Running is one of the easiest and most effective ways to improve your physical fitness. By strengthening and developing your leg muscles, you can not only avoid injuries, but also significantly improve your athletic performance.
If you want to have truly strong legs, thanks to which you can easily carry almost any load, then running training alone will not be enough. Running, despite all its health benefits, is an injury-prone sport, and many runners, regardless of age and level of training, have at one time or another encountered various injuries and injuries.
One of the main benefits of strength training is strengthening the leg muscles that are directly involved during running, which in turn significantly reduces the risk of running injuries.
In addition, well-developed muscles are slower to fatigue and make your running technique more efficient and economical. This means you will need less oxygen to maintain your target pace. Also, doing strength training involves increasing your muscles' ability to produce force.
A scientific review1 of 26 studies published in 2014 in The Journal of Sports Medicine found that strength training improved performance in competitive endurance athletes. Additionally, there are a number of studies that show that this type of training can lead to increased endurance and improved running economy2,3,4.
What muscles are involved during running?
In order to get the most out of your leg workout, you first need to understand which muscles are used when running and how they interact with each other.
Unlike walking, during running there is no double support phase (when both legs touch the ground at the same time), and both legs lift off the surface (flight phase). The faster you run, the longer the flight phase lasts and the shorter the period of contact with the ground.
During initial contact with the surface, the main load is taken by the quadriceps femoris muscle or quadriceps (and especially one of its bundles, the rectus femoris muscle). In addition, the strong contraction of the femoral heads of the quadriceps prevents flexion of the hip at the knee joint during landing. At the same time, the muscles of the lower leg - the soleus and gastrocnemius - also help absorb shock.
To ensure the lifting of the supporting leg, the posterior group of thigh muscles, hip flexors, quadriceps, gastrocnemius and soleus muscles are included in the work, the last two act as a kind of springs.
At the beginning of the flight period, the hip flexor muscles contract: the rectus femoris, sartorius and tensor fasciae lata. When moving the leg forward, the iliopsoas muscle plays an important role.
The hip extensor muscles, primarily the gluteus maximus, are important for runners. At the moment of the push, as well as during the back step of the free leg, this muscle is in a contracted state, while on the other leg it is stretched. The gluteal muscles also stabilize the pelvis and help keep the body upright.
Pumping up the calf muscles is one of the hottest issues in bodybuilding. Someone is genetically gifted and does not think about this issue at all. And someone kills himself to increase at least a couple of millimeters of volume. And a huge number of different methods only confirms that the problem exists. Today I want to talk about one approach that is not often considered. But in some cases it works very well. And my personal experience confirms this. It all started with the fact that, realizing my involvement in the “Complete absence of shin” group, I sifted through a bunch of information, trying different techniques on myself. There was definitely some result. But it’s not at all remarkable enough to talk about a system that actually works for me. This continued until I incorporated plyometrics into my workouts several times a week. Heavy jumping exercises killed not only my hips, but also my lower legs... After a month, without any measurements, I saw dramatic changes! Growth has begun. But then the training changed, plyometrics went away. Therefore, the result practically froze, despite the strength exercises that I systematically performed several times a week. But then running came into my life... Anatomy To get this discussion on track, let's take a look at the structure of the lower leg. The lower leg consists of two muscles. And for maximum results, naturally, you need to achieve hypertrophy of both. The calf muscles bend the knees, elevate the legs, and stabilize the body. They consist of both fast and slow twitch fibers. The ratio is approximately 50/50. But it is often the slow twitch fibers that predominate. The soleus muscle lies under the gastrocnemius muscle. This is what creates the width of the shin! And precisely because of its insufficient stimulation, athletes often do not see results. The fact is that the peculiarity of the soleus muscle is such that when rising on the toes in a standing position, it does not contract completely. That is, if the calves help us maintain an upright position and are active throughout the day, then the soleus muscle works little. Therefore, most people have more developed calves. Another factor is that the soleus muscle is 90% slow twitch fibers. And ordinary strength training will not work here. As you can see, thanks to many natural factors, the gastrocnemius muscle grows noticeably faster than the soleus muscle. Therefore, it is worth paying attention to overcoming these features. Running and calf muscles Running helps build beautiful calves. During it, the soleus and tibialis anterior muscles develop. This is exactly what I saw when I first took up plyometrics and then running. The slow twitch fibers of the soleus muscle are ideal for long distance running, monotonous work and static work. Also, the correct running technique involves this muscle as much as possible. If you want to build beautiful calves through running, you need to stimulate hypertrophy. Given your knowledge of anatomy, it makes perfect sense to combine explosive interval training (sprints, jumping, interval running) with periods of regular long-distance jogging. Thus, we will include both slow-twitch fibers and fast-twitch fibers in the work. It is definitely better to run outside, as it involves ups and downs (even minor ones) and different running speeds. But even on the track you can change both the speed and the angle of inclination. Running technique And be sure to say a few words about running technique. Because it is this that will influence both the result and prevent injury. The most important issue is placing your feet on the ground. Some people place their foot on the heel and then roll onto the toe. This technique requires less work of the lower leg and thigh muscles. Therefore, it seems easier and more natural. As you can see, despite the seemingly non-strength sport, it is the correct running technique that requires great strength in the legs, so that the movements are as light and economical as possible, the necessary muscles are included in the work and alternately rest in the flight phase (from push to landing). And this is an art that also requires considerable training. With this technique, there is a high risk of getting at least unpleasant sensations, and at most seriously injured. Professional runners, as a rule, use a toe-toe stance when running, or, to be more precise, a forefoot stance. With this technique, it is the calves and soleus muscles, thighs and buttocks that primarily work. And this is exactly what is needed there. Recovery should also be part of the training program. Remember that muscles need rest to grow. Therefore, periods of work must be properly combined with periods of recovery. And of course, don’t forget about nutrition. Since additional cardio training will boost metabolism, and to build muscles we need both energy and building material. Results If your muscles don't grow, you need to shock them and try something new. Therefore, if it does not conflict with your nutrition and training plan, as well as your health, I strongly advise you to start running and jumping. You cannot build up a beautiful and massive lower leg with strength exercises alone, unless you are naturally gifted. Therefore, try to supplement your workouts in the gym by systematically performing exercises that are not typical for bodybuilding. Sprints, jumping, and running can be the best helpers in working on the capricious lower leg muscles.
The article was published in the magazine “Iron World” No. 07/2015
Author - Daria Karelina
Squats
This basic exercise is aimed at developing and strengthening the thigh, gluteal and calf muscles.
Starting position: feet shoulder-width apart, back straight, arms bent at the elbows and located along the body, toes slightly turned out.
How to do it: Smoothly move your pelvis back and bend your knees until your thighs are parallel to the floor or slightly lower, and your arms simultaneously rise up to approximately chest level.
Tips: When bending, try to ensure that your knees do not go beyond the level of your feet and avoid lowering deeply, this increases the load on the knee joints.
Running and amateur bodybuilding
Strength training, aimed solely at maintaining good physical shape, and not for the purpose of performing at various bodybuilding competitions, must be supplemented with cardio. Many owners of impressive weight, pumped up and sculpted muscles visit the gym solely for one single purpose - to look good with a beautiful body. When pumping up muscles only at an amateur level, and not at a professional level, you should definitely run to be more resilient and fit, since cardio helps you lose excess subcutaneous fat.
Running while gaining muscle mass
Igor October 20, 2017
Squat Jumps
This exercise primarily develops the quadriceps, hip adductors, gluteal and calf muscles.
Starting position: feet shoulder-width apart, back straight, arms bent at the elbows and located along the body, toes slightly turned out
How to do it: Smoothly move your pelvis back and bend your knees until your thighs are parallel to the floor or slightly lower, then push off with your toes and jump up, while your elbows go back, giving momentum to the jump. When you land, lower yourself back into a squat and repeat the movement.
Tips: Try to avoid landing on your straight legs and heels.
Stepping onto a platform with a hip lift
In this exercise, the main load falls on the quadriceps, hamstrings and gluteal muscles of the thigh.
Starting position: Select a platform (bench, drawer or cabinet) and place your left foot on it fully. It is advisable to choose a height so that the thigh is parallel to the floor when walking (the angle at the knee is 90 degrees). The arms are bent at the elbows and brought together in front of you at chest level.
How to do it: Leaning on your left leg, begin the ascent by straightening your supporting leg at the knee. When your leg is fully straightened, continue the movement with your right leg, bringing your thigh in front of you until it is parallel to the floor. Hold this position for 1-2 seconds, and, bending your left leg at the knee, smoothly place your right leg back on the floor.
Hand movement. During the lifting phase, extend your arms so that at the top point they are straight and positioned at your sides, while lowering, return them to their original position.
Adviсe:
- To better load your muscles, perform exercises on one leg first, then the other, rather than alternately.
- Try to keep your back straight.
Training programs
A standard sprint training program looks like this:
| Distance in meters | Approaches | Rest after approach in minutes | Rest after the distance in minutes |
| 5 minutes at an easy pace | 1 | — | 2 |
| 100 | 5 | 1,5 | 3 |
| 200 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| 400 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| 100 | 3 | 1,5 | 1,5 |
| 10 minutes at an easy pace | 1 | — | — |
But we are starting gradually. Sprinting for muscle growth in a step-by-step mode may look like this:
Program No. 1
| Distance in meters | Approaches | Rest after approach in minutes | Rest after the distance in minutes |
| 5 minutes at an easy pace | 1 | — | 2 |
| 100 | 3 | 1,5 | — |
Program No. 2
| Distance in meters | Approaches | Rest after approach in minutes | Rest after the distance in minutes |
| 5 minutes at an easy pace | 1 | — | 2 |
| 100 | 5 | 1,5 | — |
Program No. 3
| Distance in meters | Approaches | Rest after approach in minutes | Rest after the distance in minutes |
| 5 minutes at an easy pace | 1 | — | 2 |
| 100 | 5 | 1,5 | 3 |
| 200 | 2 | 2 | — |
Program No. 4
| Distance in meters | Approaches | Rest after approach in minutes | Rest after the distance in minutes |
| 5 minutes at an easy pace | 1 | — | 2 |
| 100 | 5 | 1,5 | 3 |
| 200 | 3 | 2 | — |
Program No. 5
| Distance in meters | Approaches | Rest after approach in minutes | Rest after the distance in minutes |
| 5 minutes at an easy pace | 1 | — | 2 |
| 100 | 5 | 1,5 | 3 |
| 200 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| 400 | 1 | — | — |
Workout #6
| Distance in meters | Approaches | Rest after approach in minutes | Rest after the distance in minutes |
| 5 minutes at an easy pace | 1 | — | 2 |
| 100 | 5 | 1,5 | 3 |
| 200 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| 400 | 2 | 3 | — |
Workout #7
| Distance in meters | Approaches | Rest after approach in minutes | Rest after the distance in minutes |
| 5 minutes at an easy pace | 1 | — | 2 |
| 100 | 5 | 1,5 | 3 |
| 200 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| 400 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| 100 | 1 | — | — |
Workout #8
| Distance in meters | Approaches | Rest after approach in minutes | Rest after the distance in minutes |
| 5 minutes at an easy pace | 1 | — | 2 |
| 100 | 5 | 1,5 | 3 |
| 200 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| 400 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| 100 | 2 | 1,5 | — |
Program No. 9
| Distance in meters | Approaches | Rest after approach in minutes | Rest after the distance in minutes |
| 5 minutes at an easy pace | 1 | — | 2 |
| 100 | 5 | 1,5 | 3 |
| 200 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| 400 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| 100 | 3 | 1,5 | 1,5 |
Program No. 10
| Distance in meters | Approaches | Rest after approach in minutes | Rest after the distance in minutes |
| 5 minutes at an easy pace | 1 | — | 2 |
| 100 | 5 | 1,5 | 3 |
| 200 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| 400 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| 100 | 3 | 1,5 | 1,5 |
| 10 minutes at an easy pace | 1 | — | — |
We are arriving at this program gradually. Only with smooth progress will sprinting allow you to gain muscle mass.
Have you used sprinting to grow muscles? Share your experience in the comments!
Share link:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click here to share content on Facebook. (Opens in a new window)
Explosive Platform Steps with Hip Raise
This exercise develops explosive strength and power in the leg muscles.
Starting position: Select a platform (bench, drawer or cabinet) and place your left foot on it fully. It is advisable to choose a height so that the thigh is parallel to the floor when walking (the angle at the knee is 90 degrees). The arms are bent at the elbows and brought together in front of you at chest level.
How to do it: To give inertia to the body, lightly push off the floor with your right foot and perform a sharp rise, straightening your supporting leg at the knee. When your left leg is fully extended, take a small jump up and continue the movement with your right leg, bringing your thigh in front of you until it is parallel to the floor. Then, bending your left leg at the knee, smoothly lower your right leg back to the floor and repeat the movement.
Adviсe:
- Make sure the platform remains stable even when jumping. To better load your muscles, perform exercises on one leg first, then the other, rather than alternately
- Try to keep your back straight.
The effect of cardio on muscle gain
Scientific studies have proven the positive effect of running on muscle growth. Aerobic exercise stimulates protein production and increases testosterone, the main anabolic hormone. Cardio does not interfere, but, on the contrary, promotes muscle growth.
Running during the period of mass gain is useful because cardio:
- trains the heart muscle and has a positive effect on the cardiovascular system;
- improves endurance and helps diversify your training program;
- stimulates the burning of subcutaneous fat and makes the muscle relief more pronounced;
- accelerates metabolic processes, which leads to increased appetite, and, therefore, allows you to gain weight faster.
Aerobic exercise provides many benefits during weight gain. But, of course, only when certain rules are followed.
Split squats
The exercise involves the quadriceps, hamstrings, and gluteal muscles.
Starting position: Stand straight, take a wide step back, and place the toe of your abducted foot on the platform (box, bench or cabinet).
How to do it: Keeping your back straight, bend your supporting leg at the knee until your thigh is parallel to the floor, the knee of the abducted leg goes down, then smoothly straighten your leg and repeat the movement.
Adviсe:
- make sure that the knee of the supporting leg does not go beyond the level of the foot
- To increase the load on your muscles, you can hold a dumbbell in each hand.
What muscles work during different types of jogging?
1. Running up the stairs.
This running technique for beginners is considered the most difficult because it involves serious stress on the buttocks, legs and abdominal muscles. During the ascent, the lungs and heart muscles actively work.
2. Short distances.
Running at a distance of 30 to 400 meters – all muscle groups work, the process of fat burning increases to the maximum.
3. Interval running.
Optimal technique for middle distance running. Involves alternating a slow pace (fast walking) and maximum acceleration. This technique is aimed at training endurance and allows you to increase strength indicators. If you plan to try your hand at long-distance running in the future, start with interval training and remember that breathing technique is important - inhale through your nose, exhale through your mouth every two steps.
It is important! This technique is suitable for people with good physical fitness. If you are an inexperienced athlete and want to avoid injury, the beginner jogging technique is best for you. With proper training and a certain amount of endurance, proper running at intervals will allow you to effectively and quickly lose excess weight.
3. Treadmill.
When running on a treadmill, the same muscle groups are used that work during outdoor exercise. Features of training on the simulator:
- the load on the joints is reduced;
- You can fully concentrate on running, as you don’t need to think about the unevenness of the road.
Explosive Split Squats
This exercise develops explosive strength and power in the leg muscles.
Starting position: Stand straight and take a wide step back, the toe of your abducted leg is on the platform, your arms are bent at the elbows at chest level and placed in front of you.
How to do it: Keeping your back straight, bend your supporting leg at the knee until your thigh is parallel to the floor, while the knee of the abducted leg goes down. At the bottom, push off slightly from the floor, make a small jump up and land smoothly on your full foot. The arms go back during the jump, giving the body inertia.
Tips: the supporting leg does not fully straighten at the top point, this reduces the load on the knee joint.
Squatting on a stand on one leg
This exercise primarily targets the quadriceps and hamstrings.
Starting position: Select a platform (bench, box or cabinet) of the required height and stand with your back to it, arms bent at the elbows and brought together in front of you at chest level, your right leg raised in front of you by 15-30 cm.
How to do it: Maintaining balance, move your pelvis back and smoothly lower yourself onto the stand, without the raised leg touching the floor. Pause for 1-2 seconds, then, tensing your thigh muscles and extending your supporting leg, lift up.
Tips: Try to keep your raised leg stationary.
How your body builds muscle
Gaining muscle mass occurs when muscle protein synthesis (MPS) exceeds muscle protein breakdown (MPB) ().
Protein is an important component of muscle that can be added or removed depending on factors such as diet and exercise ().
If we think of proteins as individual bricks, SMB is the process of adding bricks to the wall, and RMB is the process of removing them. If you lay more bricks than you remove, the wall gets bigger - but if you remove more bricks than you put in, the wall gets smaller.
In other words, to build muscle, your body must produce more protein than it removes.
Exercise—basically lifting weights—is a strong stimulus for SMB. Although exercise also causes MPS, the increase in MPS is greater, resulting in increased muscle mass (, ).
Conclusion:
Your muscles grow when your body synthesizes more protein than it breaks down. Physical exercise helps this process.
One leg squat
This exercise develops coordination and dexterity, the main load falls on the quadriceps, hamstrings and adductor muscles of the thigh, the gluteal muscles are used to a lesser extent.
Starting position: Back straight, arms bent at the elbows and brought together in front of you at chest level, right leg raised in front of you by 20-30 cm.
How to do it: While maintaining balance, smoothly move your pelvis back and perform a squat. Lower yourself down until your thigh is parallel to the floor or slightly lower. Then, tensing your thigh muscles and extending your supporting leg, lift up.
Adviсe:
- Try to keep your back as straight as possible
- if you have problems with your knees, then it is better to avoid this exercise
Lunges forward
This exercise uses almost all the thigh muscles and gluteal muscles.
Starting position: feet shoulder-width apart, back straight, arms at your sides.
How to do it: take a wide step forward with your left leg so that the thigh of your left leg is parallel to the floor, while the knee of your right leg should barely touch the floor. Tightening your gluteal and hamstring muscles, take a step back and return to the starting position.
Adviсe:
- Try to maintain a straight body position and make sure that the knee does not go beyond the level of the toe
- To make the exercise more difficult, you can hold dumbbells in both hands.
Running: how to strengthen the muscles of the feet and legs?
Why is it important to strengthen your feet and leg muscles with special exercises if you are a runner, and how exactly to do this, says Nike running club coach Olga Smirnova. And Yulia shows. To run correctly and, most importantly, without harm to the body, it is very important not only to stretch and strengthen the muscles of the whole body, but also to deliberately work on the muscles of the feet and legs.
“The foot is very important in running,” says coach Olga Smirnova. “Thanks to her, you can make good progress in the training process. But often in runners the foot is “off” and its functions are taken over by the calf muscles. Plus, if the foot has a dropped arch, this leads to overstretching of the Achilles tendon, gastrocnemius and soleus muscles - and special exercises also help to cope with this. It is important to strengthen the muscles of all legs separately - lunges and steps from this complex help with this.”
A set of exercises to strengthen the foot
How to do it: start the exercises with 20 repetitions and gradually increase to 40.
Why do it: In running, the foot and push-off force play a very important role. Even after pumping up the largest muscles (hamstrings, quadriceps, glutes), you will not be able to achieve noticeable results if you have weak feet.
You can pump up your foot with these easy jumping exercises. It is better to do them where there is shock absorption - a rubberized stadium track, a forest or a park.
Jumping on the curb with both feet
It is important not to land on your heels and be constantly on your toes - both on the asphalt and on the curb. We have more than 100 muscles, ligaments and tendons on our feet, so it is important to work, pump and energize each of them. When performing this exercise, try to push off the surface as quickly as possible (this is very important when running).
Alternately running onto the curb at speed
We jump onto the curb with one foot, stand on the other, then also jump back one by one. A very useful exercise for balance and coordination. When performing it, it is important not to lower your heel onto the surface, thereby we once again work out and pump up the calf muscles.
Jumping onto a curb on one leg
This exercise is much harder than the previous ones, but even a small number of approaches will increase the push-off force and the strength of the calf and soleus muscles.
Jumping over the line
On one leg:
With this exercise, we engage even more of the small muscles of the foot that work when jumping to the side. The most important rule when performing this: you need to try to jump as high as possible without bending your leg, almost on a straight leg.
On two legs:
And back on each leg:
Lunges
Classic lunge
We make sure that the knee does not go further than the toe, the back is straight, and the arms work together with the legs.
Backward Lunges
Similar to classic lunges. When performing the exercise, we lunge back, transfer the weight from the front leg to the back and do the next lunge. When we shift our weight, it is on one leg, which also strengthens the arch of the foot. Here the back surface of the legs and biceps of the thigh, gluteal muscles are worked out, and coordination and balance are improved.
Squat Lunges
When performing advanced lunges, it is important to ensure that your head is at the same level and only your legs move. It is necessary not to straighten the knee joint and not to rise on the toes. This exercise is done in order to maximally load the quadriceps and the front surface of the thigh. The exercise is performed at low amplitude and in a half squat.
Lunges with calf raises
Transition from one foot to another with the toe raised. The exercise helps to engage the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles and give them a load; uses a lot of muscles.
It is important to ensure that the knee does not extend beyond the toe, otherwise the patellar cruciate ligament may be damaged. Keep your torso upright - do not lean forward or lean your hands on your knee, so as not to increase the load on the hip and knee joint. It is better to keep your hands behind or on your belt.
Jumping with squats up on straight legs
The main rule: during a squat, the knees should not go beyond the toes, otherwise the knee cruciate ligaments can be damaged. It is important not to bring your knees inward: this is one of the main mistakes girls and women make when performing all squats and jumps.
You need to land not on your toes, but on the entire surface of your foot. This is an exercise with a focus on explosive strength, which involves not only the foot, but also the back of the legs, biceps and biceps femoris and buttocks. We make the final push with the front surface of the foot and the big toe, which is very important.
"Frog"
Usually the exercise is performed in a full squat, but this is quite traumatic for the cruciate ligament of the knee joint, so we offer a lightweight version.
It is important to squat so that the back of your thigh is parallel to the floor.
We perform the exercise without stopping and straightening, the knee should not go beyond the toe. It is important to land on your entire foot, not on your toes. In this way, we develop explosive power, which will improve our speed and average running pace.
Note Yuli: and we do all the jumps not on asphalt.
"At the bench"
Stepping onto a bench
The quadriceps is most involved during this exercise.
Make sure that your knee does not extend beyond your toes. We stretch the gluteal muscles, and then squeeze them - thanks to this, our muscles work as much as possible. We alternate legs to develop coordination and balance.
Getting up from a bench on one leg
This exercise is popular among track and field athletes, especially sprinters. During execution, the gluteal muscles are well worked out, the back of the thigh and all internal muscles are activated.
It is important to ensure that the knee does not go beyond the toe, and the heel of the foot, which is hanging in the air, does not touch the floor.
Stepping backwards with a lunge
This exercise is designed to maximally engage all muscles. When stepping onto a bench, the front surface of the thigh and gluteal muscles work. The back of the thigh is engaged. Hand position is like when running.
We change legs one after another, this helps improve coordination.
It is useful to do this complex once a week before one of your running workouts. And your feet and legs will be strong -)
And then Olya and I froze, and I went hungry -))
Photo: Dmitry Pospelov, pospeloff.com.
Jumping lunges
This exercise develops explosive strength and power in the leg muscles.
Starting position: feet shoulder-width apart, back straight, arms bent at the elbows and brought together in front of you at chest level.
How to do it: take a wide step forward with your left leg so that the thigh of your left leg is parallel to the floor, while the knee of your right leg should barely touch the floor. In the bottom position, push off with your feet on the floor, jump and switch legs. Repeat the movement on the other side. The arms go back during the jump, which gives the body inertia.
Adviсe:
- avoid landing on your heel
- try to maintain a straight back position
Side Lunges
This exercise primarily engages the gluteal muscles, quadriceps, and hip adductors.
Starting position: legs together, back straight, arms bent at the elbows and brought together in front of you at chest level.
How to do it: Take a wide step to the right side, shifting your weight to your right leg, and bend your knee until your thigh is parallel to the floor, keeping your left leg fully straight. Accelerate your leg, return to the starting position, and repeat the movement.
Tips: try to ensure that the knee of the supporting leg does not go beyond the level of the toe.
Lunges with 180 degree rotation
This exercise additionally engages the abdominal muscles and improves coordination.
Starting position: legs together, back straight, arms bent at the elbows and brought together in front of you at chest level.
How to do it: Turn your body 180 degrees and take a wide step forward with your left leg so that the thigh of your left leg is parallel to the floor, while your right knee should barely touch the floor. As you rotate your torso in the opposite direction, take a step back and return to the starting position, then repeat the same movement on the other side.
Tips: try to ensure that the knee of the supporting leg does not go beyond the level of the toe.
Bend the torso forward while standing
This exercise strengthens the back extensors, gluteal muscles and hamstrings.
Starting position: feet shoulder-width apart, back straight, arms bent at the elbows and brought together in front of you at chest level.
How to do it: Moving your pelvis back, tilt your torso until it is parallel to the floor, if necessary, slightly bend your knees, but be sure to keep your back straight. At the lowest point, the gaze is directed forward, the neck and spine form one line. When extending, tense the muscles of the lower back and back of the thigh.
Tips: do not round your back, try to maintain a natural arch in your lower back.
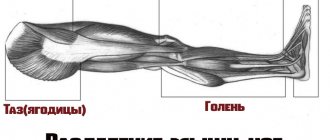
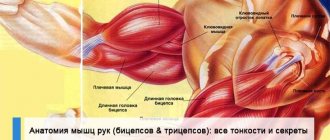
Muscles that work when running
Running allows you to work all muscle groups , although the main load is on your legs. The heart muscle, abdominal muscles and neck also work. So, the muscles working in this sport can be divided into several types :
- Leg muscles Quadriceps . Located on the front of the thigh above the knee joint, they are responsible for its movement when running. It is one of the largest muscles.
- Biceps muscles . Located on the back of the thigh, just below the buttocks. They work by bending the knee and raising the leg.
- Gluteal muscles . They are responsible for fixing the torso and also act when turning the hip. They are considered one of the strongest human muscles.
- Calf muscles . Active when running. Helps a person maintain balance.
- Posterior tibialis . Located under the calf muscle. Maintain balance and participate in rotation and flexion of the foot.
- Latissimus dorsi muscles . Occupies the lower back. They work by moving the arms back.
Bend your torso forward while standing on one leg
This exercise additionally engages the abdominal muscles and improves coordination.
Starting position: legs together, back straight, arms at your sides.
How to do it: While maintaining balance, bend forward while lifting your right leg up. At the lowest point, the torso and raised leg should be parallel to the floor, while the arms are straightened and lightly touch the floor. Tightening the muscles of your thighs and buttocks, lift your body, lower your leg back and return to the starting position.
Tips: If you lack flexibility, you can slightly bend your supporting leg at the knee.
Bonus in the form of the sea
Athletes who live close to the sea are in luck: you can use sprinting to grow muscles as part of your health system. In the summer we run directly along the shore, in other seasons we run near it. Sea air helps to significantly improve the functioning of all body systems. The sea protects against most diseases, improves skin condition, improves mood, and relieves psychological stress.
Running near the sea is perhaps the most useful thing that humanity has in its arsenal now. Plus, it's free. So if you are lucky enough to be among the lucky ones living near the sea, take advantage of this opportunity.
Jumping onto the platform
This exercise uses almost all the muscles in your legs and develops explosive power.
Starting position: select a platform (box, cabinet, bench) of the required height and stand in front of it. Feet shoulder-width apart, back straight, arms at your sides.
How to do it: Move your arms back slightly to give your body a little momentum, bend your knees and jump onto the platform. When landing, further lower your hips, this will allow you to better load the muscles, then carefully step off the platform and repeat the movement.
Tips: Try not to land with your legs straight or on your heel, this will reduce the impact on your knees.
Is it possible to pump up your legs by running?
With the help of running, you can pump up and strengthen your leg muscles, since they are well used in this sport. Using different techniques and gradually increasing the load, it is possible to lose a few extra pounds, while muscle mass will grow.
When running long distances , you will not be able to acquire too defined muscles, since the legs become more durable and more accurate than those that can often be seen in people who work out professionally in the gym.
Many people have probably heard that running often leads to a decrease in muscle mass . This happens due to the fact that after running a long distance, the body needs more energy and it finds it in the muscles, from where it takes it.
Therefore, in order not to lose muscle mass, many athletes train by sprinting . This is one of the specific techniques that involve running short distances, and also when using weights, there will be a noticeable increase in the legs, as a result of the transformation of fat into muscle.
So, if a person engages in this type of sport correctly, gradually increasing the load and without injuring his body, then he has the opportunity to quickly see the expected results . Running uses all the leg muscles and that is why it is one of the best ways to work them out, strengthen them and pump them up evenly.
Jumping onto a platform on one leg
This exercise is a more complex modification of the previous one and allows you to improve coordination and dexterity.
Starting position: select a platform (box, cabinet, bench) of the required height and stand in front of it. Raise your right leg 10-15 cm.
How to do it: move your arms back slightly to give your body a little momentum, bend your supporting leg at the knee and jump onto the platform. When landing, further lower your hip down, this will allow you to better load the muscles, then carefully step off the platform and repeat the movement.
Tips: Try not to land with your leg straight or on your heel, this will reduce the impact load on the knee joint.
Jumping with knees to chest
This exercise uses almost all the muscles of the legs, as well as the abdominal muscles, and develops explosive strength.
Starting position: feet shoulder-width apart, back straight, arms raised in front of you at shoulder level.
How to do it: with a sharp movement, jump up as high as possible, while trying to pull your knees as close to your chest as possible. During the jump, your arms are extended in front of you at shoulder level.
Advice:
- try to land with slightly bent legs, this will reduce the impact on your knees
- avoid landing on your heel