
Muscles supinating the thigh, except the iliopsoas. cross the vertical axis of the hip joint obliquely. The iliopsoas muscle supinates the thigh due to the special location of the lesser trochanter (not only anteriorly, but also medially). The muscles that supinate the thigh include:
1) iliopsoas;
2) quadratus femoris muscle;
3) gluteal muscles, of which the medius and minimus supinate the thigh only with their posterior bundles;
4) tailoring;
5) internal obturator and external obturator muscles;
6) pear-shaped;
7) twins.
What do foot defects lead to?
Deformations cause a lack of shock absorption during movement. Most often this affects the joints, as well as the spine, as the load on the skeleton increases. The body has to look for ways to adapt and protect all organs from functional failure.
Such a restructuring can lead to the development of clubfoot, flat feet, hallux valgus, plantar calluses, and damage to the Achilles tendon. The most serious pathology caused by foot deformity is arthrosis. With the disease, degenerative processes in the joints are observed as a result of impaired blood circulation caused by overpronation.
Subsequently, the joints are destroyed. Leg pathologies are characterized by latent progression. There are no symptoms for a long time; exacerbations are usually provoked by active physical activity. Treatment of the disease is aimed at preventing changes and relieving pain during walking or sports training.
Arch support. What is an instep support?
Orthopedic instep supports are products whose purpose is to support the arches of the foot (transversely or longitudinally). To put it simply, the instep support is usually represented by a simple insole that is inserted into ordinary or specialized shoes (orthopedic, sports or hunting boots). This is necessary in cases where the foot has an inward tilt or a person is diagnosed with flat feet.
Why are pronators and supinators so important? To begin with, it would be nice to understand how one differs from the other. Pronators tend to provide support to the forefoot, which is very important for transverse flatfoot. If we talk specifically about instep supports, they often support the arch of the foot longitudinally or in the heel area. It is impossible to cope without these devices if you have flat feet, since it provokes disturbances in the spring function of the feet. Because of this, the entire impact load during movement migrates to the joints, spine and brain of a person, because every step with such a pathology leads to a microconcussion.
In such circumstances, you cannot do without orthopedic products, since they reduce the intensity of pain when walking and protect the feet from possible deformations, for example, from flattening of the foot. In addition, such devices normalize the entire human musculoskeletal system.
In other words, arch supports are indispensable in such cases:
- to normalize blood flow;
- with transverse flatfoot;
- to improve overall well-being;
- to counteract excessive leg fatigue;
- after injuries or fractures of the bones of the foot and leg;
- in order to hold the arch of the foot longitudinally (with longitudinal flat feet);
- to reduce the load on the ankle, knee, hip joints, as well as on the spine.
Separately, we should dwell on the function of arch supports as assistance in rehabilitation for injuries. For example, they are absolutely indispensable for such a rare injury as a heel fracture. Naturally, in the first stages of treatment a plaster boot is needed, but after 2 months the plaster is removed and during this period it is no longer possible to do without a special instep support. Such a heel support should reduce the intensity of the load on the damaged heel. It is selected by a doctor and worn for 4 to 8 months (depending on the severity of the injury).
Local injection therapy
The conservative treatment measures listed above only work at an early stage. But most patients present with severe pain, so in 80% of cases glucocorticoid injections are used for treatment. They help quickly relieve inflammation and reduce pain. The therapy is effective in more than 90% of patients. In 58% of patients, the results last more than 1 year after 1 injection, in 73% - after 2 injections.
Indications for local administration of glucocorticoids:
- strong pain;
- ineffectiveness of initial therapy;
- disease duration up to 4 months.
Injections of corticosteroids are also possible if the pathology is up to 12 months old, but the effect is less pronounced, since by this time profound changes in the ligament occur.
Complications of treatment:
- temporary stiffness of the first finger – develops in every third patient;
- increased pain on the first day - in one case out of three;
- skin pigmentation or depigmentation - in case of superficial injection;
- impaired skin sensitivity - in case of injection of drugs into the area of the radial nerve;
- bleeding with the formation of a hematoma.
Glucocorticoids are administered along with a local anesthetic. It acts instantly, turning off the sensitivity of nerve endings. But after a few hours, the effect of the drug wears off and the pain may return. The final result from the administration of glucocorticoids is achieved only after a few days, but significant improvement is noted already on the second day.
After administration of the drug, immobilization is required for 1 to 3 days and limitation of physical labor for up to 7 days. If there is no sufficient effect from the injection, the procedure can be repeated after 2-3 weeks. However, frequent use of corticosteroids is undesirable, as it leads to soft tissue atrophy. Therefore, if there is no sufficient effect, doctors proceed to surgical treatment.