How many times should a man do push-ups?
Judging by the GTO standards, the older one does less push-ups. But in life everything depends on the person. A 60-year-old man who has set a goal for himself and leads a healthy lifestyle can do more push-ups than a 20-year-old man.
According to these standards, men 60-69 years old can do push-ups on a bench. 70 years and above – from stool.
From a medical point of view, studies have shown that men who do 40 or more push-ups have a reduced risk of heart disease and cardiovascular disease.
Table of physical education standards for schoolchildren 2020-2021 (physical education)
Nowadays, society does not attach due importance to physical education lessons at school. Some people think that at school there is nothing interesting or useful in physical education lessons and it is better for the child to do additional lessons, while others are simply lazy and he/she does not go to these lessons out of principle. An even more frightening trend is the fact that the promotion of a lifestyle in which sports plays an important and fundamental role has come to almost nothing in our country. That is why it is necessary to understand and realize the usefulness of physical education lessons at school.
Approximate standards from grades 1 to 11
Physical education standards for 1st grade
| Exercises in 1st grade with standards | Boys/score | Girls / score | |||||
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | ||
| Run 30 m (sec.) | 6.2 | 6.9 | 7.0 | 6.7 | 7.4 | 7.5 | |
| Shuttle run 3*10 m (sec.) | 9.9 | 10.5 | 11.0 | 10.2 | 11.3 | 11.7 | |
| Run 1 km | |||||||
| Run for 6 minutes (meters) | 1000 | 900 | 800 | 700 | 600 | 500 | |
| Skiing 1 km | |||||||
| Multi-jump 8 jumps (m) | 9 | 7 | 5 | 8 | 6 | 4.8 | |
| Standing long jump (cm) | 140 | 115 | 100 | 130 | 110 | 90 | |
| Raising the body 30 sec (times) | 16 | 14 | 11 | 14 | 12 | 9 | |
| Raising the body 60 sec (times) | 30 | 25 | 15 | 20 | 15 | 12 | |
| Bend forward while sitting, legs together (cm) | +6 | +3 | +1 | +7 | +5 | +3 | |
| Jumping rope 60 sec (times) | 40 | 30 | 20 | 50 | 40 | 30 | |
| Lying hanging pull-up (one time) | 12 | 7 | 5 | 10 | 5 | 3 | |
| Hanging pull-up (one time) | 4 | 2 | 1 | ||||
| Push-ups (one time) | 10 | 8 | 5 | 8 | 5 | 3 | |
| Ball throwing 150 g (m) | 20 | 15 | 10 | 15 | 10 | 5 | |
| Medicine ball throw 1 kg (cm) | 295 | 235 | 195 | 245 | 220 | 200 | |
| Throwing at a target from 6 m / 5 attempts | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | |
Physical education standards for grade 2
| Exercises 2nd grade, approximate standards | Boys | Girls | ||||
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | |
| Shuttle run 4×9 m, sec | 12,0 | 12,8 | 13,2 | 12,4 | 12,8 | 13,2 |
| Shuttle run 3×10 m, sec | 9,1 | 10,0 | 10,4 | 9,7 | 10,7 | 11,2 |
| Run 30 m, s | 5,4 | 7,0 | 7,1 | 5,6 | 7,2 | 7,3 |
| Running 1,000 meters | without time | |||||
| Standing long jump, cm | 165 | 125 | 110 | 155 | 125 | 100 |
| High jump method of stepping, cm | 80 | 75 | 70 | 70 | 65 | 60 |
| Jumping rope (number of times/min.) | 70 | 60 | 50 | 80 | 70 | 60 |
| Pull-up on the bar | 4 | 2 | 1 | |||
| Raising the body from a supine position (number of times/min) | 23 | 21 | 19 | 28 | 26 | 24 |
| Squats (number of times/min) | 40 | 38 | 36 | 38 | 36 | 34 |
| Multi-jump - 8 m jumps. | 12 | 10 | 8 | 12 | 10 | 8 |
Physical education standards for grade 3
| Exercises 3rd grade, approximate standards | Boys | Girls | ||||
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | |
| Shuttle run 3×10 m, sec | 8,8 | 9,9 | 10,2 | 9,3 | 10,3 | 10,8 |
| Run 30 m, s | 5,1 | 6,7 | 6,8 | 5,3 | 6,7 | 7,0 |
| Running 1,000 meters | without time | |||||
| Standing long jump, cm | 160 | 130 | 120 | 160 | 135 | 110 |
| High jump method of stepping, cm | 85 | 80 | 75 | 75 | 70 | 65 |
| Jumping rope (number of times/min.) | 80 | 70 | 60 | 90 | 80 | 70 |
| Pull-up on the bar | 5 | 3 | 1 | |||
| Tennis ball throws, m | 18 | 15 | 12 | 15 | 12 | 10 |
| Raising the body from a supine position (number of times/min) | 25 | 23 | 21 | 30 | 28 | 26 |
| Squats (number of times/min) | 42 | 40 | 38 | 40 | 38 | 36 |
| Multi-jump - 8 m jumps. | 13 | 11 | 9 | 13 | 11 | 9 |
| Pistols, supported on one hand, on the right and left leg (number of times). (m) | 6 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 1 |
Physical education standards for grade 4
| Exercises 4th grade, approximate standards | Boys | Girls | ||||
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | |
| Shuttle run 3×10 m, sec | 8,6 | 9,5 | 9,9 | 9,1 | 10,0 | 10,4 |
| Run 30 m, s | 5,0 | 6,5 | 6,6 | 5,2 | 6,5 | 6,6 |
| Run 1,000 meters, min | 5,50 | 6,10 | 6,50 | 6,10 | 6,30 | 6,50 |
| Standing long jump, cm | 185 | 140 | 130 | 170 | 140 | 120 |
| High jump method of stepping, cm | 90 | 85 | 80 | 80 | 75 | 70 |
| Jumping rope (number of times/min.) | 90 | 80 | 70 | 100 | 90 | 80 |
| Pull-up on the bar | 5 | 3 | 1 | |||
| Tennis ball throwing, m | 21 | 18 | 15 | 18 | 15 | 12 |
| Raising the body from a supine position (number of times/min) | 28 | 25 | 23 | 33 | 30 | 28 |
| Squats (number of times/min) | 44 | 42 | 40 | 42 | 40 | 38 |
| Multi-jump - 8 m jumps. | 15 | 14 | 13 | 14 | 13 | 12 |
| Pistols, supported on one hand, on the right and left leg (number of times). (m) | 7 | 5 | 3 | 6 | 4 | 2 |
Physical education standards for grade 5
| Exercises, 5th grade | Boys | Girls | ||||
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | |
| Shuttle run 4×9 m, sec | 10,2 | 10,7 | 11,3 | 10,5 | 11,0 | 11,7 |
| Run 30 m, s | 5,5 | 6,0 | 6,5 | 5,7 | 6,2 | 6,7 |
| Run 60 m, s | 10,0 | 10,6 | 11,2 | 10,4 | 10,8 | 11,4 |
| Run 300 m, min, s | 1,02 | 1,06 | 1,12 | 1,05 | 1,10 | 1,15 |
| Run 1000 m, min, s | 4,30 | 4,50 | 5,20 | 4,50 | 5,10 | 5,40 |
| Run 2000 m | No time tracking | |||||
| Cross 1.5 km, min, s | 8,50 | 9,30 | 10,0 | 9,00 | 9,40 | 10,30 |
| Hanging pull-up on the bar, one time | 7 | 5 | 3 | |||
| Pull-up on a low bar from a hanging position, one time | 15 | 10 | 8 | |||
| Flexion and extension of the arms while lying down | 17 | 12 | 7 | 12 | 8 | 3 |
| Raising the body from a supine position, arms crossed on the chest in 1 minute, once | 39 | 33 | 27 | 28 | 23 | 20 |
| Standing long jump, cm | 170 | 160 | 140 | 160 | 150 | 130 |
| Running long jump, cm | 340 | 300 | 260 | 300 | 260 | 220 |
| Running high jump, cm | 110 | 100 | 85 | 105 | 95 | 80 |
| Skiing 1 km, min, sec | 6,30 | 7,00 | 7,40 | 7,00 | 7,30 | 8,10 |
| Skiing 2 km, min, sec | No time tracking | |||||
| Ski technique | |||||
| Dribbling the ball while running in basketball | Technique | |||||
| Jumping rope in 1 minute | 70 | 60 | 55 | 60 | 50 | 30 |
| Jump rope, 15 sec, times | 34 | 32 | 30 | 38 | 36 | 34 |
| Swimming without time, m | 50 | 25 | 12 | 25 | 20 | 12 |
Physical education standards for 6th grade
| Exercises, 6th grade | Boys | Girls | ||||
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | |
| Shuttle run 4×9 m, sec | 10,0 | 10,5 | 11,5 | 10,3 | 10,7 | 11,5 |
| Run 30 m, s | 5,5 | 5,8 | 6,2 | 5,8 | 6,1 | 6,5 |
| Run 60 m, s | 9,8 | 10,2 | 11,1 | 10,0 | 10,7 | 11,3 |
| Run 500 meters, min | 2,22 | 2,55 | 3,20 | |||
| Run 1,000 meters, min | 4,20 | 4,45 | 5,15 | |||
| Running 2,000 meters | no time | |||||
| Cross-country skiing 2 km, min | 13,30 | 14,00 | 14,30 | 14,00 | 14,30 | 15,00 |
| Cross-country skiing 3 km, min | 19,00 | 20,00 | 22,00 | |||
| Standing long jump, cm | 175 | 165 | 145 | 165 | 155 | 140 |
| Pull-up on the bar | 8 | 6 | 4 | |||
| Lying push-ups | 20 | 15 | 10 | 15 | 10 | 5 |
| Bend forward from a sitting position | 10 | 6 | 3 | 14 | 11 | 8 |
| Raising the body in 1 minute from a lying position (press), times | 40 | 35 | 25 | 35 | 30 | 20 |
| Jumping rope in 20 seconds | 46 | 44 | 42 | 48 | 46 | 44 |
Physical education standards for 7th grade
| Exercises, 7th grade | Boys | Girls | ||||
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | |
| Shuttle run 4×9 m, sec | 9,8 | 10,3 | 10,8 | 10,1 | 10,5 | 11,3 |
| Run 30 m, s | 5,0 | 5,3 | 5,6 | 5,3 | 5,6 | 6,0 |
| Run 60 m, s | 9,4 | 10,0 | 10,8 | 9,8 | 10,4 | 11,2 |
| Run 500 meters, min | 2,15 | 2,25 | 2,40 | |||
| Run 1,000 meters, min | 4,10 | 4,30 | 5,00 | |||
| Run 2,000 meters, min | 9,30 | 10,15 | 11,15 | 11,00 | 12,40 | 13,50 |
| Cross-country skiing 2 km, min | 12,30 | 13,30 | 14,00 | 13,30 | 14,00 | 15,00 |
| Cross-country skiing 3 km, min | 18,00 | 19,00 | 20,00 | 20,00 | 25,00 | 28,00 |
| Standing long jump, cm | 180 | 170 | 150 | 170 | 160 | 145 |
| Pull-up on the bar | 9 | 7 | 5 | |||
| Lying push-ups | 23 | 18 | 13 | 18 | 12 | 8 |
| Bend forward from a sitting position | 11 | 7 | 4 | 16 | 13 | 9 |
| Raising the body in 1 minute from a lying position (press), times | 45 | 40 | 35 | 38 | 33 | 25 |
| Jumping rope in 20 seconds | 46 | 44 | 42 | 52 | 50 | 48 |
Physical education standards for 8th grade
| Exercises, 8th grade | Boys | Girls | ||||
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | |
| Shuttle run 4×9 m, sec | 9,6 | 10,1 | 10,6 | 10,0 | 10,4 | 11,2 |
| Run 30 m, s | 4,8 | 5,1 | 5,4 | 5,1 | 5,6 | 6,0 |
| Run 60 m, s | 9,0 | 9,7 | 10,5 | 9,7 | 10,4 | 10,8 |
| Run 1,000 meters, min | 3,50 | 4,20 | 4,50 | 4,20 | 4,50 | 5,15 |
| Run 2,000 meters, min | 9,00 | 9,45 | 10,30 | 10,50 | 12,30 | 13,20 |
| Cross-country skiing 3 km, min | 16,00 | 17,00 | 18,00 | 19,30 | 20,30 | 22,30 |
| Cross-country skiing 5 km, min | without time | |||||
| Standing long jump, cm | 190 | 180 | 165 | 175 | 165 | 156 |
| Pull-up on the bar | 10 | 8 | 5 | |||
| Lying push-ups | 25 | 20 | 15 | 19 | 13 | 9 |
| Bend forward from a sitting position | 12 | 8 | 5 | 18 | 15 | 10 |
| Raising the body in 1 minute from a lying position (press), times | 48 | 43 | 38 | 38 | 33 | 25 |
| Jumping rope in 25 seconds | 56 | 54 | 52 | 62 | 60 | 58 |
Standards for physical education for 9th grade
| Exercises, 9th grade | Boys | Girls | ||||
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | |
| Shuttle run 4×9 m, sec | 9,4 | 9,9 | 10,4 | 9,8 | 10,2 | 11,0 |
| Run 30 m, s | 4,6 | 4,9 | 5,3 | 5,0 | 5,5 | 5,9 |
| Run 60 m, s | 8,5 | 9,2 | 10,0 | 9,4 | 10,0 | 10,5 |
| Run 2,000 meters, min | 8,20 | 9,20 | 9,45 | 10,00 | 11,20 | 12,05 |
| Cross-country skiing 1 km, min | 4,30 | 4,50 | 5,20 | 5,45 | 6,15 | 7,00 |
| Cross-country skiing 2 km, min | 10,20 | 10,40 | 11,10 | 12,00 | 12,45 | 13,30 |
| Cross-country skiing 3 km, min | 15,30 | 16,00 | 17,00 | 19,00 | 20,00 | 21,30 |
| Cross-country skiing 5 km, min | without time | |||||
| Standing long jump, cm | 210 | 200 | 180 | 180 | 170 | 155 |
| Pull-up on the bar | 11 | 9 | 6 | |||
| Lying push-ups | 32 | 27 | 22 | 20 | 15 | 10 |
| Bend forward from a sitting position | 13 | 11 | 6 | 20 | 15 | 13 |
| Raising the body in 1 minute from a lying position (press), times | 50 | 45 | 35 | 40 | 35 | 26 |
| Jumping rope in 25 seconds | 58 | 56 | 54 | 66 | 64 | 62 |
Physical education standards for grade 10
| Exercises, 10th grade | Boys | Girls | ||||
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | |
| Shuttle run 4×9 m, sec | 9,3 | 9,7 | 10,2 | 9,7 | 10,1 | 10,8 |
| Run 30 m, s | 4,7 | 5,2 | 5,7 | 5,4 | 5,8 | 6,2 |
| Run 100 m, s | 14,4 | 14,8 | 15,5 | 16,5 | 17,2 | 18,2 |
| Run 2 km, min | 10,20 | 11,15 | 12,10 | |||
| Running 3 km meters, min | 12,40 | 13,30 | 14,30 | |||
| Cross-country skiing 1 km, min | 4,40 | 5,00 | 5,30 | 6,00 | 6,30 | 7,10 |
| Cross-country skiing 2 km, min | 10,30 | 10,50 | 11,20 | 12,15 | 13,00 | 13,40 |
| Cross-country skiing 3 km, min | 14,40 | 15,10 | 16,00 | 18,30 | 19,30 | 21,00 |
| Cross-country skiing 5 km, min | 26,00 | 27,00 | 29,00 | without time | ||
| Standing long jump, cm | 220 | 210 | 190 | 185 | 170 | 160 |
| Pull-up on the bar | 12 | 10 | 7 | |||
| Lifting upside down on a high bar | 3 | 2 | 1 | |||
| Lying push-ups | 32 | 27 | 22 | 20 | 15 | 10 |
| Bending and extension of the arms in support on the uneven bars, once | 10 | 7 | 4 | |||
| Rope climbing without legs, m | 5 | 4 | 3 | |||
| Bend forward from a sitting position | 14 | 12 | 7 | 22 | 18 | 13 |
| Raising the body in 1 minute from a lying position (press), times | 50 | 40 | 35 | 40 | 35 | 30 |
| Jumping rope in 25 seconds | 65 | 60 | 50 | 75 | 70 | 60 |
Standards for physical education for 11th grade
| Exercises, 11th grade | Boys | Girls | ||||
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | |
| Shuttle run 4×9 m, sec | 9,2 | 9,6 | 10,1 | 9,8 | 10,2 | 11,0 |
| Run 30 m, s | 4,4 | 4,7 | 5,1 | 5,0 | 5,3 | 5,7 |
| Run 100 m, s | 13,8 | 14,2 | 15,0 | 16,2 | 17,0 | 18,0 |
| Run 2 km, min | 10,00 | 11,10 | 12,20 | |||
| Running 3 km meters, min | 12,20 | 13,00 | 14,00 | |||
| Cross-country skiing 1 km, min | 4,30 | 4,50 | 5,20 | 5,45 | 6,15 | 7,00 |
| Cross-country skiing 2 km, min | 10,20 | 10,40 | 11,10 | 12,00 | 12,45 | 13,30 |
| Cross-country skiing 3 km, min | 14,30 | 15,00 | 15,50 | 18,00 | 19,00 | 20,00 |
| Cross-country skiing 5 km, min | 25,00 | 26,00 | 28,00 | without time | ||
| Cross-country skiing 10 km, min | without time | |||||
| Standing long jump, cm | 230 | 220 | 200 | 185 | 170 | 155 |
| Pull-up on the bar | 14 | 11 | 8 | |||
| Lifting upside down on a high bar | 4 | 3 | 2 | |||
| Lying push-ups | 32 | 27 | 22 | 20 | 15 | 10 |
| Bend forward from a sitting position, cm | 15 | 13 | 8 | 24 | 20 | 13 |
| Bending and extension of the arms in support on the uneven bars, once | 12 | 10 | 7 | |||
| Bend forward from a sitting position | 14 | 12 | 7 | 22 | 18 | 13 |
| Raising the body in 1 minute from a lying position (press), times | 50 | 45 | 40 | 42 | 36 | 30 |
| Jumping rope in 30 seconds | 70 | 65 | 55 | 80 | 75 | 65 |
| Jumping rope in 60 seconds | 130 | 125 | 120 | 133 | 110 | 70 |
Many parents believe that physical education teachers at school are people who have nothing to do with sports or sports education. It is immediately important to note that this statement is fundamentally not true. First of all, it is necessary to realize that these days, without being a professional athlete in the past or a person with a sports education, it is almost impossible to get a job at a school as a physical education teacher. This fact indicates that all those children who will engage in physical education at school under the supervision of a specialist practitioner or theorist (depending on the type of previous activity of the teacher) will at least be able to achieve good results in certain sports disciplines, if they want to. .
It is very important that people who attend physical education classes develop motivational qualities in themselves. If we compare in everyday life people who paid attention to sports and those who never wore a tracksuit, then the difference in life motivation is visible to the naked eye. People involved in physical education, and therefore the majority of those who attend physical education classes at school, are much more successful, since even during their school years, in physical education lessons, they develop such qualities as determination and overcoming oneself.
According to statistics, those who do not attend physical education classes on a regular basis get sick twice as often during flu epidemics as those who regularly attend physical education classes. As a result, those who get sick more often have a large number of problems with academic performance, due to the fact that they attend fewer classes at school. It would seem that skipping classes at school and not wanting to attend physical education classes are in no way connected at first glance. However, if you trace the cause-and-effect relationship described above, it becomes clear why it is so important to go to physical education classes and not look for excuses for yourself to once again sit on the bench while your classmates are taking tests or just playing sport games.
If all of the above arguments are not convincing enough, then a small experiment should be conducted. The student needs to compare his well-being over two months. Let him not go to sports at school for one month and sit on the bench. In another month, you must attend all physical education lessons and follow all the teacher’s instructions. Each day of these two days it is necessary to leave an entry in a special diary, in which the student will leave his impressions of his well-being and general condition of the body. After two months, re-read the diary and compare your entries. Surely the conclusions will be amazing for many, but what they will be can be found out by conducting this experiment.
Of course, it is quite difficult to call modern school physical education perfect. And there are many reasons for this. But if you approach this lesson more carefully, consider what the teachers offer, and do not try to evade and hide somewhere in the alley, then in the future you will be able to express huge gratitude to the teachers for this.
Now let’s move away from loud phrases and try to figure out what the real benefits of being in the gym or on the sports ground are. First of all, it's a matter of physiology. A growing young body requires mobility in order to be able to circulate blood throughout the body. This is why children tear down ceilings in hallways or classrooms during recess. And the more you try to keep them under strict discipline, the louder they will scream at recess.
Physical education classes are designed to balance this imbalance. A properly constructed physical warm-up allows you to disperse excess energy throughout the body. In this case, there is no overwork, as well as the danger of getting a sprain or other kind of injury. Moreover, thanks to active physical exercises, the body is morally recharged, when the brain temporarily switches off complex mathematical calculations or thoughts about a literary plot, giving a person the opportunity to refresh his thoughts. In the future, this helps you cope with complex tasks that were left for last.
Among other things, physical education sometimes allows a person to reveal hidden talents that in another environment he would simply be embarrassed to reveal. After all, here, in essence, everyone is equal and everyone is in equal conditions, when few people will joke about your successes. But an experienced teacher will be able to assess the possible potential and develop it in the future. This is exactly how future football players, volleyball players, basketball players, and track and field athletes manifest themselves. After visiting the gym, many people want to develop independently, improve their body and improve their health. And this is precisely what is valuable in school physical education, as a source of limitless opportunities in the future.
Benefits of push-ups for men
· Improves the functioning of the heart and cardiovascular system. Good blood circulation helps improve the overall tone of the body
· Muscle mass develops well and increases. The muscles of the shoulders, chest and triceps become more prominent
Increases strength and endurance of the body
· Metabolism improves. The fat layer is reduced
· Strengthens the hands and joints of the arms
· The body is charged with energy and vigor
· Each time increasing the load, a man trains his endurance
Strengthens the back muscles and the muscles around the shoulder joint
· Positively affects potency, because blood circulation is accelerated
Push Up Plan
Any workout, no matter what type it is, must begin with a warm-up. Therefore, before moving on to push-ups, do a little preparation; any cardio exercise will do. Three to five minutes will be enough, you just need to finish them with circular rotations of the arms (or the “Mill” exercise), as well as jerks of bent arms in front of the chest.
After which you can proceed directly to push-ups. Take a lying position, place your hands slightly wider than your shoulders, palms facing forward, feet on your toes, back straight.
Slowly and without jerking, do as many full push-ups as you can. There is no need to lie to yourself, simplifying the execution process and trying to do more repetitions at any cost.
This means that you cannot bend your lower back, lower your hips and stomach, “bump” your chest off the floor, etc.
If you manage to do 10 “clean” push-ups, great. This means your level is 14-20 push-ups for 3-4 sets.
If you didn’t get 10, it doesn’t matter, reduce the initial number of push-ups using the table below, and slowly increase the frequency and duration.
You need to exercise 3 days a week, with a maximum rest of 90 seconds between sets (preferably no more than 60).
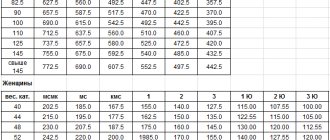
Protocol for passing standards to the TRP
Before passing the TRP, applications for participation are filled out. They are collective, but separate for boys and girls. The final protocols are divided into categories according to the type of test. Students fill out the application themselves, and the summary and final protocols are filled out by the teacher taking the exam.
The first sheets are a table that lists students, standards and their results. Below is a summary indicating the number of individuals eligible to receive the badge.
Correct technique: this is important
To do push-ups well, you need to know how to do push-ups properly. If your technique suffers, then you can not only complicate your life, but also get injured. Because of this, you won’t be able to do push-ups at all.
Besides, if you brag that you can easily do 50 push-ups on the floor and they ask you to demonstrate, it will be extremely awkward when you show off your push-ups on the floor of the bump. At best, they will laugh at you and your triumph will be a failure.
Firstly, push-ups should be full, and not so that you approach the floor a couple of millimeters and immediately return to the starting position. And your buttocks point to the heavens, eager for adventure.
Secondly, the correct and safe technique should be like this :
- palms are located under the shoulders, not in front of them;
- the body is straight, we don’t raise the pelvis, we don’t bend the lower back, we don’t lift the head up;
- we move our elbows slightly back diagonally;
- we lower ourselves to approximately a right angle at the elbow, but lower is possible.
These are the kind of push-ups you can be proud of, and not the convulsions that I so often see.
Fourth stage: 13–15 years
As teenagers go through puberty, higher demands are placed on them. The fourth stage of the GTO is designed for senior high school students.
Unlike the first three steps, the fourth significantly increases the complexity of the program. The exercises remain the same, but the load increases and the allotted time is reduced. The standards for speed, endurance and power load are becoming significantly more complicated. From this moment on, you must take 4 exercises, and nine more are available to choose from. To receive a silver and gold badge, you need to pass 1 more test: 8 and 9, respectively.