From an article in the magazine: “The dispute over this issue has divided bodybuilders into two irreconcilable camps...” Let's figure out why Catholics and Huguenots are fighting. What is the essence of the problem and does it really exist?
If you take a closer look and delve into it, it turns out that ardent fans of squats with a barbell are not averse to doing leg exercises in the simulator, but fans of the bench press, no, no, yes, cheat on their favorite exercise with a barbell. The question arises, what is all the fuss about then?
The latest research has shown...
{module 276}
Agree, an article or informational video that begins with this phrase is intriguing and attractive. So, if you set a goal, then on the Internet you will find information about some studies that have proven the benefits of both exercises. Particularly touching are phrases like: “I switched to bench press, and my results increased by 15%.”
How is this figure calculated? Where does it come from anyway? I won’t keep up the intrigue; in most cases, this confrontation is, as they say, made up out of thin air. And the “experts” who write articles about the benefits of the squat may as well glorify the bench press at the same time. Well, what really?
Execution technique
Usually, beginners are advised to extend their shins in the simulator only because it is impossible to make a mistake in this exercise. This is where internet experts are wrong. A beginner can make mistakes everywhere. For example, some individuals do not know that the back of the exercise machine is adjustable, and the support cushion can also be adjusted. They sit on the edge of the seat and strongly “push” their ankles under the car seat. From this position, the ACL turns out to be overstretched at the start. Therefore, such “techniques” are not recommended for fitness.
In order to do the exercise correctly, you need to:
- Adjust the backrest so that it is a support. Most exercise machines have an adjustable backrest and the ability to move it in and out;
- The correct starting position is that the back rests on the backrest, the thigh lies on the seat, the lower leg is fixed with the pad of the exercise machine, and the angle between the lower leg and the thigh is no more than 90 degrees;
- In rehabilitation, incomplete amplitude is allowed when the roller is attached higher than 90 degrees;
- The toes should be pointed slightly towards you; it is better to start the exercise by contracting the quadriceps
These are SEATED LEG EXTENSIONS, baby!
Watch this video on YouTube
The movement is performed as follows:
- The downward movement should not be forced, it is better to lower smoothly and smoothly straighten the lower leg;
- The back should be pressed completely against the back, the lumbar region too;
- Extension should be done while exhaling, flexion – while inhaling.
The variations are actually very diverse. The simplest thing is extension of one leg at a time. This version is for those who have imbalances in the development of their legs, and always “starts” with one hip, only finishing with the other. This option for performing the exercise is better suited if the athlete is afraid of the ACL, or already has injuries.
The second variation is extension with rubber. Sitting on a chair, the athlete extends his lower leg while fixing the rubber shock absorber on the foot. This option is suitable for those who need to strengthen ligaments and protect themselves from injuries.
The third variation is for those who do not have an extension machine. A plate is placed on the shins, the athlete sits on a chair. This option strengthens the ankle and soleus, since the weight will need to be supported by the ankles.
The fourth variation is an extension with the toes turned outward and the heels inward. There is an opinion that this technique builds more rounded hips in girls whom nature has endowed with an I-shaped figure.
Fifth – toes inwards, heels outwards. This is a rather controversial position of the feet from an anatomical point of view, but some athletes believe that this way they better work the medial head of the quadriceps.
Be that as it may, the success of this exercise lies in controlled technique, no jerking or pushing, and slowly raising and lowering the weight. Control the movement of the roller, and the exercise will not be traumatic for you.
The movement is usually performed for 12-15 or more repetitions, in 3-4 working sets; they do not work in power mode
Injury risk and squats
This is a really important point. When you squat, it's not just the target muscles that get the load. You need to maintain the weight and the more it gets, the more seriously you need to approach the exercise. It is important to position the bar correctly so that it does not put pressure on the cervical vertebrae.
To get out of the situation, they come up with all sorts of devices. There are, for example, suits that allow you to hold a barbell on your chest. If you have ever injured your spine, it is better to reduce the load on it and do leg presses.
However, this does not mean that the bench press will completely protect the spine. If you lift your buttocks from the seat while performing the exercise, you can easily injure the lumbar region. Both exercises have their own characteristics and the key to success is the correct technique.
Contraindications for leg press
There are a number of contraindications for performing leg presses that must be taken into account. Among them are:
- There is no need to resort to heavy loads for those who have intervertebral hernias or other problems with the spine.
- Scoliosis or lordosis may be the main reason to exercise in moderation and use only light weights during approaches. Also, such people are recommended to use a special athletic belt, which will help slightly reduce the load. It is worth considering that you should not tighten it too much, and breathing, even with a belt, should be even and deep.
- Those who have suffered a knee or ligament injury in the past should avoid leg presses. New activities can contribute to the recurrence of injuries and provoke new complications.
When starting a leg press in a machine, you must take into account all its features, and also pay attention to some contraindications. The most important thing is to approach it with full responsibility and work for results – efficiently and diligently.
Why is the weight different?
This question is often asked. If someone does a hundred and fifty kilograms on the bench press, then the weight on the squat will be less. Everything is simple here, you need to take into account the weight of your own body. Ordinary laws of physics. When you squat, you lift weight, plus, roughly speaking, your torso; in a bench press, you lift only weight.
This does not mean that the bench press is better, because you can hang more weights on the machine. In both exercises you need to select a working weight. There is no clear formula for moving from a squat to a bench press and vice versa.
How to increase the effectiveness of classes
To increase the effectiveness of the exercise, you can do several tricks that will make your muscles work better and build muscle mass:
- The basis of any sport is proper nutrition. It is with sufficient consumption of protein foods that muscles will begin to grow and strengthen. Otherwise, the training will be in vain;
- Changing the angle of the platform will also increase the effectiveness of training, since there is a greater load than at 45 degrees. Unfortunately, the function of changing the angle of the platform is not available on all simulators;
- Hold the platform at the highest point for 3 seconds;
- The single leg press will definitely enhance the feel of the exercise, especially towards the end of your workout. This exercise is not suitable for everyone, but it is definitely worth trying to increase the effectiveness of the press.
What to choose?
Which exercise to choose is up to you. Try one squat workout, another press workout, get a feel for both exercises. Remember that the load on certain muscles depends on the position of the legs. You may decide to combine exercises in one way or another.
{module 277}
The following position is close to me. Squats with a barbell are convenient to do, what is called classically. Feet shoulder-width apart, toes turned slightly outward. Simply put, become the way you feel most comfortable, naturally.
As for increasing the load on the buttocks or biceps of the legs, these accents are easier to place in the bench press. I repeat, I do not pretend to have the only correct answer, it does not exist. Personally, I don’t like all these experiments, like sumo squats, you have to pay too much attention to balance, body position, it’s distracting. Easier in the bench press. Calmly set your feet at the required distance, checked the position of your toes, concentrated and go ahead! Instead of twisting your toes and straightening your legs, puffing under the barbell like a tightrope walker.
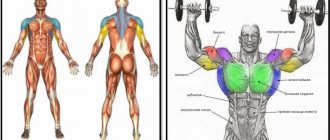
Working muscles
Quadriceps femoris, vastus intermedius. Accessory muscles: biceps femoris, semitendinosus and semimembranosus muscles, gluteal muscles, partially gastrocnemius muscles.
A simulator for performing this kind of presses is a machine statically fixed to the floor, on which there is a movable platform with places for attaching weights. More often there are machines in which the angle of attachment of the platform to which is approximately 45 degrees, but sometimes you can find rather strange, at first glance, devices in which the bench press cart is attached at an angle of 90 degrees, i.e. perpendicular to the floor. It is much more difficult to press your feet on such machines, and it is much easier to get injured.
Home workout without barbell
It is almost impossible to pump up your leg muscles with squats without weights. Exercises without weights are designed to warm up the body before strength training or complement aerobic training designed for weight loss.
Even in home exercises, to strengthen the lower extremities, it is necessary to use dumbbells, weights, and improvised objects as loads. For those who prefer independent training at home, we offer a set of exercises to work the leg muscles:
- Warm-up part. The duration of the elements is 30 seconds each. Quick squats with your own weight, jumping with high knees, running with your shins in place. After finishing the exercises, rest for 30–40 seconds and repeat the cycle.
- Squats with weight (3x15). To complete this you will need a strong backpack. We put heavy books or bottles of water in it and throw it over our shoulders. We place our feet slightly wider than our pelvic bones, turn our toes outward, bend our lower back, and move our shoulder blades back. As you inhale, gently lower your pelvis, and at the same time bring your arms in front of you. We exhale and rise.
- Stepping (3x15). To perform this, you need to choose a stable platform, such as a box or bench. The height of the stand should be at least 50–60 cm. We leave the backpack with weights on the back. We take a step onto the platform with our right foot, straighten up on it and substitute our left one. We step back to the floor in reverse order. We start the next repetition with the left leg. When performing, we try to keep our back straight, without bending forward or “rounding”.
- Bulgarian lunges (3x15). We take two dumbbells or bottles of water in our hands. We stand a meter from the sofa and turn our backs to it. We take one leg back and press the top of the foot into the seat. Straighten your shoulders, slightly bend your lower back forward. As you inhale, lower your pelvis until your thigh is parallel to the floor, and as you exhale, straighten up. After completing the set, change the position of the legs and repeat.
- Pistol squats (3x15). First you need to master the technique of exercising with your own weight. After this, you can add weights in the form of weights to your back. We stand with our right side to the window sill or any stable piece of furniture and place our hand on it. We lift the left foot and hold it in weight, trying to completely straighten the knee. Slowly squat on your right leg and simultaneously raise your left leg to a horizontal position. Having reached the bottom point, we begin to rise smoothly. Having completed the set, turn your left side towards the support and repeat.
- Deadlift (3x15). We stand up straight, place our feet close (10–15 cm). We take one kettlebell or a heavy dumbbell in our hands and lower the apparatus to the groin. Straighten your shoulders and slightly bend your lumbar region. As you inhale, gently bend over and lower the load below your knees. At the same time, slightly bend your legs. As you exhale, we slowly rise. When performing, we do not lower our heads, we constantly look forward.
- “Chair” or “wall” (3 sets of 1 minute). Press your back against the wall and smoothly lower your body until a right angle is formed between your shins and thighs. Place your palms on your kneecaps. Maintain this position for 60 seconds.
You should train according to the program no more than 2 times a week. Between classes you need to take breaks of 1-2 days.
In addition to home exercises, we recommend doing 1 intensive workout at the stadium: acceleration, jumping over barriers, running up the stairs of the stands, etc. Additional loads will help reduce fat and strengthen the muscles and ligaments of the lower body.