One leg is shorter than the other: causes and types of shortening
It is very important to understand the type of shortening diagnosed, since this directly determines the tactics of subsequent treatment: True (anatomical) - when the bones of one limb are shorter than the bones of the other. Anatomical disorders can be associated both with previous diseases (poliomyelitis, osteomyelitis) and injuries, for example, an improperly healed fracture. Often, with such shortening, static scoliosis is formed, which is caused by a change in the length of the legs. The difference in length in this case is significant - it can be more than 1.5 cm and is visually clearly visible. Functional shortening is a condition in which the actual length of the legs is the same. However, due to anatomical or neural disorders in certain parts of the body, the muscles of the pelvis and lumbar region spasm and “pull” the thigh and leg upward. The length of the short leg decreases by no more than 1 cm.
Functional shortenings are more common than others. They can be associated both with dysfunction of the sacroiliac joints and with injuries (road accidents, sports, accidental falls) and non-traumatic (postoperative adhesions in the abdomen and pelvis, dysfunction of the skull bones, kidney prolapse, problems with internal organs) causes.
Only an osteopath can differentiate functional and anatomical disorders.
What to do if one muscle is larger than the other?
It happens that the muscles are developed unevenly and the size of the muscles on the right and left parts of the body are very different. For example, one pectoral muscle is larger than the other, or the biceps on the right arm is larger than on the left. First you need to understand that for all people, the size of the muscles on the right and left side of the body is slightly different and within certain limits this is normal! For example, right-handed people often have larger muscles in the right limbs, and left-handed people have larger muscles on the left side of the body. Muscle sizes differ from person to person. everyone, it’s just that usually these differences are small, so the difference is not noticeable, but if you specifically take measurements, you will see that there is a difference. I repeat, a slight difference in muscle size is normal. Just like the difference in the strength of the right and left arms or right and left legs - this is due to nature. However, it happens that the size of the muscles differs very much, this is immediately visible to the eye and, of course, does not look very good.
WHY MUSCLES BECOME DIFFERENT SIZES
1. The size of muscles depends on their activity. Muscles develop in response to loads, therefore, if a person is right-handed and he constantly uses his right hand more, then the muscles of the right hand will be slightly better developed. Usually these differences are very small and invisible to the eye. However, there are individual differences features, and in some people the muscles differ very much.
2. Muscles may develop unevenly due to the nature of the profession. If you have to work much more with one hand, then the muscles on the more active side of the body may become larger than on the other. For example, a blacksmith who constantly works with a hammer and holds it with his right hand, the muscles on the right side will be larger and stronger than the left. Even among athletes, in those sports where one half of the body works more than the other, there are disproportions in muscle development, for example among tennis players or fencers.
3. Crooked execution of exercises when playing sports With poor technique, one part of the body will be loaded more than the other, and if you do this regularly, then over time the muscles will develop unevenly.
4. Various diseases and injuries. For example, with scoliosis due to the curvature of the spine, the back and pectoral muscles may look unevenly developed. In addition, if blood circulation is impaired in any part of the body, the muscles in this place are poorly supplied with nutrition and can dry out. Also, if a person has had injuries, for example, the arm was in a cast for a long time, then with immobility the muscles weaken and greatly decrease in size.
WHAT TO DO IF YOUR MUSCLES ARE DIFFERENT SIZES
1. During training, you need to perform exercises so that the load on the left and right sides is equal. The body builds muscles in response to loads, if you load the muscles equally, they will develop evenly! Do the same number of repetitions for the left and right sides, and follow the correct exercise technique. If you press the barbell crookedly or lift the dumbbells crookedly, then the load on one side will be greater than on the other. Therefore, follow a clear technique in all exercises, control yourself by looking in the mirror, or ask your friends to watch you do the exercise.
Some people have the idea of using dumbbells of different weights. For example, do a bench press with two dumbbells and take a little more weight for the lagging side. Remember - you can’t do this! This disrupts the technique of the exercise, develops incorrect skills in you and can lead to injury. Moreover, if one side is weaker, then what is the point of taking more weight for it? It turns out that the strong side will not work, and the weak one simply will not pull too much weight. You need to do it correctly. train, follow the technique and load the muscles equally, then the muscles will gradually equalize in size and will continue to develop evenly.
2. Exercise regularly, then you will be able to straighten your muscles. Muscle development takes time, so be patient, exercise regularly and you will notice that the muscles will begin to develop harmoniously and proportionally. If you exercise only once a week or often quit training , then where can we expect good results?
3. If the deviations are very strong, you can use additional approaches for the lagging side. For example, if one pectoral muscle is much smaller than the other, then after you have completely done all the exercises for the pectoral muscles, you can do one additional approach only for the lagging side. Also, if one biceps is larger than the other, first you train them evenly, and at the end you do one approach for the biceps that is smaller. There is no need to give a lot of additional load to the lagging side, you will simply overload the muscles, they will not recover well, and in the next workout this the side will work even worse. Train the muscles evenly on both sides, and for the lagging side it is enough to do just one additional approach at the end of the total complex.
To load the muscles on only one side, you need to use dumbbells or exercises on machines. Examples: For one pectoral muscle, you can do a dumbbell bench press with one hand. You take two dumbbells, lie down on a bench, but do the press with only one hand. You take two dumbbells in order to maintain balance and do the press evenly. You can also do the one-arm press on a special machine for the pectoral muscles. At home, you can do push-ups on the floor with one hand. For the biceps, there are special exercises that are performed with dumbbells with one hand. For example, an isolated arm curl on a special bench or one arm curl with dumbbells resting on the thigh. For any muscles, you can choose special exercises for one side - see the “Exercises” section for tips. I recommend resorting to these methods only with very strong disproportions. It also makes sense to additionally load one side if you have had injuries and need to restore this part of the body (in this case, you can do several additional approaches with light weight). In other cases, you just need to train regularly, perform the exercises technically correctly and load the muscles equally , then they will align and develop evenly.
4. In some sports where one part of the body works more than the other, athletes may experience uneven muscle development on the right and left sides. Therefore, I recommend that all athletes include general physical training complexes in their training and perform exercises that load the muscles with both sides, that is, be sure to work on the whole body! Then the muscles will develop harmoniously and this will allow you to achieve great results.
So, friends, use the right training programs, strictly follow the exercise technique and exercise regularly - then your body will be developed harmoniously!
Why is shortening dangerous?
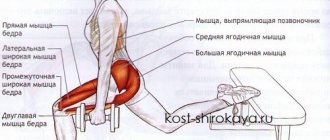
Both anatomical and functional disorders inevitably cause curvature of posture. This is logical and understandable, because the body has to adapt and seek balance. The curvature of posture, in addition to an aesthetic defect, also displaces internal organs, which usually negatively affects their functions. In addition, the gait also changes. If the limb is of different lengths (usually shortened), it inevitably begins to experience increased loads. And this, in turn, causes problems with joints - hip, knee, ankle. In addition, the difference in length leads to a shift in the center of gravity of the body towards the shortened limb, in which, as a result of overload, flat feet are formed. At the same time, flatfoot itself enhances and “complements” the anatomical disorder with a functional one, since the height of the longitudinal arch of the foot decreases. On one side, a pelvic distortion occurs with the formation of lumbar scoliosis.
An interesting fact established by our osteopaths. Unilateral spasm of the iliopsoas muscle, which most often results in one leg being shorter, is often only a reflex response of the body to dysfunction of the cranial (cranial) region.
The condition of one leg being shorter is the result of an anatomical or mechanical imbalance in the human body. Different leg lengths cause the development of scoliosis, misalignment of the hip joint, changes in the position of the vertebrae and chronic overload of the joints of the lower extremities. As a result of this, a person begins to experience manifestations of various clinical directions - pain in the back and joints, headaches and even disturbances in the functioning of internal organs.
Why do limbs become numb normally?
The reasons for tingling and the feeling that some area has become “foreign” in healthy people arise primarily from their behavior and the situations in which they, of their own free will or at the whim of others, found themselves:
- When standing for a long time
on a crowded bus, even people who know nothing about varicose veins and venous congestion can feel their toes going numb. Something similar happens if you hold onto handrails for a long time, which are located at a sufficient distance (you have to reach), hold the telephone receiver for hours without changing your ear and hand, or try to hang curtains from the ceiling (hands linger for a long time above the level of the heart), however, in such cases, problems arise in the upper extremities - the fingers go numb; - A gaze fixed on the monitor, tense muscles of the face and neck,
rapid hits on the keyboard, an inability to react to others are signs that a person is immersed in a computer game or carried away by an interesting job. When he descends “to the sinful earth,” he will discover numbness in the tips of his fingers, or even the entire hand, suffering in the gluteal muscles and tingling in the legs. Occupation is perhaps one of the most common causes of hand numbness. Performing monotonous movements day after day with hands raised above the heart, a person dooms his limbs to a constant lack of the required amount of blood, which will certainly sooner or later result in their numbness. After some time, the work associated with carrying heavy loads becomes noticeable, as well as work involving mental tension, anxiety, and stress; - Numbness of the toes and hands in frosty weather
indicates that the limbs are asking for warmth, where they will quickly warm up and come to life. An area of the face that has turned white and numb in the cold can become frostbitten if measures are not taken in time. - Sound, healthy sleep often involves lying in one position,
which does not fully ensure the movement of blood in compressed areas. Numbness of the hands, the back of the head, or some area of the face during sleep is not such a rare phenomenon, which requires taking a break from pleasant dreams and massaging the numb surface.
Healthy people's hands go numb at night because the weight of the body or uncomfortable tight clothing compresses the blood vessels, and the hand comes away after the person releases it and thus restores blood flow.
A person cannot always prevent unpleasant tingling and numbness, but he must strive for this. After all, it’s not difficult to worry in advance about comfort during sleep, choose comfortable bedding (preferably orthopedic), put on soft, luxurious pajamas, and take a comfortable position.
You should treat a walk in sub-zero weather in the same way: if you expect to stay in the cold for a long time, you need to choose the right clothes and shoes.
It is somewhat more difficult for people performing work that constitutes their functional responsibilities, however, here too you should try to alternate static loads with exercises that restore blood flow.
What to do?
Treatment methods depend on the cause of the disorder: If one leg is shorter than the other for anatomical reasons, the orthopedist may recommend wearing a thin heel support and then refer you to an osteopath to correct the associated anatomical disorders. If there is a functional difference in leg length due to flat feet or an increase in the arch of the foot, active or proprioceptive insoles are prescribed. We manufacture liners using podoscan and based on visual inspection data. Insoles can improve blood circulation in the hip joint and increase the stability of the musculoskeletal system when walking. The inserts also relieve pain and prevent the progression of existing deformities. If the problem is caused by displacement of the pelvic bones, osteopathic treatment of this disorder is prescribed. Often the problems are associated with chronic overload of the hip joint as a result of changes in the axial balance of the body and/or tension in the periarticular tissues and muscles. The hip takes an anatomically incorrect position or is compressed, the articular elements experience overload.
During the examination, the osteopath will be able to determine the shift in the center of gravity to the leg and will detect areas of overload of the hip joint in one direction. Osteopathic correction of functional disorders will restore balance to the body, eliminate compression and tension of tissues, restore blood supply and innervation in the joint, and restore the anatomically correct position of displaced internal organs.
In addition to osteopathic correction, we will refer the patient to a physical therapy specialist. Therapeutic physical education will allow you to build correct body mechanics, increase the amplitude of leg movements, increase flexibility, and strengthen the muscles and ligaments of the whole body. An integrated approach allows not only to get rid of the problem, but also to eliminate other related disorders.
Symptoms that cause particular concern
Various parts of the body go numb due to pathological changes leading to circulatory disorders:
osteochondrosis as a cause of numbness and innervation zone
- Deformation of intervertebral discs (osteochondrosis);
- Compression of the nerve in the canal (tunnel syndrome);
- Pinching of the neuromuscular bundle;
- Deposition of cholesterol plaques, which can affect the blood supply to many organs;
- Insufficient blood supply to a certain area of the brain (the cause may be various obstacles, including those listed above).
It is worth paying attention to a sudden loss of sensitivity accompanied by other signs of trouble,
clearly not similar to temporary difficulties:
- Numbness, after which movement in the arm, leg, fingers is not restored;
- It is accompanied by headache, dizziness, weakness, double vision, impaired coordination of movement;
- Involuntary stool and/or urination occurred;
- Suddenly problems with speech arose (the tongue began to slur, it was difficult to pronounce words);
- Numbness follows recent trauma to the head, cervical spine, or back area.
Stiffness plus the presence of one of the listed symptoms, even to a person unfamiliar with neurological symptoms, gives reason to suspect a serious pathology, including acute cerebrovascular accident (hemorrhage or cerebral infarction), which is a reason to call an ambulance.
Obsessively appearing and then receding numbness in different parts of the body, accompanied by disturbances in vision, speech, and gait, may indicate the development of the following diseases:
- Brain tumor. The tumor in the brain grows and expands its territory, trying to displace neighboring tissues that suffer from pressure on them and cease to function normally. This is manifested by headache, weakness, decreased interest in life, impaired coordination of movements, as well as numbness in various parts of the patient’s body, depending on the location of the tumor in the brain;
- numbness and facial deformation due to stroke
Transient ischemic attack (TIA) or dynamic (transient) cerebrovascular accident. Cerebral ischemia occurs against the background of arterial hypertension, cerebral vascular atherosclerosis or coronary heart disease and its symptoms include dizziness, numbness of the face, right arm or left arm
(depending on the location of the lesion), difficulty speaking. Due to the fact that temporary stiffness in one area can imperceptibly pass into another phase of the disease (ischemic stroke), therefore, such a condition requires immediate medical attention;
- Multiple sclerosis (MS). The formation of foci of demyelination (plaque formation) in the brain and spinal cord cannot leave the body healthy. With MS, some functions are disrupted or completely lost (speech, vision, gait, psyche, brain control over the activity of internal organs), so numbness in various parts of the body is considered a natural manifestation of this pathology.
Numbness of individual parts of the body with or without symptoms, obsessively occurring at night or due to other circumstances, can also be signs of various pathologies.