- April 15, 2020
- Workouts in the gym
- Vladislav Bolshakov
Pull-ups are a basic exercise in many strength disciplines. It perfectly develops the muscles of the upper body. Many athletes, both beginners and advanced, are wondering what is the technique for doing pull-ups on a horizontal bar and how to increase the number of repetitions? This article will address this issue.
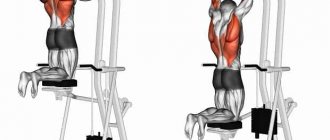
What muscles are used during pull-ups?
Before you understand the question of how to increase pull-ups on the horizontal bar, you need to understand which muscles work when performing this exercise.
As already mentioned, pull-ups are a basic exercise, that is, they involve more than one muscle group. First of all, the latissimus dorsi and biceps muscles are involved in pull-ups. It is these muscles that take on most of the load. The secondary muscle groups worked during pull-ups are the rear deltoid, trapezius, and abs.
This data will be useful a little later, when the technique of pulling up on the horizontal bar for quantity will be discussed.
Pull-ups every day: results
Many people are interested in what the results will be if they do pull-ups every day. First of all, of course, the muscles will tighten and the overall appearance will be better. If you do the exercises regularly, the results will be as follows:
Result 1
Result 2
Result 3
Result 4
Why increase by quantity?
An exercise such as pull-ups is found in bodybuilding and workout, that is, in street sports. People who work out in the gym most likely will not understand why they should do maximum pull-ups and set records in this exercise. After all, pull-ups are just a way to pump up your back and biceps. For these purposes, there is no need to set records or do failure approaches.
But people involved in workouts will say that the number of pull-ups on the horizontal bar directly indicates the physical fitness of the athlete.
So, a person who does 5-10 pull-ups is considered a beginner. An athlete who can perform up to 20 pull-ups is an amateur. An athlete with up to 30 pull-ups is considered advanced. And those who can do 30 or more are professionals.
What happens if you do pull-ups every day?
The benefits of doing pull-ups every day are much less than the harm. With daily exercise you can only achieve:
- overwork,
- decrease in progress
- “stagnation” in strength indicators.
It is difficult for overstrained and tired muscles to withstand intense loads, so it will not be possible to increase performance or achieve muscle definition with this approach. In addition, tired and tight tissues are much more likely to be injured. There is a risk of both sprains and tears. As a result, you will have to spend a lot of time recovering and the goal of increasing the number of pull-ups will fade into the background.
We recommend:
On the topic:
Joints hurt after training - what to do?
What determines the pull-up record on the horizontal bar?
Probably everyone has noticed that one person can do 10 pull-ups, and another 25, while both of these people look approximately the same in physique. The technique of pulling up on the horizontal bar for quantity can play a role here. However, in most cases it is a matter of the individual characteristics of the body.
Firstly, the number of pull-ups on the horizontal bar is influenced by a person’s own weight. Since pull-ups are performed on a bar using your body weight, the performance of this exercise is directly proportional to the person’s body weight: the greater the weight, the more difficult it is to do pull-ups.
Let's imagine two people with the same body weight of 70 kilograms. Moreover, the first has a body fat percentage of 15%, and the other has 25%. The first will have a larger percentage of muscles, since there is less fat. Accordingly, he will be able to pull himself up more, since more muscles will be able to engage in work when performing this exercise.
Types of push-ups
There are two main types of dips. Depending on the position of the torso and elbows, you can direct the load either to the chest or to the triceps.
Chest style
The main points when doing chest push-ups:
- Wide beams are used
During push-ups, the elbows are spread to the sides and slightly back. This allows the pectoral muscles to be more involved in the work.
- Body position vertically or tilted forward
The tilt allows you to additionally engage the lats, which turns the exercise into a complex one (both the chest and back swing).
- Full range of motion
When doing this, be careful not to go too low. Since movement from a very low position is carried out due to the strength of the ligaments, frequent abuse of the fullest amplitude leads to inflammation of the pectoral and shoulder ligaments in many people.
In addition, the load on the shoulder and elbow joints, which are already quite fragile, increases.
Triceps style
For triceps push-ups, narrow bars are used (approximately shoulder-width apart).
During the entire movement, the elbows are pressed against the body, the amplitude of movement is incomplete - approximately half the trajectory.
We extend our arms at the top point more than in the first option, and lower ourselves so that the elbow is not lower than shoulder level (less possible).
The division into chest and triceps types of dips is very arbitrary, since in any version both the chest, shoulders, and triceps work.
It is simply believed that the chest style activates the pectoral muscles more, and the triceps style activates the triceps brachii muscle, respectively.
Pumping up the necessary muscles (first option)
Let's move on to the pull-up program on the horizontal bar.
So, in order to pump up slow muscle fibers, you need to know certain principles by which to train:
- Since slow-twitch muscle fibers are designed to work for a long time, the time under load should be long. The approach should last from 40 seconds to 1.5 minutes.
- There should be no muscle acidification. Acidification, or pump (in sports slang), is a condition when a large amount of lactic acid has accumulated in the muscles. Feels like heaviness in the muscles and inability to perform a large number of repetitions. To prevent acidification, you do not need to do the approach to failure. That is, if your maximum is 15 times, you don’t need to try to do everything 15 times.
- It is necessary to include relaxation phases in the approach. Why, for example, do a runner’s legs not get clogged, because they have been under load for a long time? Because when running there is a relaxation phase - the moment when the leg leaves the ground and does not experience any load. The same must be repeated with pull-ups. Do 1-2 pull-ups and jump off the bar for 2-3 seconds, then do another 1-2 reps. If you feel that the exercise is too difficult, finish the set.
- Rest between sets should be from 1.5 to 3 minutes. Since it is muscle endurance that is being trained, the rest should not be too long. However, if you do not have enough time to bring your breathing back to normal, then take more rest.
- The number of approaches is from 7 to 10, depending on the level of training.
It is recommended to perform endurance training at least 2 times a week.
This was the first principle of endurance training. There are also other pull-up programs on the horizontal bar, which will be discussed below.
Recommendations for classes
Let's listen to the advice of professionals who went from doing zero pull-ups to setting records and answer frequently asked questions.
What to do if you can never do a pull-up on the bar?
Use regular dumbbell and machine exercises to build muscle mass. But don’t forget that the key to muscle growth is proper nutrition.
If you are overweight, you will have to lose weight first. By creating a calorie deficit in your diet.
Use half-range pull-ups.
Secrets of pull-ups or how to do more pull-ups
As Brett Stewart, author of the book “50 Pull-Ups in 7 Weeks,” says: “You need to strictly follow the technique when doing pull-ups!” Only in this case can you properly load those muscles that will help you achieve your goal.
The duration of classes should be no more than 40 minutes per day.
Reduce the load during training if you feel that you do not have time to recover.
What exercises can you do on the bar?
- To make pull-ups easier, use an expander
- A great exercise is low bar pull-ups.
The second option for increasing pull-ups
This method involves trying to do as many pull-ups as possible, not in one approach, but in five.
The first approach is performed to the maximum, that is, you pull yourself up as many times as possible. Subsequent sets are also done to failure or close to it.
Rest is from 3 to 5 minutes. But with each subsequent approach, the rest time should be reduced. For example, if you rested 4 minutes between the first and second sets, then you should rest 3.5 minutes between the second and third sets, and so on. It is natural that with each approach the number of repetitions will decrease or even decrease greatly as you work to the maximum.
Example of the second option for increasing pull-ups
The scheme for increasing pull-ups on the horizontal bar according to the second principle will look something like this.
Let's say your maximum in pull-ups is 10 reps. This means that in the first approach you need to get closer to this result. Then follows a rest, for example, 4 minutes. In the second approach, you also try to do as many pull-ups as possible. This could be 9, 8 or even 6. After this, you need to rest less than you rested the previous time. Let it be 3.5 minutes. In the third approach, you also try to show maximum results. After this, rest for 3 minutes. The 4th set can already consist of four or three pull-ups, but still try to do as many as possible. This is followed by a rest of 2.5 minutes, and then the last approach. This concludes the training.
Pull-ups to get the GTO badge
Pull-up chart for boys and men (high bar):
| Steps (by age) | Bronze badge | Silver badge | Gold badge |
| 1 tbsp. (6–8 years) | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 2 tbsp. (9–10 years) | 2 | 3 | 5 |
| 3 tbsp. (11–12 years old) | 3 | 4 | 7 |
| 4 tbsp. (13–15 years old) | 4 | 6 | 10 |
| 5 tbsp. (16–17 years old) | 8 | 10 | 13 |
| 6 tbsp. (18–24 years old) | 9 | 10 | 13 |
| 6 tbsp. (25–29 years old) | 9 | 10 | 12 |
| 7 tbsp. (30–34 years old) | 4 | 6 | 9 |
| 7 tbsp. (35–39 years old) | 4 | 5 | 8 |
| 8 tbsp. (40–44 years old) | 4 | 6 | 9 |
| 8 tbsp. (45–49 years old) | 3 | 5 | 8 |
| 9 tbsp. (50–54 years old) | 2 | 4 | 7 |
| 9 tbsp. (55–59 years old) | 2 | 3 | 6 |
Pull-up chart for girls and women (low bar):
| Steps (by age) | Bronze badge | Silver badge | Gold badge |
| 1 tbsp. (6–8 years) | 4 | 6 | 11 |
| 2 tbsp. (9–10 years) | 7 | 9 | 15 |
| 3 tbsp. (11–12 years old) | 9 | 11 | 17 |
| 4 tbsp. (13–15 years old) | 10 | 12 | 18 |
| 5 tbsp. (16–17 years old) | 11 | 13 | 19 |
| 6 tbsp. (18–24 years old) | 10 | 12 | 18 |
| 6 tbsp. (25–29 years old) | 9 | 11 | 17 |
| 7 tbsp. (30–34 years old) | 8 | 10 | 26 |
| 7 tbsp. (35–39 years old) | 7 | 9 | 15 |
| 8 tbsp. (40–44 years old) | 6 | 8 | 14 |
| 8 tbsp. (45–49 years old) | 5 | 7 | 12 |
| 9 tbsp. (50–54 years old) | 4 | 6 | 10 |
| 9 tbsp. (55–59 years old) | 3 | 5 | 9 |
Depending on what badge you are applying for, you can use the training plans presented in this article or other programs for beginners.
You can find preparation recommendations here and here.
How long can you expect results?
There is no clear answer to this question. Firstly, everyone has a different body and its own characteristics. One person may make a lot of progress in a month by following one of the above programs, while another will barely make any progress.
Many people believe that progress in the form of increasing the number of pull-ups per repetition is a small result. However, it is not.
Let's take an example from the previous program - your maximum in pull-ups is 10 times. Increasing your record by one pull-up is 10% of your maximum load. For example, in the bench press, 100 kg and 110 kg is a huge difference, although 110 kg is 100 kg plus 10% of that weight. It's the same with pull-ups. In the initial stages, increasing the number of repetitions by 1 or 2 is already a big progress.
When your maximum is, for example, 30 times, then the same 10% is 3 repetitions. But they are much more difficult to add to the record.
Stopping in the final phase
With stopping in the final phase of the exercise, everything is a little more complicated, since it mostly occurs due to the lack of overall strength of the athlete. “Stuck” may be accompanied by dizziness, darkening or “stars” in the eyes, and a slight headache.
If at least one of the above symptoms is present, it is necessary to include running and squats in the training process. The heart muscle is the most important muscle in our body, and strength indicators largely depend on its condition. No matter how strong your muscles are, if they do not receive enough blood, they will not be able to perform fully. It is also worth making changes to the training plan, as I wrote above - reduce the weight, but increase the number of repetitions. If you get stuck at the top with a light or medium weight on the final rep, just don't do that rep. Our task is to get used to the load, and not to test ourselves for strength.
If the previously listed alarming signs are not observed, and the cardiovascular system copes with this load, nevertheless, the problem of overcoming the final few centimeters remains relevant, perhaps the problem is a lack of energy supply to the working muscle groups. The solution to this problem is the simplest of the above - increasing the creatine intake from food. Primarily from natural sources: herring, beef, pork, salmon, and also supplement the “loading” with creatine through supplements.
How to learn to do pull-ups
Learning to do pull-ups on a horizontal bar from scratch should begin with lead-up exercises to prepare the muscles. So, you can perform negative pull-ups. You should find a crossbar that is not too high. The exercise is to jump up and be at the top point when your chin is tucked over the bar. Then you need to go down as slowly as possible.
Another lead-up exercise is the Australian pull-up. You should find a low crossbar, approximately waist-high or slightly higher. Grab the horizontal bar and hang with your legs forward. The body should take a position at 45 degrees to the horizontal. Do pull-ups. If it’s difficult, then move your feet closer.
Motion stabilization problems
Probably each of you has heard at least once: “Strength is not in muscles, but in tendons.” Despite the fact that this statement is fundamentally incorrect, there is some truth in it. Why is it wrong? Tendons by themselves do not exert force in any way. They do not contract or do work, but only transmit the movement caused by muscle contraction to the bones or, conversely, the force of gravity acting on the axial skeleton to the muscles.
What effect do they have on strength indicators? Every movement of the human body has an efficiency factor (the ratio of work done to energy expended), and in no movement is it even close to 100% (walking is only about 11%). In a pull-up, its magnitude directly depends on the stabilization of the joints: shoulders, elbows, wrists and fingers. If there is insufficient rigidity in any of them, the forces aimed at lifting the body are partially lost, thereby reducing the result. Moreover, a lack of grip strength, for example, may even turn out to be an “insurmountable barrier.” If your muscles are developed enough to lift an additional weight of, say, 70 kg, but you can only support yourself with a weight of 50 kg, this will be your “ceiling”.
In the stabilization process, there are, again, two components: physical and technical. First, I’ll tell you about common technical mistakes. Let's look at the movement of individual joints from bottom to top, starting with the shoulders.
Many athletes begin pull-ups on the bar from a relaxed position (also called passive hanging). In this position, the pectoral and deltoid muscles are relaxed and stretched, and the shoulders are at the level of the athlete's ear. If your goal is to do as many reps as possible, this position is justified and is suitable for resting in the bottom position. But if the goal is to lift a lot of weight, don’t spare any effort! The more energy we spend on stabilization, the less it will take to rise. In addition, when a muscle is stretched, the likelihood of injury is much higher than when it is shortened. Don't let your shoulders go up or to the sides, tighten your pectoral muscles. Your body should be a single structure from the moment you hang on the bar, and not after the “Start” command.
*Now about the elbows, more precisely about the excessive extension of the elbows to the sides
I won’t explain for a long time, just make it a rule: the elbow should “look” in the direction opposite to the direction of movement. We move up - the elbow is pointing down. We move up and forward (while placing the chin behind the bar) - the elbow is directed down and back. Any deviation from this trajectory shifts the load from the stronger back to the less strong biceps and deltoids.
*Brushes
When taking the starting position, the following feature can be noted: experienced athletes pay more attention to the process of grasping the crossbar, trying to wrap their palms around it. This ensures closer contact with the horizontal bar, which increases the friction force that prevents the palm from slipping, and also improves the transfer of impulse from the body to the bar. Before hanging on the horizontal bar, try to wrap your hands as tightly as possible towards yourself when doing pull-ups with a reverse grip, or away from you when doing pull-ups with a straight grip, and then maintain such tight contact with the bar.
*Grip
Even in this aspect there is a technical feature - the work of the thumb. Many do not pay due attention to it and practically do not include it in their work. How to do it? Quite simple - press it on your index finger! If the thumb does not just close the grip, but puts pressure on it, grip on the bar will improve, and with it the result in pull-ups (perhaps not immediately).
Let's move on to the physical component. Although I covered the topic of accessory exercises, there was no mention of techniques such as negative pull-ups and limited-range pull-ups. To be honest, I didn’t want to touch on such topics, since the presence of such exercises increases the risk of overtraining or even injury, but I cannot deny my positive experience using them in the past. For the same reasons, I do not recommend them for athletes below the master of sports level in streetlifting. The idea is quite simple: we load the belt with a weight that exceeds our maximum result and learn to pull ourselves up.
The first way is to practice the negative phase of the movement. We place the pedestal under the crossbar so that you can touch the crossbar with your head while simply standing on the pedestal. Using our legs (with a small jump), we take the top position and bend our knees. We fix the position for about a second, then begin to lower as slowly as possible (it will hurt). We select the weight in such a way that it is possible to lock in the upper position.
The second method is to practice movement in a limited amplitude. We construct a stand in such a way that, standing on it and holding the bar, the position of the body approximately corresponds to the position in the middle of a pull-up. Again, we jump onto the bar, then lower ourselves under control. As soon as the legs touch the stand (but do not lean on it), we rise up. This is a kind of analogue of the bar press. I do not recommend using a weight exceeding the maximum by more than 5 kg. You can work with your maximum weight or even below your maximum for a few reps. The height of the stand can also be gradually reduced, even by a centimeter.
Important! You should not perform such exercises less than a month and a half before the competition. They actively load the tendons, the recovery of which can take up to 50 days.
Factors influencing the result
If you think that you can achieve good results with just training, then you are mistaken. Progress is influenced by many factors.
Firstly, nutrition. Your diet should be balanced in proteins, fats and carbohydrates and total calories.
How does nutrition affect increasing the number of pull-ups? The most direct. Food is fuel, energy for the body. During exercise, the body expends a large amount of energy to force the muscles to work. After performing exercises, the body experiences a greater need for energy, which must be replenished with the right food. Under this condition, the muscles will recover faster and better, which means you can start your next workout sooner.
Secondly, sleep. The average person should sleep 7-8 hours a day. This is especially true for people involved in sports. Sleep is the restoration of the whole body. During sleep, healthy hormones are produced that help repair both muscles and the entire body. The amount of sleep also directly affects the result, as does nutrition.
Thirdly, a competent approach to training. The basic rule: the next workout should be after complete muscle recovery. There is such a term as muscle overcompensation. It means an increase in muscle strength after recovery. Training is stressful for the body. And the body, so that this does not happen again, restores the muscles with a reserve, that is, increases their strength, so that next time it will be easier. That is why you should train only after overcompensation has occurred, that is, after complete recovery.
These are the main factors influencing progress. By following them, you can quickly increase the number of pull-ups on the horizontal bar. Of course, if you neglect any factor, such as nutrition, then progress can slow down significantly.
Pull-up technique
Many people are concerned about the technique of doing pull-ups on the horizontal bar for quantity. There are a few secrets you can use if you're looking to break your pull-up record. However, you should first train this movement to at least 15-20 repetitions. If you can't do 15 pull-ups, the following tips won't be effective for you.
So, the method of pulling up is different for everyone. Some people pull themselves up cleanly, without using their legs, others try to pull themselves up to their chest, and so on. If we are talking about increasing the record in pull-ups, then we need to achieve as little muscle work as possible when performing one repetition and as high a speed as possible.
Less muscle work per repetition should be achieved so that the muscles can perform a larger volume of work. And a high execution speed will allow you to “fit” a larger number of repetitions into this volume.
In order for the muscles to experience less stress during one pull-up, all unnecessary movements should be eliminated. For example, you should not pull yourself up above your chin. In addition, the back muscles are much stronger than the biceps. Both of these muscles work during pull-ups. Therefore, the main load should be placed on the back. This can be achieved by gripping the bar wider than shoulder width and also pulling yourself up, trying to squeeze your shoulder blades together as you lift.
High execution speed does not mean that you have to jerk randomly on the bar. The answer to the question of how to effectively do pull-ups on a horizontal bar includes not only the number of pull-ups, but also their quality. Therefore, do not neglect the correct technique in pursuit of quantity. Try to pull yourself up to the bar as quickly as possible, and then lower yourself under control so that you can then begin the next repetition correctly.
Hand position in pull-ups
As a rule, pull-up programs involve the use of a classic straight grip - the palms are turned away from you and slightly wider than the shoulder joints.
In fact, by changing the position of the hands on the bar, you can increase or decrease the load, as well as shift the emphasis in the exercise from one muscle group to another.
Let's briefly look at popular grip options:
- Straight . Palm position: turned away from you and slightly wider than shoulder-width apart. With this grip, the biceps brachii, forearm, delta, and latissimus muscles are evenly loaded.
- Reverse . Position of the palms: turned towards you and spaced at the width of the shoulder joints. The emphasis of the load shifts to the biceps of the arms, and the lats are additionally involved.
- Different grip . The position of the palms is: one is turned towards you, the second is turned away from you. The distance between the brushes is small. The biceps and anterior deltoids are mainly loaded.
- Narrow . Palm position: turned away from you and brought close to each other. When performing pull-ups this way, the lower lats, biceps, and anterior deltoids are worked out.
- Wide . Palm position: turned away from you and spread wide (80–100 cm). Pull-ups work the lats, biceps, and a little bit of the pecs. When pulling up behind the head, the trapezius, lats, and biceps are included.
- Parallel . Palm position: facing each other (a special horizontal bar with narrow parallel stops is used). The main load is taken by the biceps; the lats and brachialis work additionally.
The effectiveness of training on the horizontal bar can be increased by using pull-ups with different grips in one program. The torso muscles will be more fully involved, and this will allow you to quickly achieve your goals in developing an athletic physique.
Don't forget about the lower body. To develop your figure harmoniously, add various squats, lunges, deadlifts, and plyometric elements to pull-ups. Such exercises will help to form developed muscles of the legs and buttocks.
Adviсe
- Always warm up before physical activity. Lack of warm-up can lead to injuries, which will negatively affect the final result.
- Drink water during your workout. Water has a beneficial effect on all processes in the body, including muscle function.
- Stop training if you feel pain in any area. It's better to avoid injury but finish your workout early.
- Stretch after your workout. Stretching has a beneficial effect on further muscle recovery.
- Create your own standards if you are training for yourself. The standards for pull-ups on the horizontal bar are different everywhere, so create them yourself if you are training for yourself.