What is load cycling?
Home ▸ Articles ▸ Training ▸ What is load cycling
Cycling is the process of repeating cycles of different durations within separate periods, which is one of the means of providing variability in training.
Cycling is the most important means of restoring an athlete and increasing the effectiveness of training. This is facilitated, first of all, by the correct distribution of loads in training cycles of varying duration.
Properly organized cyclicity of the training process (a relatively complete circuit with partial repeatability of individual exercises, classes, stages and entire periods within certain cycles) is one of the basic principles of athletic training.
Training cycles are divided into three types:
- microcycles. They usually coincide with weekly cycles, but may differ from them by 3-4 days, that is, have a duration of 4 to 12 days;
- mesocycles. Usually coincide with the monthly cycle, but can, at the athlete’s request, last from 20 to 50 days;
- macrocycles. They last from 3-6 months to 1 year.
Microcycles should alternate between load and rest, as well as higher and lower loads.
The positive effect of training can be achieved only if one or several “work” microcycles are followed by a relatively unloading microcycle, which allows restoring the body’s functional capabilities and ensuring the most effective course of adaptation processes. Otherwise, there may be a threat of physical and nervous exhaustion for the athlete.
The main condition for progress in bodybuilding is the constant systematic development of fitness as a combination of strength and endurance.
The development of fitness is carried out by reaching an increasingly higher level of training load and mastering it. But for successful, effective training, mastery of active cycling is absolutely necessary.
The duration of training is determined by the level of preparedness of each athlete and his well-being. But in the first 2-3 months, novice athletes should not train more than 1 hour a day or a little more. In the 4th month of regular training, their duration can be increased to 1.5-2 hours. Experienced bodybuilders usually spend about 3 hours in the gym, training 2-3 times a day for 40-60 minutes.
It is not advisable to perform the same exercise for more than 3 or less than 1 month. You can find an alternative replacement for any of the most effective exercises. Experienced bodybuilders usually have 2 to 3-5 interchangeable exercises available.
For several microcycles (one mesocycle), a bodybuilder needs to have a basic and at least 2-3 replacement exercises to train one or another muscle group. Subsequently, these additional exercises can replace the main one. Such a system will not allow the muscles to adapt to the same exercises.
To properly distribute loads, there are special programs that provide certain options for combining exercises. But in fact, each athlete develops his own unique cycling program over time, which allows him to achieve the best results.
When planning cycle training, the correct sequence of exercises begins to play a particularly important role, so in the process of creating and implementing it, some recommendations should be taken into account.
Beginning athletes should not spend a lot of time choosing one or another training method. They can easily train their muscles according to the scheme described above.
It is better to start training with the upper muscle groups (neck, shoulders, chest), and after that move on to the muscles of the back, arms and calves.
If at the beginning you perform exercises for the chest muscles, then you can replace them with exercises for the back muscles; exercises for the triceps should replace exercises for the biceps. After performing exercises for the synergistic muscles, the turn of exercises for the antagonist muscles begins.
To most successfully eliminate the lag in the development of any muscle group, it is necessary first of all to include in the training exercises that are most effective for this particular muscle group.
You can influence a specific muscle group in two ways:
- after completing the planned exercise in one series, move on to another;
- use super series, the number of which may depend on the level of physical fitness and experience of the athlete.
But the first series of exercises, one way or another, should train the synergist muscles, and the one that replaces it should train the antagonist muscles. It is recommended to include back stretching exercises in your workouts, such as hanging on a bar in between sets.
Having completed complex exercises (squats, bench press, etc.), you should move on to relaxation exercises, performing them with low to medium load.
Question Types of training cycles. The principle of cyclical training process.
Forms of organizing sports training classes
1) Educational and training sessions - a permanent schedule.
2) Participation in sports competitions - in accordance with the calendar, regulations and rules.
3) Independent training sessions - UGG, home exercises, work, hikes, etc.
Sports training is a long-term and year-round process.
A multi-year training plan creates an overall picture, defines the goal, objectives, and basic means.
For each year, a particular goal is determined - the role of sports results.
The training process is built on the basis of a certain structure, which represents a relatively stable order of combining the components of this process (its parts, sides, links), their natural relationship with each other and the general sequence of structural sports training is characterized by:
1) An expedient procedure for the relationship of various aspects of the content of training for athletes of general physical training and physical training;
2) Necessary ratios of the parameters of the training load volume and intensity;
3) A certain sequence of various parts of the training load.
In accordance with the gradations of cycles of the training process, it is necessary to distinguish three scales of its structure:
1. Microstructure – the structure of microcycles in one lesson.
2. Mesostructure – the structure of mesocycles, consists of 3-6 microcycles.
3. Macrostructure – large training cycles (six months, a year, several years).
24.4.1. Structure of small training cycles (microcycles)
The duration of the microcycle is from two to several sessions. The training session is an element of the microcycle structure. This lesson consists of 3 parts: introductory (warm-up), main and final. The content of the training session follows primarily from the focus on achieving the maximum training effect in relation to the chosen sport. Classes can be very different in content: 1) basic training sessions with expanded volume and intensity (40-60 hours or more); 2) additional classes to refine the main lesson or recovery.
A separate construction of a microcycle contains 2 phases: 1) cumulative – the total effect of all activities; 2) restorative – restorative in nature, rest.
During classes you need to pay special attention to:
— content, number of classes of various directions, load size;
— dynamics of processes – fatigue and recovery;
— the general lifestyle of the athlete (study, work);
— the place of microcycles in the overall system of the training process.
Types of microcycles:
- actual training microcycles - general physical training and physical training are divided into ordinary (uniform loads, high volume and intensity) and shock - high volume, high intensity.
— leading microcycles – a system for leading an athlete to competitions.
- competitive microcycles - participation in a series of competitions.
24.4.2. Structure of average training cycles (mesocycles)
The duration of the mesocycle ranges from two to six weeks. One mesocycle includes at least 2 microcycles and more often 3-6 microcycles. Their selection depends on the general training process.
The external signs of a mesocycle are the repeated reproduction of a number of microcycles (ordinary - shock - recovery) in a single sequence. Mesocycles allow optimal management of the cumulative effect.
24.4.3. Structure of multi-month training cycles (macrocycles)
The duration of the macrocycle ranges from six months to a year or more. The construction of a training macrocycle is based on the patterns of acquisition, maintenance and temporary loss of sports form.
24.5. Periodization of sports training
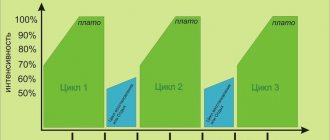
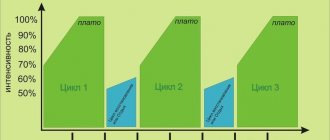
The annual (macro) cycle of sports training consists of three periods: preparatory, competitive and recovery (Figure 20).
Preparation period
lasts from 2-3 months (in a six-month cycle) and up to 6 months in a yearly training cycle. The task of this period is to significantly increase the overall level of functional capabilities of the athlete’s body at the stage of general training and develop the physical, technical and mental qualities necessary for specialization in the chosen sport (Figure 21).
The structure of the preparatory period is built from the following mesocycles: retractive (smooth increase in the volume and intensity of loads); basic (the main volume of training loads is performed); control and preparatory (where the actual training work is combined with the participation of athletes in control competitions, assessments, testing); grinding (intended to eliminate identified deficiencies in technical and physical training).
Competitive period
consists, as a rule, of two competitive stages - the first and second - and lasts from 2 to 5 months. During this period, the athlete achieves athletic fitness and participates in both secondary and major competitions.
At this stage, the athlete’s training is based on the following cycles:
1. Pre-competition – it simulates the regime of the upcoming competition and achieves sports form;
2. First competitive – where the athlete participates in low-rank competitions (region, city championship, etc.);
3. Rehabilitation and preparatory, intended to prepare the athlete for his main competitions;
4. The second competitive stage is the athlete’s participation in important competitions.
Recovery period
lasts from 3-4 to 6 weeks and consists of two mesocycles: recovery-maintenance, which is characterized by a smooth decrease in load, and recovery-preparatory, which develops (as the athlete’s body recovers) into a retractive mesocycle of the preparatory period of the next training cycle.
Instead of a recovery period, a short-term phase is sometimes introduced; this happens with a “double macrocycle”, where after the competitive period there is a second preparatory period, and then a second competitive period, and only then a recovery period.
. Classification of physical exercises based on the structure of movements: cyclic exercises (walking, running, rowing, etc.); acyclic exercises (gymnastics on apparatus, martial arts, etc.); mixed exercises (sports games, running long jumps, etc.), which combine cyclic and acyclic actions.
Basic principles of the principle of cyclical sports training
The main content of the principle of cyclical training process for athletes can be expressed in the following basic methodological provisions:
1. When building a training process in sports, it is necessary to periodically repeat its structural components. It is also necessary to periodically change the content of training cycles in accordance with the logic of preparation for the main competitions and the patterns of development of sports form, in order to guarantee the athlete’s optimal readiness to perform in the main (main, target) competitions.
2. It is necessary to consider any element of the training process in its relationship with larger and smaller components of the structure of the training process. It must be taken into account that the structure of microcycles is largely determined by their place in the structure of mesocycles, and the structure of mesocycles is determined, on the one hand, by the characteristics of its constituent microcycles, and on the other hand, by their place in the structure of the macrocycle, etc.
3. Training loads should be normalized, as well as their dynamics should be regulated depending on the structural components of the training cycles. The dose of load, its dynamics, as well as any exercises and methods of using them in training, no matter how good they are, lose their effectiveness if applied at the wrong time and place.
4. Selection of training means (exercises), i.e. The content of the training, the nature and magnitude of the loads must be carried out in accordance with the period of the athlete’s training process.
5. When building the training process for athletes, the body’s biorhythms should be taken into account.
The training process is characterized by a clearly defined cyclicity. Cycles are a relatively complete sequence of links and stages of the training process (micro-, meso- and microcycles), alternating as if in a circuit.
Each successive cycle is a partial repetition of the previous one and at the same time expresses the development trends of the training process, that is, it differs from the previous ones in updated content, partial changes in the composition of means and methods, an increase in training loads, etc.
The entire training process is built in the form of cycles - from its elementary links to the stages of long-term preparation. Depending on the time scale within which the training process is built, micro-, meso- and macrocycles are distinguished. All of them form an integral system of rational construction of the training process.
The main provisions of the principle of cyclical training process:
• Sports training is built from weekly, monthly cycles and larger structural units, which are systematically repeated and at the same time the elements of their content change in accordance with the logic of the development of the training process.
• When solving problems of appropriate use of training means and methods, it is necessary to find their appropriate place in the structure of training cycles.
• It is necessary to normalize and regulate training loads in relation to the patterns of construction of micro-, meso- and macrocycles of training (wave-like changes in the dynamics of training loads - small, medium and large waves in these structural formations of the training process).
• It is necessary to consider any fragment of the training process in its connection with larger and smaller cyclic structures. The structure of microcycles is largely determined by their place in the structure of mesocycles, and the structure of mesocycles is determined, on the one hand, by the characteristics of their constituent microcycles, and on the other, by their place in the structure of the macrocycle.
Construction of the training process on the basis of various cycles makes it possible to systematize the tasks, methods and means of training and implement the basic principles of sports training: the unity of general and special training, a gradual increase in loads and a tendency towards maximum loads, the undulation of load dynamics.
Article section: Basics of sports training
Cyclicity as one of the main patterns in sports
01/19/2015 Article category Articles, Running
The process of sports training is characterized by a clearly defined cyclicity, which means the circulation of training stages with partial or complete repeatability, both individual training exercises, training sessions, stages, and entire training periods within certain time cycles.
In the training process of various sports, including orienteering, the following time cycles of training activity can be observed:
— microcycles (include a short period of time, for example, a week);
— mesocycles, a composition that includes several microcycles;
- macrocycles, which include several mesocycles (this can be a year-long preparation cycle).
As you know, the basis of any training activity is its planning, which is based on previously achieved results and their planned growth.
Planning is based on macrocycles, which, as a rule, last a year, while their calendar dates do not coincide with generally accepted ones.
In Olympic sports, in addition to the annual macrocycle, they often use a 4-year training cycle, the task of which is to be optimally prepared to approach the most important start of the four-year period - the Olympic Games.
The next stage of planning is the distribution within the macrocycle and its constituent parts of mesocycles.
Here, depending on the goals of the cycle, you can most often find the following list of mesocycles:
- Retractive or preparatory mesocycle. Its main task is to prepare the athlete’s body for subsequent serious loads.
- Basic mesocycle. Lays the foundation for future high results. During this period, the body is subjected to serious stress, which is aimed at achieving serious functional changes in the athlete’s body, the same applies to technical changes.
- Pre-competition mesocycle. Aimed at preparing the athlete for future intensive work, a kind of transition period between the basic and the next, competitive mesocycle.
- Competitive mesocycle. This period coincides with the competitive season, and consists of participation in competitions and proper recovery and preparation for them. Moreover, this cycle is planned in such a way that the most optimal physical and technical form occurs at the key competitions of the season.
- Transitional or recovery mesocycle. It occupies a kind of off-season period, concentrating on restoring the body after the training loads of the season, and smoothly transitioning the athlete into the next training year.
After completion of planning by mesocycles, specific planning is carried out using microcycles.
The most widespread are weekly microcycles, which organically fit into work activities, which are also planned weekly.
But at the same time, there are examples of other microcycles, for example, our fellow countryman, Sergei Nazarovich Bubka, used a 4-day microcycle in his preparation.
#Sekta: information portal
I would like to make this the shortest post in the history of posts:
|
It's good if these rules are enough for you. As for me, I met them many times, but did not take them seriously. I thought that these rules were invented for lazy weaklings, that more training equals more results, that daily exercise is the only way to build the body I want.
If someone had clearly explained to me then what I was doing wrong, I would have had the body I have now five years ago.
| It's very simple: it should always be as difficult for you as it was at the beginning.. |
Yes, for me, running 15 laps of the morning interval is just ridiculous. But as soon as I rest for two or three weeks, I’m exhausted even after five! I don't try to push my training to the max right away, because that way I'll reach my comfort zone too quickly and the training will become mentally exhausting for me and useless for my body.
To give your best, work on your technique and constantly improve, you need passion. To keep the excitement going, you need to see the results. In the mirror or in the numbers of a fit test - it’s up to you to decide. But if there is no excitement, you need to take a break.
| Taking a break is a great decision at any time. |
I'm always really happy when I gain a little weight and get out of shape! This means that as soon as I start practicing, my old result will quickly come and bring more with it. Losing shape forever is impossible. It can only be temporarily lost until a new stage in your sports activities.
Previously, I only stopped when I was sick, or when my psyche gave out, I had a large-scale nervous breakdown, I hated myself, my body, I punished myself with food, for a long time I could not return to a healthy lifestyle and nutrition as manifestations of love to yourself. I took good, right things, but I did not know the extent of them. I pushed myself and suffered from fatigue and lack of results. All that was needed was to learn to relax. I noticed this when I was practicing yoga like crazy, every day, for many hours.
I have genetically very weak hip joints, and I injured them. I practiced through pain until my body refused to do even the simplest asanas. I violated the main principle of yoga - non-violence, in order to be sure that I was not lazy, that I was a warrior, that I had not lived my day in vain. It was quite natural that my subconscious associated an ocean of pain with yoga, and I dreamed of returning to classes, but I could not do this because I could not stop in time, and my subconscious saw a return to yoga as a return to this pain.
When, after several months, I returned to practice with healed injuries, I discovered that I could do those asanas that had not been given to me before. All the most difficult asanas were mastered by me in rest mode. That is, I tried to make them, and they didn’t work out, and after the break I just did them, as if I had always been able to.
Why couldn't you just take a break and not take it to the extreme?
It's the same with training. One day I got up to 3 full workouts a day. Naturally, this did not make me slimmer or more attractive. I was very tired and didn’t have time to do anything in life except these activities, and their uselessness was killing me. In addition, it seemed to me that without these trainings I would be destroyed, which made me even more unhappy.
It turns out that all you had to do was give up training for a while and gradually introduce them into your life: one, two a week, in order to see their effectiveness again.
The main secret is not a gradual reduction in the load, but a full rest, after which you start all over again, and keep your load at the “middle of the scale” level, where the maximum is what you did when you paid all your attention only to your body .
| Remember: your maximum is the danger zone, a temporary measure followed by psychological devastation. |
When a person meets his limit, it is a test, and after it you cannot immediately return to your normal life.
If you have questions about this topic, be sure to write in the comments.
| How do I see the ideal regime? |
The ideal regime is always changing. Either this is several weeks of morning training with additional blocks of the most difficult exercises, then it is marathon running, then evening workouts, then morning and evening workouts. Sometimes training 3 times a week, sometimes two. This could be a month in the gym with free weights and a month of cycling, a month of yoga, then a month of rest.
| Don't wait until the body is sick to protect itself from your attacks. And most importantly: have fun! |
Author: Olga Marques
More on the topic
- Week 6: Workouts
- Week 4: Body Types
- Week 8: Olya Marquez about motivation to work with your form
- How to maintain health during an epidemic: a reminder for older people
25