Back exercises on a fitball are a universal therapeutic and preventive complex that can be mastered by people of any age and any level of physical fitness. A fitball, as a sports equipment, is a large gymnastic ball with a diameter of 45 cm to 95 cm.
On top it is made of durable elastic polyvinyl chloride or latex, and inside it is filled with air. Initially, the fitball was intended exclusively for the rehabilitation of patients who had suffered injuries or spinal surgeries. Over time, exercise balls began to be used for fitness in order to prevent diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Fitball quickly gained popularity among pregnant women and young mothers. In the first case, training with a ball helps prepare for childbirth, in the second, it contributes to the harmonious physical development of the child. Exercises on an elastic ball are also successfully practiced in “Health Groups” created for people of advanced age.
What are the benefits of training with a fitball?
Regular sports activities allow you to restore, maintain or improve physical fitness. In particular, gymnastics with fitball helps:
- straighten your posture;
- strengthen skeletal muscles and myocardium;
- lose extra pounds;
- get rid of muscle hypertonicity;
- pump up your abdominal muscles;
- improve the coordinated functioning of the muscular system (coordination).
Exercises on a gymnastic ball “accelerate” blood and lymph flow, stimulate metabolic processes in tissues, and normalize pulse, respiration, and blood pressure. To improve your health, you can attend organized classes in medical institutions and fitness centers or train at home.
Important! Before using a fitball at home on your own, you must examine your spine and consult with a physical therapy doctor.
Press crunch
This exercise on a fitball is perfect for those who experience back discomfort when performing abdominal crunches on the floor or bench. Also, with the help of a fitball, you can ideally feel the abdominal muscles, understand and consolidate the correct movement technique, which you will use in the future in other abdominal movements.
- Sit down on the exercise ball, and then a few steps forward, place it behind your back, closer to your lower back.
- Then, in reverse steps, roll the exercise ball so that you are completely lying on your back on it.
- Place your elbows bent near your ears.
- As you exhale, twist, lifting your body up.
- As you inhale, return to the starting position, fully stretched.
Perform 4 sets of 15 reps.
As you lift your torso up, focus on bringing the bottom edge of your ribs toward your pelvis—this is exactly how your abs work, as they attach just above the bottom edge of your ribs on one side and near your iliacus bones on the other.
At the top point of the positive phase, try to squeeze your abdominal muscles as much as possible, making an additional forced exhalation.
During the negative phase, always straighten your body completely, moving it as far back as possible, while trying to move the lower edge of the ribs as far as possible from the iliac region, thereby completely relaxing the abdominal muscles.
Who should exercise with fitball?
As a preventive measure for spinal diseases, training with a ball will be useful for absolutely everyone. First of all, such classes are recommended for spinal curvatures (kyphosis, scoliosis, lordosis) and osteochondrosis, as well as for other disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
In addition, exercise therapy with a fitball is indicated:
- for women during the perinatal period to relieve the lumbar muscles;
- for children with muscle hypertonicity to relax skeletal muscles;
- for people leading a sedentary lifestyle, to maintain muscle activity and restore blood circulation.
A set of exercises on the ball is selected individually, depending on the specific goal, age and physical capabilities of the person.
What is the effect of exercises for the back on a fitball?
The gymnastic ball forces you to keep your muscles in constant tension so as not to lose your balance. Exercises with it get rid of excess fat, tone muscles and develop flexibility. By changing body position, it is easy to vary the load. The more the fitball is inflated, the greater the tension in the muscles. Dumbbells are used for deep muscle development.
Before you start exercising, decide on the size. Back exercise balls come in different diameters - 40-95 cm in round and oval shapes. Sit on the sphere and control the position of your knees. If they form a right angle, the equipment is selected correctly.
Read more about choosing a fitball →
Who should not train on the ball?
Lower back exercisers
Exercise therapy with a gymnastic ball is contraindicated for diseases such as:
- intervertebral hernia;
- sclerosis;
- malignant and benign tumors of vertebral structures.
The development of a special training plan using sports equipment is required after injuries and spinal surgeries. Cardiology patients need extreme caution when handling the ball. Severe cardiac pathologies are a contraindication to exercise.
Contraindications for gymnastics
Intervertebral hernia is a serious disease, and therefore self-diagnosis and self-medication are not acceptable here. If all the symptoms point to a disc herniation, you should definitely undergo examination at the clinic, and after confirming the diagnosis, discuss treatment methods with your doctor. Only a specialist can choose the right type of exercise for the spine to eliminate any negative impact on the affected area.
Intervertebral hernia
The main contraindication to gymnastics is the acute phase of the disease and the postoperative period, when any load on the spine should be avoided. You should temporarily stop exercising if pain appears after exercise or if accompanying symptoms increase - numbness, tingling in the limbs, spasms, paresis. In such situations, even light physical activity can provoke an exacerbation, and treatment will take longer.
For spasms and numbness of the extremities, exercise therapy is contraindicated
There are also contraindications not related to intervertebral hernia:
- the presence of inflammatory processes and infections in the body;
- severe pathologies of the cardiac and respiratory system;
- exacerbation of diseases of internal organs;
- oncological diseases and metastases in the spinal column.
Poor health, exacerbation of diseases - direct contraindications to exercise
If you have chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system, gastrointestinal tract, or problems with blood pressure, it is recommended to conduct classes under the supervision of a specialist, at least at first.
If you want to learn in more detail how to perform Shishonin gymnastics for cervical osteochondrosis, and also familiarize yourself with the purpose of the technique, you can read an article about it on our portal.
If the pressure is unstable, it is unacceptable to conduct classes
Tonometers
What types of fitballs are there?
There are several types of elastic gymnastic balls:
- Balls with handles (“horns”) to maintain balance. Special handles help prevent falling from the machine. These exercise balls are more suitable for children and the elderly.
- Regular smooth fitballs of round shape. The most popular option for exercise therapy.
- Balls with soft spikes. They do not slip on the floor, and at the same time act as sports equipment and a massager.
- Large oval balls. They have increased stability; their surface can be smooth or rough (with spikes for massage).
When attending organized classes, a physical therapy doctor or fitness trainer will help you choose a suitable ball. The choice of ball depends not only on the shape and additional functions. The size of the fitball is of great importance for the comfort and benefits of training. It must match the height of the person training.
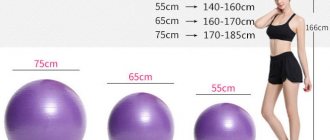
size table
| Human height (in cm) | more than 180 | 170-180 | 160-170 | 150-160 | up to 150 |
| Ball diameter (in cm) | 85-95 | 65-75 | 65 | 55 | 45 |
Note: A ball that is too large will not allow you to rest your full foot on the floor, which will result in an incorrect load on the muscles.
Fitball - gymnasticsconsultation on physical education on the topic
"Fitball - gymnastics"
Introduction
In my work, preserving and strengthening the health of children is a priority, and I am constantly looking for new effective means and methods of increasing the physical activity of children. Motor activity is a powerful biological stimulator of the vital functions of a growing organism. The need for movement is one of the main physiological characteristics of a child, being a condition for its normal formation and development.
Large bright fitballs have been used in working with children abroad for about fifty years, in our country for a little more than eight. The fitball-gymnastics technique was first presented in 2002 by the authors: candidate of pedagogical sciences, associate professor T.S. Ovchinnikova, and Candidate of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor A.A. Potapchuk in the program “Motor play training for preschoolers,” which was tested for five years in kindergartens in St. Petersburg. In this program, the authors described the physiological effects of fitballs on the child’s body and the methods of conducting classes, the high effectiveness of which was demonstrated in work with preschoolers.
G.V. Kashtanova, E.G. Mamaeva, O.V. Slivina, T.A. Chumanova in the practical manual “Therapeutic physical education and massage. Methods for improving the health of children of preschool and primary school age” have developed their own methodology and sets of exercises for fitball gymnastics, which can be used in educational institutions.
Distinctive properties of health balls.
Fitball gymnastics is one of the modern means of physical education. Fitball allows children to quickly and efficiently master a variety of motor skills and comprehensively develop physical qualities. Fitball as a training device is unique, since its elasticity, weight and size can be varied. The diameter of the ball for children 3-5 years old should be 45 cm, for children from 5 to 6 years old - 50 cm, from 6 to 7 years old - 55 cm. The fitball allows you to perform exercises in various starting positions: sitting on it, lying on the floor, lying with your back on the ball or on your stomach with your hands or feet supporting the floor, standing next to you, as well as exercises in motion, various types of throws. The ball can be inflated to its maximum elastic state, then it is used in sports training. For exercises with preventive and therapeutic purposes, the ball should be less elastic. If, when landing on the ball, the angle between the thigh and shin is equal to or slightly more than 90°, then the ball is selected correctly. An acute angle in the knee joints creates additional stress on the ligaments of these joints and impairs the outflow of venous blood, especially if the exercise is performed while sitting on a ball. For activities with preschool children, the ball should not be very elastic
T.S. Ovchinnikova and A.A. Potapchuk in his program “Motor Game Training for Preschoolers” describes the sensory features of fitballs. The ball has the shape of a sphere. No body of any other form has a larger surface of contact with the palm; this contact gives the fullness of the sensation of the form. It is not without reason that one of the outstanding German pedagogues and philosophers of the 19th century, Friedrich Froebel, considered the ball one of the great gifts of pedagogy and called it “an ideal means for exercise.” The ball sends optimal information to all analyzers. The joint work of the motor, vestibular, visual and tactile analyzers, which are activated when performing exercises on the ball, enhances the effect of the exercises.
Balls can be not only of different sizes, but also of different colors. Different colors have different effects on a person’s mental state and physiological functions. In addition to the color effect on the body, the balls also have a vibration effect. Authors of the practical guide “Therapeutic physical education and massage. Methods for improving the health of children of preschool and primary school age” G.V. Kashtanova, E.G. Mamaeva, O.V. Slivina, T.A. Chumanova reveal the vibration effect of fitball gymnastics. Mechanical vibration has a specific effect on almost all human organs and systems. Continuous vibration has a calming effect on the nervous system. The vibrations of the ball affect the spine, intervertebral discs, joints and surrounding tissues. With a systematically increasing load, a strong muscle corset is created around the spine, blood and lymph circulation in the spine, and metabolism in the spinal discs improves. The brain also receives impulses, as a result the development of new conditioned reflex connections is accelerated, especially necessary for the mental and intellectual development of children. The ability to self-control and introspection improves. From a very early age, vestibular functions should be developed and trained (the normal functioning of the cerebellum, which is the child’s motor brain, is of great importance).
Mechanisms of the therapeutic effects of vibration:
- The vibration that occurs while sitting on a ball is similar in its physiological effects to horse riding, which is described in the medical literature as a method of treating osteochondrosis, scoliosis, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, coronary heart disease, obesity, and neurasthenia.
- Exercises in the initial sitting position help train the pelvic muscles, the functional failure of which is often detected in pathologies of the urinary system (enuresis, prolapse of the kidneys or other internal organs, etc.).
- Vibration makes coughing easier, helps reduce the negative effects of hypoxia and improves pulmonary circulation.
Methodology for performing fitball gymnastics.
The program “Motor play training for preschoolers” was tested for five years in kindergartens in St. Petersburg, which showed excellent results in improving the health of children. The authors have developed their own methodology for performing fitball gymnastics.
Classes with children of the fourth year of life do not have a strictly defined three-part form. These are fairy tale classes. Exercises are performed by children as they tell the story. As a rule, these activities do not have a large muscular load; they are dominated by many exercises for the development of fine motor skills (grasping, throwing, stroking objects, various types of rhythmic clapping, onomatopoeia, as well as various games with extensive speech content).
The subject of special attention is working on posture, since a heavy gait (on the entire foot), lateral swaying of the body, half-bent legs, lowering the head, and uneven steps are usually the main problem for children at this age.
Children's attention is extremely unstable, emotional excitability is increased, there is almost no volitional effort when performing exercises, so it is advisable to perform all tasks by imitation, and not by verbal instructions.
The main activity at this age is play. Children get pleasure not from learning how to perform this or that movement, but from being transformed into a game image and from the game process itself. Exercises on balls can be carried out during a whole lesson, but with children of primary preschool age it is more advisable to use exercises on balls as a fragment of the lesson, for example, in the main part, give a set of general developmental exercises, and in the final part - outdoor games with a ball.
The movements of children of the fifth year of life are more coordinated and precise. Kids already perform uniform rhythmic movements and regulate tension and relaxation voluntarily, willingly and repeatedly repeating the exercises. Children can monitor their posture, master various types of walking, their steps become more even, but their arms are not yet energetic enough, and walking and running with friendly movements causes many difficulties. If in the younger group the main attention was paid to working on tone, static coordination and maintaining a given posture, then in the middle group the main task was to learn the technically correct performance of general developmental exercises and the development of motor coordination.
Children of the sixth year of life have more coordinated movements, which are controlled by consciousness and can be regulated and obey their own volitional order. Children become more persistent in overcoming difficulties and can repeat exercises many times, work in a team, carry out all commands given by the teacher, in an organized and disciplined manner. In this age group, children already relate their actions well to music, so it is useful to introduce musical accompaniment in a series of exercises.
In the seventh year of life there is a transition from play activities to educational activities. The child sits for a long time in class, receiving increased stress on the spine. This inevitable load can be reduced by fitball gymnastics exercises. In children of the seventh year of life, muscles and ligaments become stronger, their volume increases, and muscle strength increases. At the same time, large muscles develop earlier than small ones, so children are more capable of strong, sweeping movements, but have a more difficult time coping with small, differentiated movements that require great precision. At this age, more attention should be paid to the game exercises of the warm-up part, which includes tasks for the development of attention, perception, self-control and self-regulation.
After strong excitement with the emotional main part, with its increased motor activity, the final relaxation part is especially necessary at this age. Learning relaxation techniques helps children in the future independently regulate their psycho-emotional state, processes of excitation and inhibition. Despite the fact that gaming activity turns into educational activity, play for children of this age continues to occupy a very important place. Communication, psychocorrectional and team games with elements of sports are becoming increasingly important. It is very important to monitor the physical condition of children. Children are not able to regulate their condition themselves, and responsibility for their health lies with the teacher.
When performing fitball gymnastics, the following recommendations must be taken into account:
• Select a fitball for each child according to their height.
- Start classes with simple starting positions and exercises, gradually moving to more complex ones; This is how the problems of creating a muscle corset and improving movement control are solved.
- Make sure that no exercise causes pain or discomfort.
- Avoid fast and sudden movements, twisting in the cervical and lumbar spine, intense tension in the muscles of the neck and back. Sharp turns, twisting, and axial loads damage the intervertebral discs, which act as shock absorbers.
- When performing exercises while lying on your stomach and back, your head and spine should form one straight line.
- When performing exercises in a prone position on your stomach with your hands resting on the floor, your palms should be parallel at the level of your shoulder joints.
- Monitor the technique of performing exercises, follow belay techniques.
- At each lesson, strive to create a positive emotional background, a cheerful mood.
- In order to develop communication skills, exercises can be performed in pairs or included in outdoor games and team competitions.
For children of older groups with a low level of physical fitness, additional classes can be organized in order to develop their motor and functional abilities and prevent postural disorders.
Club work should be carried out in the following directions:
1. Strengthening physical health
• Development of body functions, strengthening of muscles that support correct posture, and prevention of flat feet.
- Satisfying the need for movement by increasing motor activity in physical education classes, using elements of fitball-gymnastics and fitballs in outdoor games.
- Increasing the level of physical fitness of children.
2. Strengthening psychological health
• Relieving psychological and emotional stress, developing communication skills.
The structure of classes in the circle is close to the structure of physical education classes in the senior group. The introductory part is the gradual preparation of the body for physical activity. Includes walking and running exercises, moderate mobility games, game exercises, and line changes. The main one is the development of physical qualities, training of various muscle groups, physical functions of the body, prevention of postural disorders and flat feet. The final part is a gradual transition from increased muscle activity to calm. Lesson duration: 25 minutes (once a week).
Regardless of the age and physical condition of children, it is necessary to gradually master exercises with the ball.
At the first stage, it is necessary to introduce children to the fitball, its properties, teach them the correct position, the basic positions when performing exercises while sitting, lying down, or squatting.
At the second stage, children should be taught to maintain correct posture when reducing the area of support and balance in different positions on the fitball, as well as to relax muscles and maintain correct posture when performing exercises for the arms and legs in combination with rocking.
At the third stage, you can teach how to perform a set of general developmental exercises using a fitball at the same pace for the entire group; teach stretching exercises.
At the fourth stage, it is advisable to improve the quality of performing exercises in balance.
In order to achieve high results, it is necessary at each stage to consolidate the material covered in outdoor games, to carry out systematic work based on knowledge of the physiology and psychology of preschool children, methods of physical education in general and fitball gymnastics in particular.
During classes, it is necessary to provide children with psychological comfort, access to fresh air, tolerance for mistakes, alternation of work and rest, and comfortable clothes.
The results of diagnosing the level of physical fitness of children who worked out with fitballs showed positive dynamics. Children mastered the skill of maintaining correct posture when performing exercises for arms and legs in combination with readings on a fitball. In addition, they maintain balance quite well when performing general developmental exercises from different initial additions and have learned to relax their muscles.
Conclusion.
Practical work on the use of fitball gymnastics in preschool educational institutions allows us to draw the following conclusions:
- High effectiveness of classes can be achieved subject to a clearly organized system of work, which includes the interaction of all areas: work with children, parents, educators, cooperation with other specialists and interested organizations, as well as the availability of programmatic, methodological and material base.
- Teaching children fitball gymnastics in compliance with the basic requirements for the implementation and sequence of stages leads to the following results:
- the musculoskeletal system is strengthened;
- the cardiovascular and respiratory systems are improved;
- the child’s physical qualities develop, performance increases, and fatigue decreases;
- the processes of self-regulation and self-control improve.
Of course, fitball gymnastics has a wide range of healing effects on the child’s body, promotes the development of creativity in children’s imagination and emotionally liberates children.
In addition, in the process of motor activity, self-esteem of preschoolers is formed: the child evaluates his “I” by the direct efforts he made to achieve his goal. In connection with the development of self-esteem, personal qualities such as self-respect, conscience, and pride develop.
Thus, fitball gymnastics, which is currently an innovative direction in the physical education and health improvement of children, combines all the necessary components for the harmonious development of a child.
Sources:
- Kashtanova G.V., Mamaeva E.G., Slivina O.V., Chumanova T.A. Therapeutic exercise and massage. Methods for improving the health of children of preschool and primary school age. – M.: ARKTI, 2006. – 104 p.
- Ovchinnikova T.S. Outdoor games, physical exercises and general developmental exercises with speech and music. – St. Petersburg: KARO, 2006. – 136 p.
- Ovchinnikova T.S., Potapchuk A.A. Motor game training for preschoolers. – SPb.: RECH, 2002. – 176 p.
- Nechitalova A. Fitball - gymnastics as a means of preventing postural disorders in children of senior preschool age. – magazine “Preschooler’s Health” No. 4, 2010.
- Zhavoronkova T. N. Fitball is more than a ball. https://www.rybso.ru/info/teacheryear/2009/gavoronkova.htm
Examples of exercises
Exercises with a ball for the spine are performed in different positions:
- lying on your stomach, chest or back on a fitball;
- sitting on a ball;
- using the ball as a support for the legs or arms;
- catching the ball with your feet or hands.
The full gymnastic complex includes more than 15 exercises with constant changes in body position relative to the equipment.
Ball under belly
The exercise is called “Swing”. Lying on a fitball, you need to take turns raising your arms and legs, maintaining balance. Duration of execution – 4-6 minutes.
"Swing"
Back on the ball
"Relaxation". The position is extremely simple: the ball under your back, hands behind your head, legs bent at the knees and resting on the floor. While swinging on the fitball, try to relax. Execution time – 5-8 minutes.
"Relaxation"
Supporting your feet on the ball
With your feet on the ball, bend your arms at the elbows. Alternately sliding your feet along the ball, try to roll it first to the right, then to the left. It is important that only the lower body is worked. Perform 4-8 times.
Exercise helps strengthen the muscles of the lower back
Hyperextension
The most effective and popular exercise that helps relieve muscle spasms in the back. Place the fitball under your stomach and place your feet firmly on the floor. Clasp your hands behind your head, spread your elbows to the sides.
Stretch your body as straight as possible, but do not bend back at the lower back. Freeze in this position for 5 seconds, then relax for 5-10 seconds. Repeat alternating tension and relaxation for 3 minutes.
Hyperextension on a fitball
Flexible spine complex
For such training you need the most elastic fitball. There are three main exercises:
- Sitting on a gymnastic ball with a straight back, sway back and forth. Then make circular movements with your lower body. Next, jump on the ball. Perform for 5-7 minutes.
- Sit on the fitball, spread your arms to the sides. Raise your leg straight, trying to maintain body balance. Leaning on one leg, jump on the apparatus several times. Perform 10 times, then change legs and continue.
- Get on your knees, then lower your buttocks onto your heels. Place your hands on the ball. As you exhale, roll the ball as far as possible, straightening your back. At the entrance - take the starting position. Execution time – 5 minutes.
You need to do gymnastics at a leisurely pace, focusing on your feelings.
Squats
The fitball will teach you how to squat better than anyone else in the world! With its help, you will consolidate the ideal technique of this movement in the shortest possible time. To do this, in addition to the ball, you will need a wall.
- Stand with your back to the wall and place the exercise ball behind your back so that it completely covers your lower back.
- Place your feet slightly wider than shoulder width.
- As you inhale, perform a squat.
- As you exhale, rise to the starting position.
Perform 4 sets of 20 repetitions.
During the negative phase, try to keep the fitball from coming off your lower back - to do this, when you squat, try to place your hip joint lower under the fitball.
When performing squats, make sure that your knee joints do not go beyond the projection of your toes. This will be eliminated if you follow the advice given above.
About the Bubnovsky system
An effective set of exercises with a fitball, developed by Professor, Doctor of Medical Sciences S.M. Bubnovsky. This is a new technique called kinesitherapy, that is, movement treatment (“kinezis” - from the Greek movement, “therapy” - treatment).
According to Bubnovsky’s system, the spine and joints can be treated without surgery or medications. The author's technique is patented. She actively practices exercise therapy classes in many clinics that specialize in diseases of the musculoskeletal system. You can learn more about this training system on the Internet.
Examples of exercises for the back from the system of S. Bubnovsky
What is fitball?
A fitball is an elastic, large-diameter exercise ball made of heavy-duty PVC and inflated with air. This type of sports equipment is also called orthopedic or Swiss - after the place of its invention. The idea was developed in the mid-twentieth century by pediatric physiotherapist Susan Kleinvogelbach, who was involved in the rehabilitation of children with cerebral palsy. Since the 60s, the invention has been used throughout the world. And two decades later, the American doctor Joan Posner Mauer included exercises with a fitball in the rehabilitation program for patients after injuries to the musculoskeletal system, and the ball began to be used in physical therapy. Later, the popularity of this simulator increased and it spread throughout the world.
Fitball translated from English is a combination of the words “slimness” and “ball”: and the name exactly matches the content. This is an effective exercise machine that is accessible to everyone, which you can simply deflate and put on a shelf and easily take with you on the road! In the manufacture of this projectile, Anti-Burst System technology is used, which prevents the ball from bursting: as a result, it can withstand a load of up to 300 kg!
People paid attention to the possibilities offered by a gymnastic ball - a universal, inexpensive sports equipment, and began to use it for exercise not only in gyms and rehabilitation centers, but also at home. Training with a fitball strengthens the muscle corset, helps recover from injuries, lose weight, get rid of cellulite, and develop dexterity and coordination of movements.
The peculiarity of exercises with a ball is the simplicity and effectiveness of their use, which allows this apparatus to be used by people of all ages, gender and health status. And one more important positive point: with all its advantages, fitball is affordable for anyone - both a student and a pensioner. And in terms of popularity, gymnastic balls can compete with dumbbells or expanders.
Attention! A fitball should not be confused with a medicine ball - a medicine ball. The latter has small dimensions, weight - from 1 to 12 kg and is used as an alternative to weights or dumbbells.
Types of gymnastic balls
Despite the simplicity and versatility of gymnastic balls, they have several varieties. Fitballs differ in color, diameter, hardness and texture. The diameter of the Swiss ball ranges from 45 to 95 centimeters and is selected in accordance with the needs and individual characteristics of the person. Stiffness depends on the degree of inflation of the ball and the density of the material from which the fitball is made. Swiss balls are divided into several categories based on their texture.
- Smooth.
This is a universal type of fitball; it can be seen more often than others in gyms. Such equipment is used for relaxation, relaxing the back muscles, and strengthening the abs. - Hoppers are balls with horns.
Recommended for children and pregnant women. It is easier to maintain balance on a ball with handles while performing exercises. - Studded (with pimples).
This is a massage type of fitball: exercises with it accelerate the blood and have an anti-cellulite effect.
This is interesting! The color of the fitball is not particularly important, however, if you choose a ball of your favorite shade, there will still be benefits: scientists have proven that our body and psyche are sensitive to the color spectrum. For example, blue tone calms, red adds energy, green relieves fatigue, and pink and yellow colors improve mood and drive away depression.
Basic rules for performing exercises on a gymnastic ball
Like any incorrect physical activity, gymnastics with a fitball can cause harm if you do not follow the safety rules:
- start with short workouts;
- master 2-3 exercises in one lesson, and not the whole complex at once;
- breathe correctly (deep smooth inhalation, slow exhalation);
- do not change the rhythm throughout the entire workout;
- do not make sudden movements;
- increase the load gradually.
Before starting classes, it is recommended to warm up your muscles a little. For this, a light warm-up is suitable, with which regular morning exercises begin.
Gluteal bridge
The exercise is ideal for the fair sex. This is an interesting alternative to the classic buttock bridge, in which the body support is fixedly fixed on the shoulder blades. When performing a glute lift with your back on the ball, your buttocks will be forced to contract more intensely in order to at least bring the hip joint to the level of the body line, and the unstable surface of the fitball will force the gluteal muscles not only to work in their usual form of contraction, but also to include the function of stabilizing the lumbar areas relative to the horizontal axis.
- Lie with your back on the ball.
- A few steps forward, bring your body to a semi-vertical position, lowering your pelvis almost to the floor.
- Bring your arms bent at the elbows to your chest, crossing them.
- As you exhale, push yourself off the floor with your legs, lifting the iliac region as high as possible, directing it towards the ceiling.
- As you inhale, return to the starting position.
Perform 4 sets of 20 repetitions.
At the peak of the positive phase, try to squeeze your buttocks as much as possible with an additional contraction - this way you will get more benefit from the exercise.
Experiment with foot placement. The width of your foot stance will affect not only your balance, but also the segments you work on your gluteal area.
The ideal option is four sets with four different foot positions, starting with the widest possible and ending with the narrowest (right down to the touching of the medial ankles).
If you are in good physical shape or the bridge on two legs loads you less than before, then it is worth improving it with a stand on one leg. In this case, use the starting position with your legs as narrow as possible, and then lift one of your legs off the support.
Also, a good alternative to the classic bridge is the option of resting your back on the floor, where your feet are on the ball. In this case, the fitball can be placed near the wall.
- Place the fitball near the wall.
- Lie on your back near the ball and place your feet on it.
- As you exhale, resting your feet on the ball, lift your pelvis as high as possible, directing your iliac region toward the ceiling.
- As you inhale, return to the starting position.
Perform 4 sets of 20 repetitions.
Rules for gymnastics
In order for exercises to bring only benefits, you need to follow the exercise regime, listen carefully to your feelings and not overdo it, because excessive zeal can cause even more harm than inaction. If you have a hernia, you cannot restore your health in a week, so you will have to be patient and strictly follow your doctor’s recommendations. There are several important rules, without which you will not be able to get rid of a hernia:
- You need to practice daily, 2-3 times a day. In the first week, it is enough to devote 20-30 minutes to exercises per approach, then gradually increase the duration of exercises to 1 hour;
- before the main exercises, you should definitely do exercises to warm up your muscles well;
- all movements must be performed slowly and smoothly, avoiding twisting of the spine, strong bends or intense stress in the lumbar area;
- It is recommended to complete the classes with a spinal stretching exercise, but it must be done very carefully.
Back stretching exercise
Prices for mats for yoga and fitness
Self-massage is very useful for relaxing muscles after gymnastics: while sitting or standing, you need to lightly massage the lower back and sacral area with both hands until a pleasant warmth appears in your back.
Basics of self-massage techniques
You can increase the intensity of exercise only if there is no back pain, muscle pain or discomfort, and before doing so, it is advisable to check again with a doctor. Also, consultation with a specialist is necessary if you decide to change the technique.
If you want to know in more detail what you need to pay attention to when performing exercises for the spine with a hernia in the lower back, you can read an article about this on our portal.
How to choose the right ball size?
Selecting a ball size is quite simple. You need to stand up, bend your leg at the knee joint and bring your thigh parallel to the floor. The ball should fit exactly under the hip and should not be the same height as the top of the leg.
For lovers of numbers and statistics, there is also a plate with the height of those involved and the diameter of the fitball:
| Ball diameter | Athlete height |
| 65 cm | 150-170 cm |
| 75 cm | 170-190 cm |
Balls with a diameter of 45 cm are intended for children.