Let's start with the largest muscle group in humans - the muscles of the lower extremities. In this material I will try to briefly, but in sufficient detail, analyze all the questions regarding the structure and anatomy of the leg muscles. I will also give you the best exercises for their development.
No one argues that reading such topics is very tedious. It’s much more interesting to look at publications from the series “How to enlarge your butt” or “How to pump up your abs to a six-pack.” But it is impossible to grow big buttocks without pumping up your legs, without clearly understanding which muscle works in a particular movement.
So get ready to read carefully. At the end, a pleasant bonus awaits you - a selection of the best exercises for developing the muscles of the legs and buttocks.
Separation of leg muscles
The lower body has more than 30 muscles. But we are not interested in everyone. Since we are not trying to pass the medical examination. Our goal is to develop the core muscles that will help us achieve outstanding results in the gym. And also, give shape to the lower part of our body. Anatomically, we can divide the leg into 4 parts:
- Pelvis (buttocks)
. These muscles are not exactly part of our leg. But since they are attached to the femur, we take them into account too. And it’s very difficult not to engage your glutes when performing most leg exercises. This muscle group is located on the back side of the body. In the area between the lower back and thigh. Of greatest interest to us are: the gluteus maximus, the gluteus maximus and the gluteus minimus. - Hip. This is the part that almost all athletes want to develop. It is what gives our legs their shape. It starts from the pelvic bone (to which some muscles are attached) and ends at the knee. Its main functions include flexion and extension of the lower leg and thigh. As well as bringing the legs to the body and their rotation (rotation). Conventionally, this group is divided into parts. Anterior, medial (internal) and posterior.
- Shin. These are not large, but very durable muscles that occupy the lower part of the leg. From knee to foot. We are interested in the back group. This includes the triceps and plantaris muscles. All other muscles are responsible for flexion and extension of the fingers. Therefore, we will not consider them.
- Foot.
This is our support. Which is responsible for balance. The muscles located in the foot mainly start from the lower leg. And they are responsible for the movement of fingers. Their flexion and extension. As well as sideways movement relative to each other. And for the turns of the foot. When performing any exercise that requires balancing the body, they are actively involved. Therefore, we will not do separate exercises for these muscles. Still, our task is to devote most of our time to the larger groups.
We can also divide the leg muscles according to the degree of their location:
- Superficial . These are the muscles that are located in plain sight directly under the skin. We can easily touch them with our hands. These muscles give that visual appearance.
- Deep. Located under the surface. And even though they are practically invisible. But they also play a huge role in the formation of legs.
But don't forget one more point. When training our legs, we not only strive to give them one shape or another. We also face the task of making these muscles stronger. This will increase the stability of our body and we will be able to lift heavier weights. And for people involved in strength sports, load progression is one of the key factors.
Functions
1 The largest muscle group during training that burns a large number of calories, increasing the metabolic rate.
2. They add muscle volume and mass during development.
3. Develop performance and strength by performing various strength exercises.
4. Strengthen muscles, making the corset more reliable. Testosterone and muscle building hormones are produced when performing various leg exercises.
5. The muscles of the arms, shoulders and back (upper body) develop.
6. They build a body that is more proportional in appearance (if you compare the top and bottom).
7. Develop a more powerful connection between muscles and the brain, that is, neuromuscular.
8. Strengthens concentration and willpower.
9. Strength training helps prevent certain diseases, osteoporosis and arthritis.
To avoid suffering from these joint diseases, you need to perform leg exercises with a moderate load.
10. Strong legs prevent getting any blows and various sprains.
11. Training has a good effect on the cardiovascular system and the functioning of the heart itself.
12. Beautiful, slender legs do not need to be hidden under clothes, so you can wear looser clothes.
13. Buttocks with good volume and elasticity will attract the attention and affection of men. After all, it is physiologically inherent that this determines the fertility and health of a woman.
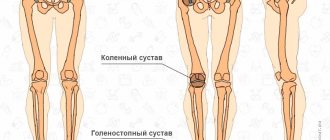
Anatomy of the skeletal bones of the lower limb (leg, pelvis)
Before we start looking at the leg muscles, we'll talk a little about the bones they are attached to. We won’t go too deep, since this is the topic of a completely different article. Below in the picture we can see the skeleton of our lower part.
As you can see, it all starts from the pelvis. Which consists of two iliac bones. The muscles of the pelvis and thigh are attached to their edges, namely the iliac crest. There is also a sacrum, which is attached to the spine. It allows us to keep our body upright. And already at its end, there is a coccyx. Below are two pubic bones. The edges of which serve as the attachment point for the adductor muscles and the back of the thigh. Now let's move on to the leg bones. The largest of them are the femoral ones. At their ends there are two so-called heads, which are attached to the ilium. Next to these heads, there are two protrusions, these are the greater and lesser trochanters. At the lower ends of the femur, there are two epicondyles. Medial (internal) and lateral (external). Also, there are two bones in our lower leg. Tibial and fibular. At the top of the tibia, located are two condyles. Medial and lateral. They serve as places for muscles to attach to them. All the bones of the leg connect to form the knee. There is a small bone there called the kneecap. Better known to everyone as the kneecap. And of course, don’t forget about the bones of the foot. Where are the phalanges of all our fingers located? And the large calcaneus.
This information will be enough to give you an idea. And it will be easier for you to perceive further information.
Muscles of the pelvic region
As I said earlier, this includes the gluteal muscles. For the sake of the development of which, a large number of girls in the hall shed a lot of sweat. But this does not mean that men avoid training them. It’s just that their priority is not the round shape, but the strength of these muscles. For example, in powerlifting and weightlifting, the development of the gluteal muscles is given great importance.
Gluteus maximus
It is a very large (hence its name) and flat muscle. The shape is vaguely reminiscent of a rhombus. Its development among all gluteal muscles is a priority. It is located on the surface and covers all the other muscles of this group. At the top it is attached to the posterior surface of the ilium. And also to the lateral edge of the sacrum and coccyx. Directing obliquely downward with its upper bundles, it is woven into the fascia lata (the protective sheath of the muscles). And the lower ones are attached to the gluteal tuberosity of the femur.
Functions:
Extends the hip, abducts it to the side and is responsible for its outward rotation. With fixed legs, rotates the pelvis.
Gluteus medius
This muscle is located immediately under the gluteus maximus. The shape resembles a triangle. Attaches to the outer surface of the ilium wing. Heading down, it turns into a powerful tendon. And is attached to the outer surface of the greater trochanter of the femur.
Functions:
Extends the hip. Participates in hip abduction and is the most powerful muscle that performs this movement. The position of the pelvis stabilizes when we stand on one leg. Also involved in lateral and medial rotation (outward and inward rotation).
Gluteus minimus
This is the smallest and deepest muscle of the three gluteal muscles. The top is covered by the middle one and completely resembles its shape. Just a smaller size. And it is attached in the same places. Above to the outer surface of the iliac wing. And below to the outer surface of the greater trochanter of the femur.
Functions:
Together with the gluteus medius, it moves the leg to the side. Also helps maintain balance when walking. Participates in internal rotation of the hip. That is, in its rotation.
Does genetics affect the shape of the buttocks?
The answer is clear: yes, it does.
First, genetics determines muscle shape, and it varies from person to person. And no matter how hard you try, there are no exercises that can change the shape of a particular muscle. Strength training for the buttocks will help increase muscle volume, cardio exercises and a balanced diet can rid you of excess subcutaneous fat, but the shape of the muscles cannot be changed.
Secondly, the appearance of the buttocks is also determined by the width of the pelvic bones and the visual ratio of the width of the waist to the width of the pelvis. And you won’t change this indicator either.
But you shouldn’t justify everything by genetics. If you are overweight, then the point here is not that “the bone is wide,” but rather the excess weight. Only when you lose weight can you really judge the width of your hips, focusing on the width of the pelvic bones, and not the “thickness” of the subcutaneous fat tissue above it.
And if you are ready to move from theory to practice, then try my
Exercises to train the gluteal muscles
From what was written above, we can notice that these muscles connect the pelvis and thigh. Thus, they become stabilizers for our legs. They also move the leg to the side. But the most important thing is the participation of the gluteus maximus muscle in hip extension. In order to develop them, you need to select exercises where these functions are present. There are several most effective ones:
- Sumo squats. All conditions are met here. Due to the wide stance of the legs, the leg abduction function is activated. When you come into a standing position from a sitting position, the hip extension occurs. And in order not to lose balance, the stabilizing function of these muscles comes into play.
- Romanian cravings. This exercise is aimed at working the buttocks. And it is one of the best for these purposes. The main function it involves is hip extension. Thus, it actively activates the gluteus maximus muscle. And by bending the legs at the knee joint, the biceps femoris muscle is excluded from the work.
- Leg abduction in crossover.
You can move your leg in different directions. Back, focusing on hip extension and working the gluteus maximus. And to the side, engaging the middle and small muscles.
How to pump up your buttocks
In order to understand how volumes are formed at the back, it is worth diving into the anatomy.
The gluteus maximus muscles are the largest and strongest. They keep the body upright and allow you to rotate the hip and rotate it outward. These muscles have a diamond shape, and they determine the size of the buttocks globally.
The gluteus medius muscles are located on the side under the gluteus maximus muscles. They are smaller and weaker, but they also significantly affect the shape of the butt. I will make a reservation that, of course, this very form depends on genetics, but it can be completely corrected with the help of training.
The gluteus minimus muscles are the smallest of the trio. Their function is auxiliary: they also allow you to hold your body vertically and move your leg to the side, but they only do this in tandem with their larger brothers. Therefore, it is simply impossible to train them separately.
Is it possible to pump up your buttocks with isolated exercises?
If you do only them, you will not be able to increase the required volume. And if you perform only basic exercises, you will have to rely solely on your own genetic structure.
The buttocks are the largest muscle group. However, a workout that fully includes them is a set of exercises to work the thigh muscles, as well as the gluteal muscles themselves. Additionally, I would recommend adding work on the muscles of the shoulder girdle and abdominal muscles.
It is also important to know about the periodization of the training process. There is a misconception that if you “pump up” your buttocks and legs every day, you can achieve quick results
The glute program somehow stimulates hypertrophy of muscle tissue, so if you train too often, the contractile proteins simply will not be restored, which will lead to overtraining - and muscle growth will stop. For example, how can you build a training process: work on the muscles of the legs and buttocks with the addition of the shoulder girdle and abs - 2 times a week, work on the muscles of the back, chest and arms - 1 time per week, functional training for all muscle groups - 1 time per week week.
The best exercises for the buttocks
Basic:
- various squats (classical, sumo, with dumbbells or barbell);
- Romanian deadlift;
- lunges (in place, with alternating legs, with movement, with dumbbells and your own weight).
Isolated:
- hip extension (in a crossover from a lower block or on the floor in a knee-elbow stance with a weighting device);
- hip abduction and adduction in a sitting machine;
- hip abduction (in crossover from the lower block and from the knee-elbow position);
- gluteal bridge (supported on a bench or lying on the floor);
- flexion of the lower leg in a lying machine.
How to pump up your buttocks without pumping up your legs
The anatomy of the human body is such that all the most effective basic exercises for the gluteal group actively affect the work of the thigh muscles. But it is impossible to disable the quadriceps in a basic exercise - the muscle can only be turned off if it is cut off, no matter how cruel it may sound.
When performing squats, the buttocks act as auxiliary muscles. Then why do the legs sway? It's very simple - because the gluteal muscles are weak, and the stronger muscles take on the maximum effort. This is how our body works: it tries to accomplish any work with as little cost as possible.
In many girls I see pumped up legs and at the same time a flat butt. This occurs due to the inability to engage the buttocks. What to do? Learn to perform basic exercises with the correct technique, brought to automaticity. You should feel, first of all, the work of the target muscles (in this case, the gluteal muscles), and not the quadriceps or something else. My recommendation: if you are just at the very beginning of your journey or, on the contrary, you have been training for a long time, but without any significant changes, work out under the supervision of an experienced trainer - and then the result will not be long in coming.
And under no circumstances should you look up to girls from Instagram with big, round and high butts and thin legs without pronounced biceps and quadriceps. With a 99% probability, their figure is the result of plastic surgery, not sports achievements. I believe that only a harmonious, evenly developed body looks truly beautiful, natural and cool. And I think the majority will agree with me.
An example of a workout that maximally engages the glutes
- Basic squats: 10-12 reps × 3
- Romanian deadlift: 10 reps ×3
- Walking Lunges: 20 reps x3
- Crossover hip extension: 15 reps ×3
- Seated hip abduction: 20 reps ×3
- Gravitron pull-ups: 10-12 reps ×3
- Straight crunches: 20 ×3
LAB is a World Class group workout with an emphasis on the muscles of the legs, buttocks and abs - what you need to create an ideal rear view. But don't forget about the gym!
Thigh muscles anterior group
It is this group that forms the thigh from the front. For men, the development of these muscles is of paramount importance. Several main muscles can be identified.
Sartorius
The shape resembles a narrow ribbon. And it is the longest muscle in our body. Its upper end originates from the anterior surface of the ilium. Then it descends obliquely down the front surface of the thigh. And is attached to the tuberosity of the tibia.
Functions:
Participates in flexion of the thigh and lower leg. With fixed hips, the pelvis tilts forward. It also participates in turning the hip inward.
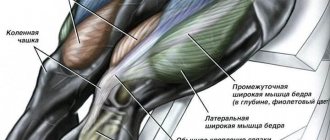
Quadriceps femoris (quadriceps)
This is the largest muscle in our body. From the name it is clear that it consists of 4 heads:
Rectus muscle
The largest of the 4 heads. Located centrally on the front of the thigh. It is this muscle that forms the thickness of the leg. It originates from the lower surface of the ilium. Heading down, it passes into the common tendon. Which is attached to the tibial tuberosity.
Functions:
Due to the fact that the muscle crosses two joints: the hip and knee. She can not only straighten her leg at the knee. But also bend it at the hip.
Important:
When leaning forward during squats, this head is less involved in the work.
Vastus medialis
Located on the anteromedial (inner) surface of the lower thigh. From above it is slightly blocked by the rectus muscle. The shape resembles a drop of water. When well developed, it gives the thigh an expressive shape. From above, a thin tendon is attached to the inner side of the femur. Next, its fibers go down and pass into the broad tendon. With them it partially passes into the common tendon. And the remaining fibers are attached to the inner edge of the patella.
Functions:
Leg extension at the knee joint. Turn the shin inward. Stabilizes the knee, preventing it from falling inward.
Vastus lateralis muscle
Located on the outer part of the front surface of the thigh. Occupying almost the entire area. Slightly covered by the rectus muscle. This head gives shape to the thigh from the outside. Making your legs more massive. In bodybuilding, it is given special importance compared to other strength sports. It originates from the outside of the femur. Heading down, it passes into the common tendon of the 4 heads. And in some bundles it is woven into the lateral (outer) edge of the patella.
Functions:
Leg extension at the knee joint. Rotate the shin outward. Acts as a knee stabilizer. Not letting it fall out. That is, it performs the opposite action of the medial head.
Vastus intermedius muscle
Located on the front of the thigh, immediately under the rectus muscle. It is the weakest among all heads. The upper edge is attached to the anterior surface of the femur. And heading down it passes into the common tendon.
Functions:
Participates in leg extension at the knee joint.
Your dream plan. Where to begin
The plan for building the butt of your dreams contains 4 points:
- Nutrition (normalization, stabilization),
- Cardio training (burn fat, burn fat completely!)
- Strength training (making a flat butt sexy)
- Consistency (we consolidate the results).
You will see changes from correcting your diet much faster than from proper training. What is this connected with? With the characteristics of the female body.
A woman accumulates fat much more easily than a man. On the other hand, if you are calorie-deficient based on your daily energy expenditure, you will burn fat faster than men (as nature intended).
Body beauty is the main feature of the female body
Excess carbohydrates in women are much more easily converted into glycogen - an energy reserve for your muscles (but only if there is a need for this, i.e. the muscles will receive nutrition faster), but if the lifestyle is sedentary - this excess carbohydrate (in excess of what you spent during the day) will turn into fat.
Women have a slower metabolism. You spend the energy you acquired from food more slowly, unlike a man (again, this is how nature intended).
The upper body in women is less developed than in men. What does it mean? Since there are fewer muscles, a woman needs less food to “feed” them. All excess goes straight to fat.
Therefore, before starting training, you should reduce the size of the fat layer on the buttocks. You can achieve this by normalizing your diet. By adjusting your diet, we will start fat burning, and by adding cardio training, we will speed up this process. But first things first.
Exercises to train the front of the thigh
As you already understand, this muscle group extends the leg at the knee joint. The most effective exercises that fit these functions include:
- Front squats . Due to the fact that the bar is located in front, we will be forced to tilt it back a little. So as not to drop it. Therefore, most of the load will fall on the quadriceps. The main function involved in this exercise is leg extension.
- Bench press in a machine with narrow legs. Due to the narrow setting, the gluteal muscles are not included in the work. To shift the emphasis to the lateral head, place your feet together. On the medial side, place shoulder width apart.
- Stepping onto the platform. In this exercise, we focus on leg extension. And this is the main function of the quadriceps.
- Leg extension in a sitting machine.
It is a very dangerous exercise. Therefore, you should not use it on an ongoing basis. To avoid damaging your knee joints. From the name it is clear that it meets our requirements. Namely, it extends the leg at the knee joint. When we turn our toes to the side, we load the lateral head more. And inside, medial.
Medial thigh group: adductors
This area is very problematic. And most athletes are developmentally delayed. Because they are not given due attention during training. And without their development, the thigh will not look aesthetically pleasing. Large and developed from the outside. And atrophied from the inside. This group includes the following muscles:
Thin muscle
It has the most superficial location, on the inside of the thigh directly under the skin. The upper edge is attached to the anterior surface of the pubic bone. Then it goes down, around the medial epicondyle of the femur. And is attached to the tibial tuberosity.
Functions:
Takes part in hip adduction and flexion. It also rotates the lower leg inward and takes part in its flexion.
Adductor longus muscle
This is a flat muscle, vaguely shaped like a triangle. Located slightly in front, closer to the quadriceps. It originates from the pubic bone. As it moves downwards, it widens and attaches to the middle part of the femur.
Functions:
Hip adduction, flexion and internal and external rotation.
Adductor brevis muscle
It also has a triangular shape. It is located slightly deeper than the adductus longus. Starts from the front surface of the pubic bone. Next it goes down and is attached just above the middle of the inner surface of the femur.
Functions:
Involved in hip flexion and hip retraction. Stabilizes the pelvis, preventing it from tilting back.
Adductor magnus muscle
This is a wide and thick muscle. She is the strongest of the adducting group. It is located deeper than the long and short muscles, on the inside of the thigh. It originates from a powerful tendon from the bottom of the pubis and ischium. Heading down, it spreads out like a fan onto the wide tendon. And it is attached to the entire inner surface of the femur, and partly to the medial epicondyle.
Functions:
Adducts the hip. Takes part in its bending. Participates in stabilizing the pelvis.
Your dream plan. Where to begin
The plan for building the butt of your dreams contains 4 points:
- Nutrition (normalization, stabilization),
- Cardio training (burn fat, burn fat completely!)
- Strength training (making a flat butt sexy)
- Consistency (we consolidate the results).
You will see changes from correcting your diet much faster than from proper training. What is this connected with? With the characteristics of the female body.
A woman accumulates fat much more easily than a man. On the other hand, if you are calorie-deficient based on your daily energy expenditure, you will burn fat faster than men (as nature intended).
Body beauty is the main feature of the female body
Excess carbohydrates in women are much more easily converted into glycogen - an energy reserve for your muscles (but only if there is a need for this, i.e. the muscles will receive nutrition faster), but if the lifestyle is sedentary - this excess carbohydrate (in excess of what you spent during the day) will turn into fat.
Women have a slower metabolism. You spend the energy you acquired from food more slowly, unlike a man (again, this is how nature intended).
The upper body in women is less developed than in men. What does it mean? Since there are fewer muscles, a woman needs less food to “feed” them. All excess goes straight to fat.
Therefore, before starting training, you should reduce the size of the fat layer on the buttocks. You can achieve this by normalizing your diet. By adjusting your diet, we will start fat burning, and by adding cardio training, we will speed up this process. But first things first.
Exercises to train the adductor muscles
As you can see, these muscles are responsible for a stable position. Don't let your pelvis fall back. And of course they bring their legs towards each other. Their development will help improve your posture. Strengthen your inner thighs. Due to this, we can increase strength in many basic exercises. The following are good for their development:
- Plie squats. This is a great basic exercise. Which meets all anatomical functions. By placing the legs wide and turning the feet, we stretch the adductor muscles as much as possible. Also, when coming out of a squat, the thighs are brought towards each other.
- Leg abduction in the simulator. From the name it is clear that the exercise meets our requirements. But when performing it, you must follow the correct technique. There should be no jerky movements. To avoid injuring the adductor muscles.
- Adduction of the leg in a crossover
. Also a common exercise that allows you to work the adductor muscles.
Thigh muscles posterior group
These muscles are antagonists for the anterior group. That is, they perform opposite functions. The front one extends the leg, and the back one bends it. In their training, the main thing is to exclude the gluteal muscles from the work as much as possible. If we don't do this then they will take on most of the load. This group includes:
Biceps muscle (biceps femoris)
Located along the outer (lateral) edge of the back of the thigh. This muscle is the main one in this group. And most of the exercises are aimed at its development. Consists of two heads:
- Long. Which starts from the ischial tuberosity, with a small flat tendon.
- Short. It originates from the inner surface of the lower half of the femur.
Below, these two heads unite into one powerful abdomen. Which passes into a narrow tendon. And bending around the back of the lateral epicondyle of the femur, it is attached to the head of the fibula.
Functions:
Extends the thigh together with the gluteal muscle. Bending the leg at the knee joint. And in this position it can turn it outward.
Semitendinosus muscle
This is a long and thin muscle. It is located closer to the inner (medial) edge of the back of the thigh. Starts from the ischial tuberosity. Heading down, it passes into a thin tendon that wraps around the medial epicondyle of the femur from behind. And is attached to the tuberosity of the tibia.
Functions:
Participates in hip extension and leg flexion at the knee joint.
Semimembranosus muscle
Located along the inner edge of the back of the thigh. Covered below by the semitendinosus muscle. It originates from the ischial tuberosity. Heading down, it goes around the epicondyle of the femur and attaches to the medial condyle of the tibia.
Functions:
Extends the hip. Bends his leg. It also turns the shin inward with the knee joint bent.
Hamstring workout
That is, as we see, exercises should perform two main functions. This is hip extension or leg flexion. We can also use foot rotation in some exercises. When bringing your toes together, the semitransverse muscle is loaded more. When extended to the sides, hamstrings.
- Deadlift on straight legs . This is a basic exercise. Which engages the hip extension function when coming out of a bend. Thus, all the muscles of the posterior group are activated. And since the legs remain straight when tilted. Most of the load will be taken by the back of the thigh.
- Squats with wide legs. Also applies to basic exercises. Involves two functions. Bend the leg at the moment of the squat itself. And hip extension when returning to the starting position. Squats also work all 3 gluteal muscles. And the adductor muscles receive a small share of the load.
- Leg bending in the simulator. Here I think everything is clear. The exercise gives us the opportunity to work the back of the thigh in isolation. By bending the leg at the knee joint.
- Taking the leg back in a crossover. This exercise is mainly performed by girls. It allows you to work all the muscles of the posterior group in isolation.
Training program for men and women
Correct mistake
Buttocks
are the most attractive part of the human body. As psychologists have established, men primarily evaluate their buttocks and chest, while girls are intuitively interested in the width of their shoulders and the volume of their buttocks.
According to anthropologists, the buttocks are one of the main factors of attractiveness for both men and women because they reflect a person's ability to run long distances, which was an important evolutionary factor for survival.
A 2015 study by a team from King's College London found that developing leg strength could improve brain function as you age.
In a 2016 study, British scientists concluded that larger buttocks have a positive effect on the health and intelligence of women due to the high content of omega-3 fatty acids in the lower body.
additional approaches must be used.
(in order of importance).
If you are overweight:
If you have a thin build:
Anatomy of the buttocks and pelvis
Anatomy of the gluteal muscles: side viewAnatomy of the gluteal muscles
To choose the right exercises for the buttocks, you need to know their anatomy and morphological features well.
Women's pelvis naturally has a slightly greater forward tilt than men's, which increases the lumbar lordosis of the spine and emphasizes the convexity of the buttocks. Poor posture and weakened hamstrings also cause the buttocks to appear disproportionately large.
The buttocks are formed by three main muscles:
- The gluteus maximus
is the largest and most prominent of the gluteal muscles. It has a diamond shape and is located above all other gluteal muscles; it plays a large role in fixing the torso and hip extension. - The gluteus medius
is a small muscle that sits laterally on top of the gluteus maximus. It is visible when viewed from the side or behind. The gluteus medius muscle works in hip abduction and in exercises that involve the pelvic area; its anterior bundles are involved in inward rotation of the thigh, and its posterior bundles are involved in movements where the thigh rotates outward. - The gluteus minimus
is a small muscle located laterally under the gluteus maximus and is therefore not visible at all. The function of the gluteus minimus muscle is similar to that of the gluteus medius. The gluteus minimus muscle is worked during leg movements and all movements that involve the pelvic area and torso.
The glutes support the hamstrings when you need to increase your speed. When you walk slowly they barely work. But when you speed up and start running, your buttocks are actively involved in the work.
The gluteal muscles help the quadriceps to extend and rotate the thigh outward, and together with the muscles of the back of the thighs, they extend the torso from a tilted position. In addition, they tilt the body to the side.
Helpful advice
Lack of mass in the gluteal muscles automatically means their weakness, and with it low results in all leg exercises, from squats to jumping and running.
If you sink into squats with a barbell on your shoulders, but cannot get up, this suggests that you should equally increase the strength of your quadriceps and buttocks. Leaving the glutes alone means reducing the lifting force by almost half.
Shapes of female buttocks: 1. Inverted “V”; 2. Square; 3. Round; 4. “Heart” An easy way to instantly “pump up” your buttocks
Basic exercises for pumping up the buttocks
The gluteus maximus muscles are well worked when performing basic leg exercises - squats, lunges and deadlifts.
But for the medium and small bundles of the gluteal muscles, you need to perform special exercises - swinging your legs in a block device, or with leg weights.
To fully work out the “minor” muscles of the gluteal region, you need to perform these exercises both in a standing position and lying on your side.
Exercises for the gluteus maximus muscle
Exercises for the gluteus medius and minimus muscles
Read more:
Exercises for buttocks and legs
Calf muscles
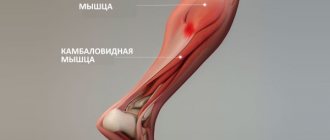
These muscles are stabilizers for our feet. And is involved in bending the leg at the knee joint. The muscles of the anterior group are responsible for turning the foot, flexing and extending the fingers. But as I said earlier, we will not consider them. We are more interested in the back group. Which includes:
Triceps surae muscle
This is the main muscle that can be trained, and we can influence its shape.
Consists of two muscles:
Calf
lies on the surface and has two powerful heads.
- Medial. It is located closer to the inner part of the back surface of the lower leg. And it is more powerful. Starts from the posterior surface of the medial epicondyle of the femur.
- Lateral. This head, on the contrary, is located closer to the outer part of the lower leg. And it starts from the posterior surface of the lateral epicondyle of the femur.
These two heads are directed downwards and in the middle of the lower leg they are connected into one powerful tendon. The second muscle is the soleus.
This is a flat muscle. Located under the calf. One edge is attached to the head of the fibula. And the other to the inner surface of the tibia. And going down, it connects to the tendon of the gastrocnemius muscle. Which attaches to the heel bone. This tendon is known to many as the Achilles tendon.
Functions:
Participates in bending the leg at the knee joint. Flexes the foot. It is also a stabilizer for the lower leg muscles.
Plantaris muscle
This is a very short muscle that has a long and thin tendon. It originates from the lateral condyle of the femur. It goes down and passes into a narrow tendon that lies between the soleus and gastrocnemius muscles. Attaches to the heel bone.
Functions:
Helps bend the leg at the knee joint. Participates in raising the foot. Tenses the capsule of the knee joint.
Anatomy
Origin of muscle
- Posterior gluteal line of the ilium (outer surface)
- Dorsal surface of the sacrum and coccyx.
- Aponeurosis of the erector spinae muscle.
- Sacrotuberous ligament.
- Gluteal aponeurosis.
- The muscle is attached to the thoracolumbar fascia, through which it communicates with the multifidus muscle and the latissimus dorsi muscle, forming posterior oblique and deep longitudinal myofascial bands.
Attachment
- The larger, proximal portion of the muscle, constituting ¾ of its fibers, is woven into the iliotibial tract of the fascia lata. The remaining fibers are indirectly attached through the lateral intermuscular septum to the linea aspera of the femur.
- The deeper fibers of the distal portion of the BMU form an aponeurosis, which is attached to the gluteal tuberosity of the femur.
Innervation
- The gluteus maximus muscle is innervated by the inferior gluteal nerve (L5, S1 and S2).
- The innervation of the skin of the gluteal region occurs mainly through L2 and L3.
Calf muscle training
Based on what was written above, we can draw a conclusion. That this muscle group receives part of the load in almost any exercise for the legs where we bend them at the knee joint. Plus, they act as a stabilizer for the foot and are also used when rising onto the toes. There are several specialized exercises:
- Calf raises in a special machine. There are a lot of such simulators. There is an option where we perform the exercise standing, sitting and even lying at an angle. Therefore, choose any exercise machine that is in your gym and start raising your toes.
- "Donkey." Refers to a number of rarely seen exercises in modern gyms. But by bodybuilders of the golden era, it was in demand. By tilting the body forward, we stretch the buttocks and the back of the thigh. Therefore, they will not be able to turn on and take the load from the calf muscles.
- Calf raises with dumbbells. This is similar to the first exercise, but instead of a machine, a dumbbell weight is used. For greater stability, take it in one of the hands and perform lifts on each leg in turn.
As you can see, anatomy is an interesting science and its knowledge is very useful. Especially for people who want to develop their body. You don't need to know all the scientific terms. The main thing is to understand what the muscle is roughly attached to. To the pelvis, to the thigh or lower leg and what function it performs. Then you can choose the right exercises.
Good luck to everyone in your training!