Share:
The abdominal corner exercise is one of the most effective static tools for pumping up the abdominal muscles. Unlike dynamic loads, which promote muscle growth and the appearance of relief, static exercises allow you to increase muscle fiber strength and develop endurance.
Therefore, the “corner” abdominal exercise is less suitable for beginners. In addition, in order to achieve a toned figure, it is better to spend more time during the training process on dynamic exercises, and leave static ones to “finish off” the trained muscles at the very end. There are different variations of this exercise for different levels of training of the athlete. Next, we will look at the features of each of them, study the technique of execution, and also find out the effect on specific muscles when choosing a certain type of “corner”. The most popular types of this exercise are as follows:
- Corner on the floor;
- Corner on the wall bars;
- Corner on the horizontal bar.
Corner: what muscles work
When performing this exercise, the muscles of the abdomen, shoulder girdle, neck and back work.
The load also occurs on the tensor fascia lata and the rectus femoris muscle. Typically, the “Corner” exercise is positioned as training the lower bundles of the rectus abdominis muscle. Nevertheless, there is an isometric effect on this entire muscle. The shoulder muscles also work. The load is placed mainly on the rotator cuff, and in the area of the scapula - on the serratus anterior muscle and the lower band of the trapezius muscle. The rhomboid muscles also work, so the effect on the muscles is complex. Even the neck, which, it would seem, is not directly involved, is also trained, so that the sternocleidomastoid muscle is affected.
Are there any benefits to doing dips?
Of course, this exercise should not be ignored, since it is multi-joint and involves not only several muscles, but also involves stabilizers. Let's take a closer look at why dips are useful:
- Helps effectively develop the torso. When performing push-ups, the entire pectoral muscle takes part in the work, in particular the lower chest, which is not worked out in the classic bench press and push-ups. Also, the triceps are fully involved, all three bundles. Due to the participation of the deltas, the flexibility of the shoulder girdle improves.
- High availability. You can train not only in the gym, but on any sports ground and even at home. In addition, various variations of this exercise are available on the uneven bars, which allow you to develop muscle flexibility and create an athletic silhouette. Ability to focus on different muscles. Achieved by changing the angle of inclination of the body.
- If you lean forward, the emphasis falls on the pectoral muscle. In the vertical position, the triceps are maximally used.
- High functionality. As mentioned above, to increase strength and muscle mass, dips alone are not enough; they must be performed in combination. But learning to work with your own body weight - they are ideal for this task. Today, there are many parallel bars tricks that can be used to develop flexibility and functionality.
- Strengthens joints and ligaments. Due to this, an increase in working weights is achieved in all bench press exercises.
- You can work both on mass and strength, and on relief. It all depends on the training program and goals. By using weights you can increase your strength and build muscle mass.
However, in addition to the benefits, there are also certain negative aspects:
Exercises for developing the press on the horizontal bar
Wah. Hang on the horizontal bar and, bending your legs at the knee joints, begin to lift them towards your stomach
It is very important to perform the movement slowly and only through the strength of the abdominal muscles. Perform this movement for three sets of 25 reps each.
The rest period between sets should not exceed 30 seconds.
Raising your legs to the bar. This is a rather complex movement that can only be performed by an athlete with sufficiently developed abdominal muscles. Also, from hanging on the horizontal bar, you should raise your legs straight to the bar. Be sure to pause at the end point of the trajectory. The exercise is performed in three sets of 30 repetitions each.
Twisting. The starting position is similar to the previous movement. Having bent your legs at the knee joints, begin to slowly lift them towards your chest. To complicate the exercise, you can move your legs alternately left and right. This will give you a great workout for your oblique abdominal muscles.
Bicycle and scissors. These two exercises are quite similar. Once you have hung from the bar, begin to perform movements with your legs similar to riding a bicycle. When performing “Scissors”, you need to raise your straight legs one at a time. The exercise is performed for the longest period of time.
Tick tock. From a hanging position on the horizontal bar, raise your legs at an angle of 45 degrees. After this, begin to move them left and right, imitating the movements of a clock pendulum.
Dimensional push-up diagram for beginners
As a rule, beginners and girls have an underdeveloped upper body. And this strength is not enough to fully work with your own weight. Accordingly, you have to learn how to do push-ups on uneven bars from scratch. Here are some practical tips:
- Use the gravitron. It is a special exercise machine with a system of counterweights, thanks to which you can partially compensate for the weight of your own body. With its help it will be easier to perform the exercise. However, it is not present in every room.
- Partial amplitude. As one of the ways to strengthen muscles. The lower you lower your body, the more difficult it is to lift it to the top point. Try to go down to the middle, but gradually increase this value.
- Partner help. At first, someone can help you climb up, supporting your legs. Thereby compensating partly for the weight. Some kind of analogue of a gravitron.
- Movement in a negative phase. Only perform the downward motion, but keep the movement slow and controlled. This will prepare the body for the entire exercise by strengthening the muscles and ligaments.
- Train your chest and triceps strength. If you can't do even a few push-ups, it means the target muscles are weak. Strengthen them in other exercises, increase volume and strength.
Kinds
Another common variation of the ab corner exercise is performed on parallel bars. It’s immediately worth noting that this type of exercise is suitable for advanced athletes. It is performed as follows:
- Rest your hands on the bars, legs straight;
- Slowly, standing on straight arms, raise your straight legs up until they form a right angle with your body;
- Stay in this position for several counts, and then also smoothly lower your limbs.
Having mastered this type of abdominal exercise, you can try to perform it with additional weight. It is recommended to use special weighted cuffs that are attached to the ankles as weights. Be sure to include this exercise in your
It might be useful to read:
- Guru or spiritual guide in tantra;
- Exercises for the stomach;
- How to get rid of cellulite? ;
- Stages of cellulite development;
- Autogenic training (basic exercises);
- Four Yogas of Swami read, Four Yogas of Swami read for free, Four Yogas of Swami read online;
- Yoga: tips for beginners;
- How to do yoga correctly;
Contraindications
You cannot perform push-ups on uneven bars if:
- there is an injury to the rotator cuff (rotator cuff), insufficient or uneven amplitude,
- there was a tear, separation or rupture of the pectoral muscle;
- there is tendinitis of the ligaments of the elbow or wrist joint;
- the movement feels uncomfortable, the trajectory breaks, the nerves seem to be “shooting” in the process of work
- there were any injuries to the shoulder joint within six months before work. You can start doing push-ups smoothly if your shoulder doesn’t bother you, but it’s better not to act too actively so as not to aggravate your situation
A set of abdominal exercises at home
For many reasons, not everyone has the opportunity to visit a fitness center or gym. What then to do if the desire to have a beautiful body is present, but there is no opportunity to take care of yourself on a professional level.
The most useful exercise for a beautiful figure: Plank - before and after photos (results)
Then complex exercises designed to pump up the abdominal muscles at home will come to the rescue. Perform each complex in 2-3 sets of 15-20 repetitions.
Lower abs exercises
There are several types of exercises, the most effective and easy to do at home are the following:
- Lie down and raise your ankle about 30 cm and make walking movements.
- From the same position, raise your pelvis and try to reach your chest with your knees.
- Stand in a plank position with straight arms, muscles tense; alternately pull your knees to your chest, simulating running movements.
Side exercises: obliques
The most effective are the following:
- Lie on your side, knees bent, lower arm supporting your head. Exhale - body up, hold, inhale - return to the original position.
- The body position is the same, the lower arm rests the elbow on the floor, the upper arm rests on the waist. Exhale - straight legs up, hold, inhale - lower.
- On the floor. Exhale - stretch your right elbow to the same heel. Inhale - take the starting position. Do the same for the other side.
Upper abs exercises
The following are recommended:
- Lie down with your knees bent and raised above the floor. Do twisting of the body, the legs do not change position.
- The same position: raise your shoulder blades with your arms raised. Accept the original position.
- On the stomach, palms clenched into a lock on the lower back. Raise your body up with a delay. Go back. Make sure your lower body remains motionless.
Standing Ab Exercises
Do the following:
- Hands up. Do 15-20 lifts first with your right foot, try to reach your toe, then with your left.
- Feet shoulder-width apart, palms on waist. Turn the body left and right for at least 3 minutes. The pelvis is motionless.
- At the same time, pull your right knee towards your left elbow. Do alternately with the left knee.
Exercises for pumping up the abs
Effective:
- Lie down with your palms under your buttocks. Legs raised vertically, raise the pelvis. Stay longer. Return to original position.
- Remain in the same position, raise your legs above the floor. Arms and legs reach towards each other. Stay longer. Go back.
- Take a lying position, stand on your toes. Do push-ups quickly with your hands off the floor.
Exercises for the abs and waist
Do these:
- Feet shoulder-width apart, arms down. Perform inclined movements alternately to the sides.
- The same position, spread your arms to the sides. Bend over, turn your torso, trying to reach the toe of the opposite leg with your left hand. Without straightening, change position.
- Lie down with your legs up. Lower them to the left, then to the right.
Static abdominal exercises
Recommended:
- Lie down, stomach tense. Exhale - slightly raise your legs and hold for a short period of time.
- Remain in the same position, raise your shoulder blades and stretch forward, holding for a short period of time.
- In a kneeling position, tilt the torso back and hold for 0.5 minutes.
Exercises for losing weight of a large belly in women
Effective:
- Dumbbells are held with your hands, legs over your shoulders. Tilt to the left, the projectile is directed upward. Return. Do this for the other side.
- Palms face in front of you, keep your legs above the floor about 20-25 cm. Press your knees to your chest and hold. Go back.
- Lie down and bend your legs, raise your pelvis as high as possible, keeping your butt muscles tense. Stay longer. Return to original position.
Abdominal exercises for diastasis (after childbirth)
The following are recommended:
- Stand at shoulder distance from the wall at about 450 and press your back against it, holding the ball with your knees. Squat down parallel to the floor. Wait 15 seconds and come back.
- Lie down, bend your knees, tense your stomach. Slowly, raising your head, try to reach your chest with your chin.
- On knees. Exhale - the stomach is tense, stretch one leg back. Inhale - return to the starting position.
Be careful: if you have diastasis, you should not perform exercises that can overstrain the abdominal region, as this can aggravate the situation.
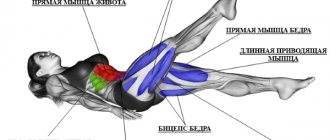
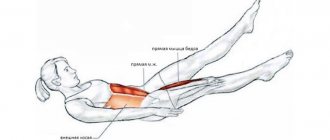
"Corner" on the floor
The abdominal corner exercise on the floor is performed by lifting and holding the body on the hands in a fixed position. Recommended time: 30 seconds, 3-4 sets. It is no coincidence that we chose this type of exercise first, since we recommend that all beginners begin their progress in the corner with it.
Execution technique
There is no limit to perfection: for example, gymnasts hold the corner in such a way that their legs are very close to their face
Features of preparation
As can be seen from the technique of execution, this exercise will require the use of your arms - albeit small, but if you have very weak ones, then at some point you will stop progressing in abdominal exercises precisely because of your arms, which will not be able to hold the body straight in for a long time. If you encounter such a problem, we recommend alternating the corner with push-ups to strengthen the arm muscles. In addition, for progress on the abs, we recommend alternating the corner with strength exercises for the abs, for example, sit-ups and V-sit-ups - then the effect will be maximum!
If exercises in this form are difficult, you can make the method of execution a little easier. For example, it is much easier to perform a “corner” with your legs tucked to your chest:
Common mistakes
As with any other exercise in a corner on the floor, athletes make a number of mistakes when performing it. Let's look at them.
Medium overhand grip
This is a classic option. This type of pull-up is performed both in physical education classes and by American special forces. The main emphasis is on the biceps and back muscles.
To perform this stretch, you must do the following:
- grab the horizontal bar with your hands spaced shoulder-width apart;
- hang and bend your back a little;
- cross your legs so that your body does not become loose;
- pull yourself up, bringing your shoulder blades together.
When the body is at the extreme point, you need to touch the crossbar with your upper chest. Muscles are best stretched when the arms are fully extended. Otherwise, it will not be possible to achieve full stretching.
Nuances
How to perform it correctly and how to learn to do the exercise without discomfort are other important questions that interest “newbies” who have unsuccessfully completed the exercise. Spasms, pain, tension are the consequences of incorrect tactics to give the lower body an attractive appearance.
Before starting a class, beginners make a common mistake - they start without warming up. Achieving a right angle the first time is also problematic, so for “beginners” a gradual increase in height is allowed.
Some athletes lift their limbs jerkily, which is unsafe. Experienced athletes have created other variations of the Corner that help increase the load.
- weights. Objects (light dumbbells) are placed on the ankle. This activity is suitable for people with highly developed abdominal muscles.
- increase in height. The legs are raised to an increased height. The load increases the flexibility of the body.
- leg spread. Classic execution on a horizontal surface, but with the limbs open. Holding each leg separately helps develop your thigh muscles.
- bent leg. The second limb remains straight (alternately changing), the exercise helps to tighten the oblique abdominal muscles.
Unlike other exercises, it allows you to visually highlight all six abs, but other techniques often do not allow you to work out the lower 2 abs. Muscle blocks are hidden behind a layer of fat, which can be easily removed with static exercise.
It is not recommended to do it in an overexcited state: the smoothness of the movements requires the presence of inner peace.
Exercise technique
You can perform pull-ups on the horizontal bar either daily or a couple of times a week. There is no need to perform them to the point of exhaustion; a load of 70 percent is optimal. Performing 7-8 pull-ups helps develop muscle strength, and subsequent repetitions of the exercise are aimed at developing endurance. When and how to increase the number of pull-ups on the horizontal bar is decided individually during the training process.
Before you start doing pull-ups, it’s a good idea to do some warm-up exercises, such as push-ups. The pull-up program depends on what you want to achieve: develop arm strength or increase muscle mass.
- Hang on the horizontal bar, choosing the width and grip method you need.
- Make an upward movement while exhaling. The movement should be carried out due to the movement of the shoulder blades. There is no need to try to pull yourself up with the strength of your biceps, since the latissimus dorsi is a much stronger muscle group. The same applies to various jerking movements of the pelvis and legs - this is not permissible in the classic version of pull-ups. Try to focus on the position of your elbows. You should “press” them down as you lift your body - this will maximize the load on the latissimus dorsi muscles.
- The movement is best performed in full amplitude. At the top point, the chin should be located above the level of the horizontal bar, and the elbows should be practically pressed against the body.
- Slowly lower yourself down while inhaling. The descent in time must be equal to the ascent. At the bottom point, fully straighten your arms and relax your back muscles. pause for one second, then perform another repetition.
General characteristics, benefits of the exercise
This type of pull-up is a more complicated version of the regular pull-up. Over time, when basic exercises are sharpened to the limit, the muscles no longer exert enormous effort and develop more slowly. Therefore, there are various complicated versions of certain exercises for an advanced level that should be included in your training plan.
The benefits of corner pull-ups are as follows:
- this is one of the most accessible exercises: there are horizontal bars in every yard, and it’s not difficult to go outside and do a couple of exercises;
- Corner pull-ups can significantly strengthen the muscles of the back, arms, abs, chest and shoulder girdle;
- coordination of movements improves;
- develops strength and endurance;
- strengthens posture and spine, which helps prevent diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- muscle spasms are eliminated.
Exercise technique
The technique for performing horizontal pull-ups is as follows:
- Hang from a low bar (bar, rings, TRX loops, etc.). Take a couple of steps forward and straighten up completely. The horizontal bar should be approximately at chest level. An acute angle should form between the floor and the body.
- Place your hands slightly wider than your shoulders. The wider the grip, the more the rear deltoids and trapezius work. Accordingly, for the latissimus dorsi and biceps, a grip approximately shoulder width is more suitable. Use a middle ground. It is better to hold the horizontal bar with a closed grip and use magnesium, since the time under load will be quite long. You should not use straps here; learn to feel the work of your back in such simple exercises with your own weight.
- Begin to pull your body towards the horizontal bar, bringing your shoulder blades together. If you reach the horizontal bar with your chest before you have completely retracted your shoulder blades, it means that the amplitude of movement is too small. In this case, you need to take it one step further or use the foot support we talked about in the previous section. Lifting the body should be done while exhaling. At the same time, you should keep your elbows closer to the body, so the tension will not go away from the back muscles. if you move them apart, the load will transfer to the rear bundles of the deltoid muscles.
- If you did everything correctly, then at the top point there should be literally 3-5 cm between the horizontal bar and the solar plexus. At this moment, you should statically tense your back muscles as much as possible for greater effect. To do this, bring your shoulder blades together completely. Stay in this position for 2-3 seconds.
- Smoothly lower yourself down while inhaling. Fully straighten at the bottom. At this point, many people make the mistake of relaxing the spinal extensors. This causes the thoracic spine to “sag” downwards. It is not recommended to start repeated pull-ups from this position. This is not dangerous, but you are unlikely to be able to effectively work out your back muscles.
Efficiency Tips
- For beginners, it is not so much the weight of the weight in push-ups that is important, but the correct passage of the eccentric phase. You shouldn’t go through it with a “jump” and “squeeze” the body out of the dead center. You need to move carefully so that the muscles feel the load, and not just determine the trajectory of movement
- If you can’t complete an approach without compensation, this is not a reason to refuse the exercise. Girls, complete beginners, and those who, for some reason, cannot move with good amplitude, must compensate for part of their body weight using rubber shock absorbers, or the “gravitron” system. If elastic bands are used, they must be secured to the bars so that you can rest with straightened legs so that the trajectory of movement is not disturbed.
- Simply directing your gaze upward helps keep your body upright. If your eyes are down and your head is tilted, it is easier to do the “chest” version of the exercise.
- You can pump up your triceps quite well if you take a short pause at the point of maximum muscle contraction and statically contract them at the top of the range of motion.
Dips: Triceps will grow if you don’t make 3 MISTAKES.
Types of pull-ups on the horizontal bar and muscle groups
First, let's look at what types of pull-ups exist, and also analyze in detail the technical aspects of this or that movement.
Classic/military pull-ups
The most popular type of pull-ups is taught in physical education classes at school. They call it military because in the army this is really the most common exercise, along with classic push-ups, since it is accessible to everyone and is generally applied and universal.
Technically, classic pull-ups are extremely simple:
- hands on the bar shoulder width apart;
- closed grip: the thumb covers the middle finger, that is, the fist is clenched;
- in the starting position, the arms are extended, like the whole body;
- at the start, we take a small breath and with our hands (the key work here is on the biceps and forearms) we pull the body up, the task is to cross the projection of the crossbar with the chin;
- Ideally, the legs should be static so as not to lighten the load with jerking movements.
Reverse grip pull-ups
This is also a fairly common type of pull-up, which allows those who find the classic method difficult to set the desired load vector. Often this type of pull-up is taught in elementary schools when children are just learning how to do pull-ups.
The technique, in essence, does not differ from the classics with the only difference being that the grip is reversed, that is, the hands are turned out. Also, the range of motion in this exercise is somewhat shorter - this is due to the nature of the load and which muscle group we intend to apply it to. But more on that later.
Parallel grip pull-ups
Although the least known on our list, such pull-ups are still widely used among the masses, especially where there is a so-called monkey bars. In gyms, unfortunately, there are not always bars that allow you to use a parallel grip.
Technically the movement is extremely simple. The grip, as can be seen in the video, is parallel, the range of motion is shortened, and the bar is ideally touched by the chest, but you can also use the classic “chin over the bar” option.
Wide grip pull-ups
Until recently, they were not in great demand, but the future of this movement was given by gyms, where this version of pull-ups is much more popular than the three described above.
Subsequently, wide-grip pull-ups smoothly flowed into the street culture of sports activity and are now used everywhere.
Technically, they are identical to the classic ones, with the only difference being that the grip in this movement is much wider.
An open grip is often used, that is, the thumb does not cover the middle finger. This is done for a slightly different innervation of muscle groups. Otherwise, everything is the same: the body and legs are static, rise as you inhale, lower as you exhale.
Now let's move on to biomechanics, that is, which muscles swing when doing pull-ups on the horizontal bar.
Lifting straight lines with a turn
An exercise in the style of “two birds with one stone.” Here you get an equally good load on your arms and on your abs. However, we must warn you that performing this exercise is much harder than it might seem at first glance.
1. Stand on straight arms, bringing your legs slightly bent at the knees slightly forward. 2. Smoothly raise your legs above the bars. The slower the better. 3. Now, without lowering your legs, turn first to the right and then to the left. 4. After this, return to the starting position, lowering your legs down. Then repeat.
For different muscles
For lower abs
These are the same exercises for perfect abs that, if done correctly, will give you six-pack. These include 90° leg raises with pulsation, with a fitball, hanging, all types of crunches, captain's chair (in a dip machine), pulling the knees to the chest and TRX frog loops, corner, and complex plank variations.
Exercise 13. “Fold” with a ball (fitball)
Turning your face to the floor, place your feet and calves on a fitball. Focus on straightened arms, with open palms resting on the floor. The body is as tense as possible and elongated in one line. Tighten your abs and, as you exhale, roll the ball to your hips. Pause for a second. While inhaling, return to IP.
See more exercises for this part of the abs here.
For upper press
Exercises for the upper abs are needed for relief and general pumping. Many will be surprised, but almost the entire base applies to them. In particular, all kinds of lifting/lowering of the body and all types of twisting, as well as exercises on a Roman chair or an inclined bench.
Exercise 14. “Penknife”
Lie on your back on a flat surface. Press your lower back to the floor. Raise your arms straight up. Lightly lift them and your head off the floor along with your legs. As you exhale, jerk both parts of your body together, holding your feet with your hands at the top point of contact. As you inhale, straighten up, but do not touch the floor with your feet, head and hands until you have completed the required number of repetitions.
For side press
Exercises for the lateral press, which are made up of the oblique muscles, form a slender silhouette of the figure and create a toned torso. These include bend overs, lateral raises, crunches, lumberjacks, side planks, and even leg swings.
Exercise 15. “Lumberjack” with dumbbells
Stand up straight. Straighten your back. Place your feet shoulder-width apart. Straightened arms with dumbbells are lowered along the body. Turn sideways to the right as far as possible. Bring your hands together and lift the dumbbells over your right shoulder. As you exhale, turn to the left and lower your hands with dumbbells (without spreading them) to your left thigh. The movement is diagonal.
Many people ignore exercises for the oblique abdominal muscles, and then do not understand why their results were not what they wanted.
Diagonal push-ups
In this exercise you need to slightly swap your legs and arms. Simply put, it must be performed strictly upside down.
1. So, place your palms on the ground slightly wider than your shoulders, and place your straight legs on the bars: one leg on one bar, the other on the other. 2. Make sure that the body is in a single line with the legs. There is no need to raise your pelvis and bend your knees. Even if you stand diagonally to the floor, there is nothing wrong with that. 3. It’s very simple - bend your elbows, bringing your face as close to the floor as possible. 4. Return to straight arms and repeat all over again.
You can perform exactly the same diagonal push-ups. In this case, for each repetition the emphasis is placed first on one edge and then on the other. The emphasis point forms a sort of straight line with the leg, keep this in mind.
Back exercises on the wall bars
The wall bars perfectly help maintain the health of the spine, strengthen the back and prevent pain.
If you have certain pathologies, consult a specialist before starting training.
Pay attention to the following complex:
- The left leg is on the wall. The foot is parallel to the floor surface. Hands are placed on the bar at the shoulder line. Rotations of the lower limb are performed in the hip area 8-10 times.
- Same starting position. Spring flexions are performed in the knee joint area (5-6). Hands take hold of the crossbar. The torso must be kept stable. The foot of the active limb is located horizontally.
- From the same starting position, grab the bar on the sides of your leg with your hands. Make 8-10 bends towards the straight limb of the body without changing the position of the foot.
- Place your foot on the bar and tilt your body, resting your hands on the apparatus. Place your other foot at an angle of about 45 degrees. Pull the pelvis forward towards the wall, rotating the limb in the hip area. A deflection is performed in the lower back, and the body leans forward towards the leg, which is on the wall. The second limb then does the same.
- One leg is straightened and placed on the wall. Do 6-10 smooth springy bends with your body forward, placing your hands on the foot of this leg. When doing the last repetition, stay at the bottom for 10-15 seconds. The same is done for the second leg.
- Stand with your side to the wall, place one leg pointing to the side at a right angle on the crossbar. Make 8-10 body tilts towards the straightened second leg, trying to touch the floor with your fingers or palms. When performing the last incline, hold for 10-15 seconds. Do the same for the second limb.
- Stand facing a wall with your feet wide apart and grasping it near your chest. Make 8-10 rotations alternately inward and forward with both legs at the hip joint, trying to spread your legs as wide as possible.
- Similar starting position. Turn to the left and lower yourself as far as you can into a split position, performing springy movements. Turn around and go into a split on the other side.
- Stand with your right side facing the apparatus and grab the bar with the same hand. Keep your feet together. Perform 10 steps forward with your left leg straightened, gradually increasing the amplitude. Then turn to the other side and repeat the same for the second limb.
- You need to stand in front of the wall. Take the bar with your right hand and place your left hand at waist level. Place your legs together and make 10 swings with one of them, tilting your body. For the other side the actions are similar.
- You need to stand with your right side to the wall, grab it with your right hand along the chest line, and with your left hand along the waist line. Lower limbs together. For each of them, 10 back swings are performed.
- Stand against the wall with your right side. Bend the leg next to you at the knee joint and place it point-blank on the bar. Grasp the projectile with your hand slightly below the knee. Spring bends with the torso forward are performed. You need to try to reach the surface with your fingers or palms. For the other leg, the manipulations are similar.
- Stand with your back against the wall. Lean on your left leg and throw the other one over the bar. Place your right hand above your leg, approximately in line with your shoulder. Bend your back and perform 10 repetitions back and forth in the hip area. The same is done for the opposite side.
- Stand with your back to the wall. Grab the step above your face and bend your lower back. body back, each time grabbing the lower bars.
Photos will help you better understand how to perform the exercises.
Pectoral dips
The emphasis on the pectoral muscles can be shifted if you choose a projectile with a wider handle arrangement. This will make it easier to perform the exercise with elbow extensions. However, finding such bars is not always possible if the athlete has outstanding anthropometry. In this situation, parallel push-up stands help; they can be positioned so that it is convenient to spread your elbows during push-ups.
Taking the starting position
This stage differs only in that the grip will initially be wider, but the palms will also be directed towards each other. The body remains vertical, the spine is perpendicular to the floor. The arms are bent at the elbow joints, the body is lowered clearly vertically. The legs can be bent at the knees so that the center of gravity of the body shifts, thereby giving the body the correct vertical position.
Movement
When lowering while exhaling, the elbows spread, the body smoothly lowers down, the angle between the forearms and the body is approximately 40 degrees;
The push-up occurs in a smooth, controlled manner, but insertion of the elbows should be avoided. This will protect not only the ligaments from inflammation, but also the joint itself from destruction.
Attention
Lowering the body down must be controlled. “Throwing” the body down is not recommended, it can lead to loss of control over the muscles. The kicking style, often practiced in gymnastics and workouts, is not the most effective for pumping up muscles.
If the goal is to work the chest muscles, there is no need to bring your elbows towards the body and shift the load. Performing the exercise on wide parallel bars is not recommended for chest muscle injuries.
Options
With weights . The weight is attached to the body on a special belt. You can put the weights on a belt chain, or attach a weight or dumbbell to it. It is important to secure the load chain so that lowering is controlled
Other options for weights are holding a weight between your knees, or wearing a vest. Holding is not recommended; usually the lifter's pressing capacity exceeds his ability to hold the weight between his legs.
Big Chest on Bars! (Working for MASS)
Execution technique
Regardless of the type of exercise, the “base” is the athlete’s positioning of the legs and torso in a position that can be called a straight degree. The position of the back is maintained in a straight position, the legs are tightly connected together, fixation of the position lasts for at least 10 seconds.
Floor
This is where you begin to get acquainted with the statistical load on the abs, but the abdominal muscles are prepared during the transition to the lesson (a series of the classic approach is performed while lying down for 2 weeks). Breathing is voluntary, but as you exhale the muscles tense and then relax. The total time (per approach) takes 3 minutes, 1 minute between sets.
Algorithm:
- lean on your buttocks and stretch your legs;
- lean your body on your hands;
- legs lift off the floor and stretch in the air;
- the limbs are directed towards the body and held.
Horizontal bar
Exercising on the horizontal bar is acceptable and beneficial for the abs. Hanging on a sports structure, the athlete raises his legs, holds his breath and pulls his toes towards the body. Experienced athletes take a series of rapid inhalations and exhalations, lowering their limbs in the final part.
Common mistakes:
- arch of the back;
- rocking;
- jumping from the horizontal bar.
When performing the exercise, keep your hands shoulder-width apart; when lowering, your elbows are not apart, but are directed towards the body.
Bars
Advanced load option: on the uneven bars the load is higher, because the athlete does not hang, but maintains the position with his torso using his arms. The athlete jumps onto the bars and tries to raise his legs above the level of the sports structure, and after crossing the mark, he holds the position for 3-5 seconds. The decrease in retention time is dictated by the increased load.
Complicated options for training on uneven bars:
- raise your legs to face level;
- hang weights on your feet;
- increase the holding time to 20 s.
To enhance the impact of the hands, they are bent at the joint (a push-up effect is created).
Swedish wall
At home or in the gym, perform the load comfortably on a wall bars adjacent to the wall of the room. The technique closely resembles the procedure for receiving a load created by a horizontal bar. However, the wall bars provide more options - hanging (while grabbing the top bar) and support (on the side handles). Some models do not contain protrusions, but attachments can be purchased and integrated into an existing structure. Exercises on the wall bars are carried out without lifting your back from the vertical surface.
Common mistakes
A violation of technique when performing an exercise on the floor is considered to be bending the knee joints. Legs must be kept straight with toes pointing forward throughout the entire cycle of sports movements. Flexion of the knee joints is allowed only for beginner athletes at the stage of muscle strengthening. Shoulders should be kept raised without retracting them. When practicing the wall bars, the main mistake is related to the position of the back.
It must be pressed tightly against the sports structure without bending, which leads to overstrain of the spine and increases the risk of sprains. When lifting the legs on the Swedish wall, the main effort is performed by the abdominal muscles. You cannot help yourself with twisting movements of the hip joint or lumbar area. A typical mistake when practicing on the horizontal bar is swaying the body. The body must remain motionless throughout the entire exercise.
Lifting your legs by inertial force reduces the effectiveness of your workout. The body is fixed on the horizontal bar not by the effort of the muscle groups of the arms, but by the tension of the abdominal, femoral and gluteal muscles. The legs should be lowered smoothly, and not thrown down with a sharp relaxation. Flexing the knee joints reduces the load on the target muscles and, accordingly, reduces the effectiveness of the workout. They must be kept straight at all times.
Another common mistake when performing exercises on the horizontal bar, parallel bars or gymnastic rings is incorrect placement of the hands. The grip must be straight and as strong as possible.
The correct technique will speed up the achievement of the desired result and avoid injury. The Corner exercise is considered effective for developing the abdominal muscles. Techniques performed on the floor, rope, and trampoline differ in individual nuances and additionally involve various muscle groups in the process.
Recommendations for training the abs for women
I think most girls have understood how to quickly pump up their abs at home. Now let's take a closer look at other aspects on which the achievement of your cherished goal - an elastic and sculpted abdomen - depends.
Frequency and intensity of training
It is much more difficult for women to gain muscle mass, including abdominal muscle mass, but achieving good relief and muscle development is quite possible. But, of course, it is unlikely that any girl will be able to boast the same “meaty” and hypertrophied abs as an experienced male athlete.
I am a proponent that girls should exercise their abs more often than men, but do it less intensely and hard. By training your abs 2-3 times a week, you will maintain your abdominal muscles in constant tone, and also increase the consumption of burned calories and fat cells, which will have a beneficial effect on weight loss
However, it is important to observe moderation; do not perform more than three exercises in one workout. No sets to failure, rest between sets until breathing is completely restored.
Nutrition
The principles of a proper diet for a woman are practically the same - more protein, less carbohydrates and fats, giving up bad habits, sweets, flour, fatty foods, etc. However, the diet aspect is somewhat complicated by the fact that girls still need to maintain a certain level of fat consumption (including saturated fats) to maintain stable functioning of the reproductive system. If you give up fats completely, expect problems with your menstrual cycle.
Training process
In medicine there is such a term as gynoid type of obesity. It means that the female body is more inclined to accumulate fat cells in the hips, buttocks, waist and lower abdomen. At the same time, visceral (on internal organs) fat is practically not deposited in women. This means that girls should pay more attention to the oblique abdominal muscles, upper and lower abdominals, since fat deposits in these places are larger than in other parts of the body, and the relief here will be less noticeable. Therefore, I recommend that girls reading this article do exercises such as side plank, crunches in various variations, pump, corner, etc.
But women don’t have to worry too much about training the transverse abdominal muscle (performing a vacuum exercise), since due to the lack of visceral fat, waist size will decrease as you lose weight overall.
artinspiring – adobe.stock.com
Benefits and harms
The corner is a popular exercise that allows you to form a press with parameters that are in demand in sports competitions. The benefits are also obvious for beginners - the body becomes attractive.
Benefits from doing the lesson:
- elimination of fat deposits on the abdomen;
- increased muscle fiber strength;
- increasing endurance;
- formation of a “wasp waist”;
- reducing the “orange peel” effect.
Threats lie in the strong tension that is exerted on the abdominal muscles, which remain in an unusual state for a long time. If you have certain diseases, harm from exercise is acceptable.
Development of pain syndrome with:
- cystitis;
- vertebral hernia;
- first month after birth;
- postoperative period.
Severe pain is possible in the presence of abdominal, inguinal or umbilical hernia, in which physical activity is completely contraindicated.
Warning: Cannot be performed in the presence of hypertension, arrhythmia, aneurysm.
What to replace
Running frog
If there are physical limitations or difficulties in performing the activity, it is wise to choose alternative options for exposure, but also those that will also help to draw the relief.
- Press while standing. Having taken a position against the wall, a person alternately raises his limbs and connects them with the lowering arm.
- Wah. The athlete grabs the horizontal bar and bends his legs at the joints. The torso rises 25 times. The recommended number of sets is 3, breaks between sets are half a minute.
- Bike. It is practiced on the uneven bars, imitating the movements that are used when riding a bicycle. Work until you feel tired.
- D. In the prone position, the legs are raised and touch the outstretched arms (palms facing down). The exercise is made easier by relieving tension from the back. A set for taking the “G” position consists of 10–20 repetitions.
- Twisting on blocks. The athlete kneels, grabs the cable and, as he exhales, begins to bend towards the floor. As you inhale, you return to the starting position.
It is also useful to use a sports bench, which will help to effectively work out the lower abs.