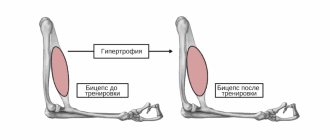
The general condition of the human body, its real capabilities, performance, can be called physical fitness. This is usually achieved through strength training. The more systematically and in-depth a person deals with his body, the higher his preparation. At a good level, a person has resistance to various diseases, is less susceptible to stress, emotional and nervous shocks, is stronger and more self-possessed. The respiratory and circulatory systems of such a person are much better developed than those of an unprepared person, and mental potential, together with the ability to concentrate, allows one to achieve success in work or study.
What does it give
A person who has excellent self-training has good resistance to various diseases, stressful situations and the influence of other negative factors. He has well-developed respiratory and circulatory systems and metabolism. Such a person’s thinking, attention and memory are less prone to developing fatigue. All these features give a person the opportunity to achieve excellent success in educational, competitive and work practice. The maximum level of physical fitness is acquired through the endurance and diligence of students.
What does it depend on?
The physical development and physical fitness of a person is largely determined by the characteristics of his body. Unfortunately, the environment for the most part negatively affects the body as a whole. And here physical exercise, nutrition, giving up bad habits, as well as daily exposure to fresh air are of great importance.
Physiological formation, like birth and death, is considered a natural process for humans. The processes of physical development and puberty are interconnected, and at this stage noticeable changes occur in the body, and people also change externally. However, such processes still significantly depend on sanitary, hygienic, social, economic and other circumstances.
Indicators of physical fitness are also determined by people’s belonging to different age categories. It is much easier for the younger generation to develop beautiful and even posture, perform a certain number of exercises, and also withstand some strength loads. An elderly person will no longer be able to do many things in training, since his health simply will not allow him to cope with the additional work.
Read also[edit | edit code]
- Sports diagnostics
- Sports metrology
- Analysis of training activities
- Assessment of physical development Anthropometric methods Methods for measuring body length and weight
- Girth measurement
- Caliperometry
- Intensity of physical activity
Characteristics of sports training
A high degree of such readiness gives good indicators of mental and muscular performance. The concepts of “training” and “development” are very often confused. It is necessary to take into account that physical fitness is the achievement of significant success as a result of long and grueling exercises that are carried out to acquire the necessary professional skills. And a person develops simply physiologically, according to external signs, without the help of any kind of strength training.
Such training also contributes to the development of various body systems (muscular, cardiovascular, respiratory) and the acquisition of abilities such as flexibility, agility, strength, stamina, and speed.
Physical fitness assessment
Many people do not understand what is meant by physical fitness testing, or how something like this can be assessed. After all, each person is individual, different from the other, and therefore his preparation is also different. It's time to explain what we are talking about, as well as provide some numbers for a better understanding. Such a characteristic is given only after an assessment of the general physical functional state. There are a number of tests, measurements and tests that have been developed and selected for a long time.
Keeping a self-control diary
The main, main method of monitoring physical fitness is keeping your own diary, where you will record all the changes that occur to your body during training. To do this, you just need to line a regular notebook, where you enter data about the work of different body systems, mood, successes, for a certain date.
- Pulse at rest and after exercise.
- Orthostatic test.
- Volumes and characteristics of loads.
- Breathing rate before and after exercise.
- General information about your health.
- Mood: positive or negative.
- Recovery time.
Keeping such records gives a general idea of the athlete's health status, as well as his functional indicators. It’s even useful to do them purely for yourself in order to understand what you should pay more attention to.
Physical fitness standards
A whole set of indicators has been developed that are considered average and also the same for everyone.
For schoolchildren and students
A certain part of the tests relates to assessing the physical fitness of students in schools, technical schools, universities and other educational institutions. By how the physical fitness indicators of the same person have changed, for example, over the course of a semester, one can generally judge the preparation work done. This includes the use of special tools, equipment, as well as physical education methods.
For the army
The armed forces are a separate area of physical training. There are different types of testing that show a soldier's compliance with generally accepted standards of a particular country. They can vary quite significantly from country to country. They are freely available, so let's look at just a few for comparison.
Pull-up on the bar
- Great Britain – 12 times.
- USA – 10 times.
- Germany – 12 times.
- France – 8 times.
- Russia – 12-13 times.
Running 1000 meters (1 kilometer)
- UK - 4.7-5 minutes.
- USA – 7-8 minutes.
- Germany – 6 minutes.
- France - 3.5-4.6 minutes.
- Russia – 3.3-3.25 minutes.
Methods for assessing physical fitness (tests)
To monitor the physical training of students or military personnel, a set of special tests (tests) is provided. They are general, intended for the average girl or guy, as well as special ones if a person has already completed or is not able to complete them.
Are common
- Standing long jump.
- Raising and lowering the body from a sitting position.
- Bend the body forward on a gymnastic bench.
Medical group
- Pull-up on the bar.
- Swimming.
- Cross-country skiing.
- Abdominal exercises (for women).
- Arm curl (lying position).
- Flexibility tests.
- Jumping rope.
- Cooper test.
- Running (1, 2, 3 kilometers).
- Standing long jumps.
To assess the cardiovascular activity of the body, it is usually customary to use the so-called Ruffier test, as well as the Harvard Step Test Index (HST).
Cooper test
This test was invented back in 1968 by the American military doctor and scientist Kenneth Cooper. It is designed for healthy people in good health at the age of no more than thirty-five years.
- Warm up (3-15 minutes).
- Run (bicycle, swim) to measure distance with maximum “extension” in 12 seconds.
- Hitch.
Moreover, the value of this test is not in its results for a certain period, but in the dynamics of change as physical training progresses.
IGST
This is a much more stressful test, which is offered only to already trained athletes. For beginners, such methods are ineffective, since they generally fail to meet the standards. The essence of the test is simple: in 300 seconds a person must steadily (marching) ascend and descend onto a chair or bench. After this, you are given one minute to rest. The index itself is calculated using a formula.
IGST = tx 100 / (F1+F2 + F3) x 2
Here the values F1, F2, F3 indicate the pulse measured respectively in the second, third, fourth minute after the load. There is another, averaged, simplified formula.
IGST = tx 100 / fx 5.5
Where:
t — ascent time in seconds.
f—HR (pulse, heart rate).
Norms for playing sports
There are basic parameters and indicators of physical fitness that must be adhered to.
- Aerobic endurance is the ability to do moderate exercise for a long time and resist fatigue. The aerobic method uses oxygen to convert carbohydrates into energy. With prolonged training, fats and partly proteins also participate in this process. Aerobic exercise is almost ideal for burning fat tissue.
- Rapid hardening – the ability to resist fatigue in submaximal work.
- Strength endurance is the ability to withstand fatigue during fairly prolonged power loads. After all, health and physical fitness depend on this. Energy endurance demonstrates how much muscle mass can withstand additional loads and over what period such tone can be maintained.
- Speed-strength endurance is the ability to perform energy-strength training that is quite long in time with maximum speed.
- Plasticity is the ability to perform body movements with a large amplitude due to the flexibility of muscles, ligaments and tendons. Excellent elasticity reduces the possibility of damage during exercise.
- Speed is the ability to alternate between muscle contraction and relaxation as quickly as possible. The physical fitness of students largely depends on this criterion.
- Movable muscle strength - agility when working extremely quickly with heavy weights. In this case, there is an instant release of energy, which practically does not require significant oxygen consumption. Regular muscle tension usually leads to increased power and changes in muscle shape. In addition, the more developed the muscles, the less prone they are to injury. A person’s weight is normalized because muscle tissue consumes more calories than fat tissue, even during rest.
- Flexibility is the ability to perform coordinated and complex activities. This quality is more required in gymnastics, and participation in such sports leads to the development of flexibility. Children's physical fitness requires improving flexibility.
- The structure of the body depends on the ratio of muscle, fat and bone tissue. These proportions partly reflect fitness and health status by age and weight. Excessive fat content increases the likelihood of heart disease, liver disease, diabetes, and increased blood pressure.
- Weight, height and body proportions. Such criteria determine the shape of the body and its structure. These ratios determine the athlete’s maximum readiness to achieve specific results in competitions.
Physical training (concept, goal, objectives, principles)
Sports preparation (training) is the appropriate use of knowledge, means, methods and conditions, which allows for a targeted influence on the development of an athlete and ensures the necessary degree of his readiness for sports achievements. Currently, sport is developing in two directions with different target orientations - mass sport and elite sport. Their goals and objectives differ from each other, but there is no clear boundary between them due to the natural transition of some trainees from mass sports to “big” sports and back.
The goal of sports training in the field of mass sports is to strengthen Health, improve physical condition and active recreation.
The goal of training in the field of elite sports is to achieve the highest possible results in competitive activities. However, as for the means, methods, and principles of sports preparation (training), they are similar both in mass sports and in elite sports.
Competitive training method
It is used both in relatively elementary forms (a way to stimulate interest and activate students when performing a separate exercise in the classroom), and in independent form as a test or official sports competition. The main feature of the competitive method is the comparison of the strengths of those involved in conditions of orderly competition for superiority or high achievement. The competitive method is used to solve a variety of pedagogical problems. This is, first of all, the improvement of skills in difficult conditions for the development of physical, moral and volitional qualities. The factor of rivalry in the process of competition creates a special emotional and physiological background, which significantly enhances the impact of physical exercise and contributes to the maximum manifestation of the body's functional capabilities. This method must be used after special preliminary preparation.
General physical training (GPP)
helps to increase functional capabilities, overall performance, and is the basis (base) for special training and achieving high results in a chosen field of activity or sport. The following tasks may be assigned to the general physical training program:
• achieve harmonious development of body muscles and corresponding muscle strength;
• acquire general endurance;
• increase the speed of performing various movements, general speed abilities;
4 pp., 1869 words
The influence of physical activity on the psychological state of students
... The influence of physical activity on the psychological state of students The influence of physical activity on ... social effects (health, physical development, physical fitness, features of mental self-regulation, ... physical education have shown that feelings of joy, excitement, satisfaction are more often experienced from sports activities ... the general tone of the cerebral cortex brain, as a result of which its overall...
• increase the mobility of the main joints, muscle elasticity;
• improve dexterity in a wide variety of (domestic, work, sports) activities, the ability to coordinate simple and complex movements;
• learn to perform movements without unnecessary stress, master the ability to relax.
General training principles:
- consciousness and activity, visibility,
- availability,
- systematicity,
- dynamism.
However, in the field of physical education and, in particular, in the field of sports training, these principles are specified and filled with content that reflects the specifics of the process.
The principle of accessibility - uh
This principle obliges us to strictly take into account age and gender characteristics, level of preparedness, as well as individual differences in the physical and mental abilities of those involved.
Accessibility does not mean the absence of difficulties in the educational and training process, but presupposes a feasible measure of these difficulties that can be successfully overcome. Most often, the entire group is given tasks of average complexity, accessible to the “middle part” of students (frontal approach).
The negative side of this approach is that the strongest part of the group works in easier conditions, and the weakest in more difficult conditions.
As the teacher becomes more familiar with the study group, he increasingly uses the so-called group approach,
when microgroups within the study group are determined according to the degree of their preparedness for a specific task.
The principle of systematicity -
This is, first of all, regularity of classes, rational alternation of loads and rest. Regularity of classes involves a rational alternation of psychophysical stress and rest. Any load has four phases: energy consumption, recovery, super-recovery, return to baseline. It is necessary, however, to take into account that if the training session is followed by too long a break, then this effect is gradually lost to one degree or another (reduction phase).
Repeatability and variability in the use of various exercises and tasks in optimal time periods are also mandatory components of the principle of continuity.
The principle of dynamism
, or gradual increase in requirements, consists in setting increasingly difficult tasks as the previous ones are completed. This is expressed in the gradual complication of motor tasks, in an increase in the volume and intensity of loads (subject to the principle of accessibility).
When implementing the principle of dynamism, it is planned to regularly update educational material, as well as increase the volume and intensity of loads. Straightforward
increasing loads is used when their overall level is relatively low and you need to gradually get involved in work.
Stepped
the dynamics sharply stimulate training based on the work already done.
wavy
fluctuations in loads in weekly, monthly, annual cycles are a kind of background on which linear and stepwise dynamics are superimposed.
6 pages, 2789 words
INDEPENDENT MOTOR ACTIVITY AS A MEANS OF MOTOR...
... directions of physical education and propose new approaches to assessing the motor development of preschool children, based on the results of many years of research. Preschool age is the period of the most rapid development of the structure and functions of the child’s body. ...