general information
The flexor carpi ulnaris has a complex structure and performs many functions.
The tendon has two heads:
- humeral, which is located in the medial epicondyle of the shoulder in the fascia of the forearm,
- ulna, the process originates at the elbow, which is located in the proximal two-thirds of the posterior edge of the ulna, covering the arm in the region of the fascia of the forearm.
The extensor radialis brevis is attached at the pisiform bone above the pisiform-uncinate ligament to the hamate bone and above the pisiform metacarpal ligament to the base of the fifth metacarpal bone.
The functions of the flexor are very diverse:
- flexion at the wrist joint,
- elbow abduction,
- forearm flexion.
The elbow serves as a flexor of the joint, in which it is significantly assisted by the flexor carpi ulnaris.
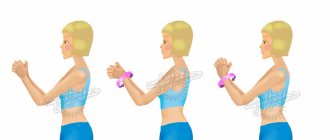
Extension of the arms at the wrists with an overhand grip of the bar[edit | edit code]
Extension of the arms at the wrists with an overhand grip of the barbell
- Isolated/single-joint
- Traction
- Open circuit
- With a barbell
- Beginner and advanced levels of fitness
This exercise is ideally combined with the exercise “bending the arms at the wrists with an underhand grip of the barbell.”
Brief description of the exercise
Extend your wrists with the backs of your hands facing you as you lift the barbell. Return to the starting position and repeat the exercise.
Stabilizing muscles
- General stabilization of the torso.
INITIAL POSITION
- Sitting forward. Take the barbell with a narrow overhand grip or a medium grip, shoulder-width apart.
- Rest the outer surface of your forearms on your thighs so that your hands hang from your knees.
Tips on proper exercise technique
:
- Maintain a balanced posture; the spine is in a neutral position.
- Perform a slow, controlled movement, do not use inertial force.
| Motion Analysis | Joint |
| Joints | Radiocarpal |
| Directions of joint movements | Up - extension Down - flexion |
| Mobilizing muscles | Extensor carpi radialis longus Extensor carpi radialis brevis Extensor carpi ulnaris |
How to pump up
The flexor carpi ulnaris can be pumped up even at home. This does not require special simulators or equipment. Yoga classes give the best effect.
Many people are interested in the question: how to pump up a tendon. This is required during intense physical activity, as well as during excessive weakness, if a person cannot even do everyday work. To do this, you can do a simple exercise: clench your fists and stretch your arms forward, then raise your arms and lower them, straining your hands. It's good if you can touch your forearms with your fists.
You can also pump up this tendon using acupressure. It needs to be done every day for the best effect. The procedure will make your hands stronger and keep your muscles in good shape. In this case, the impact is carried out on the area located at the base of the palm between two small bones. It is best to do this massage twice or thrice a day.
In bodybuilding, the best impact comes from push-ups and exercises with dumbbells. You should not expect quick results; the effect will be visible only after 1-2 months of training. An expander also works well. When choosing, it is better to choose a round one with a hole inside. A combination of soft and hard expanders is effective. The first is used for warming up, and the second for direct work. Spring expanders with a stiffness adjustment system are also suitable for professionals.
You can use a small expander anywhere at any time, but to begin with, you should not strain your hand for more than 15 minutes.
Read also[edit | edit code]
- Biceps - exercises and training features
- Dumbbell biceps curl
- How to create a training program
- The best training programs for mass
- Barbell Curl
- Standing barbell curl for girls
- Crossover Curl
- Hammer grip dumbbell curls
- Seated dumbbell curl
- Seated dumbbell curls for girls
- Incline Dumbbell Curl
- Scott Bench Curls
- Seated biceps curl
- Barbell curl
Why does the tendon hurt?
If the elbow flexor becomes overstrained or otherwise damaged, tendinitis can develop. In this case, swelling develops, small cracks appear, which destroy the mucous membrane. If measures are not taken in time, the tendon may collapse and lose its function. It most often suffers from lateral epicondylitis, also called “tennis elbow.” In this case, the person suffers from severe pain in the epicondyle of the shoulder. This injury can occur due to chronic fatigue and overuse of the tendon. This injury often occurs in golfers as well.
Read also: Maclura or Adam's apple: recipes and methods for treating joints
Safety
To protect your own muscles and joints from possible injuries, you need to thoroughly study the technique of this exercise. In addition, it is important to use light weight. In no case should you “be a hero” with a heavy barbell or massive dumbbells. You can only do a few repetitions, after which your arms will quickly become tired or even injured.
In order for the muscles to receive additional protection from injury, you need to minimize any weight swinging . It is important to hold the barbell firmly, preventing it from moving from side to side. If it suddenly starts to fall, the athlete will have to make sudden movements to return it to its normal position. In this exercise, any jerk, even a small one, can lead to injury.
Rehabilitation
Flexor carpi ulnaris is treated using traditional methods. If you suffer from severe pain, you can reduce it with the help of pain-relieving ointments: Troxevasin, Rescuer, etc.
During rehabilitation, his condition is controlled:
- supination of the hand on a flat plane (for example, on a table),
- stabilization of the side directed upward against gravity,
- bending the wrist (while keeping the fingers down).
This test makes it possible to assess the condition of the flexor, since it clearly protrudes on the surface of the forearm.
Repair involves innervation of the ulnar nerve. The mobility test is performed towards the forearm. One hand fixes the forearm, and the other resists the elevation of the little finger. The doctor palpates the tendon on the hand from the inside and assesses the degree of its recovery.
Common mistakes
A significant portion of all errors in barbell wrist extensions involve excessive body swing . Some athletes, having taken on too much weight, try to lift it using the strength of their legs and back muscles. This leads to the fact that a significant part of the load from the arms is transferred to the back, and the exercise loses its effectiveness. In addition, such movements can harm your posture, so it is better to work with less weight.
Many people forget about doing a light warm-up. To prepare your wrists for work, you need to perform rotational movements with your hands. This will help warm up the joint and also protect you from all kinds of injuries.
There is no need to make unnecessary movements with your hands . Beginners find that their wrists will be subject to more stress if they move from side to side. In fact, it turns out the opposite - the effectiveness of the exercise decreases, and the joint gets tired very quickly, and the athlete cannot complete the set efficiently.
Participation in sports
The tendon, as the main flexor of the hand, performs both static and dynamic loads. It does static work in fencing, tennis, and hammer throwing. Dynamic work is more varied. It is required during handball, weightlifting, kayaking, crawl swimming, gymnastics, etc. The ulnar abduction function is used in breaststroke swimming. As a flexor of the forearm, the tendon takes part in the work during:
- rock climbing,
- gymnastics,
- boxing,
- handball,
- cycling,
- judo, etc.
Recommendations
- You can place your hands on the bench or rest them on your knees - both options are correct. Everyone chooses for themselves what is more convenient for them.
- Another option is to squat in front of a bench, place your elbows on the bench and pick up a barbell. This technique is used when the width of the bench is not enough to sit comfortably and spread your arms.
- During execution, you need to watch your elbows. They should remain in one position, the entire movement being performed only by flexing and extending the wrist.
- The exercise is performed with the wrist joint; the biceps and shoulders are not involved in the work.
- If the athlete helps himself with his body, swings or brings his elbows forward, you should take less weight, as this indicates too much stress on the forearm.
- The movement when lifting the barbell should be concentrated, without jerking or swinging the body. The whole body is static during execution, only the wrists work.
What are the benefits of forearm and hand exercises?
Many athletes, intensively working their triceps and biceps, do not pay enough attention to their wrists and forearms. Remaining undeveloped, they prevent the athlete from realizing his full potential. Thanks to the forearms and wrists, the most effective exercises are carried out on the deltoids, biceps, triceps, back, and chest. They must be strengthened and become part of every training.
Complaints regarding weak and thin arms are primarily associated with a lack of proper attention to this part of the upper body. This also applies to the legs, by the way. If they are not developed, they remain underdeveloped. Changing the position allows you to constantly work on your hands. It is necessary to perform wrist exercises regularly, and then even weak and undeveloped wrists and forearms will become stronger
Exercise "mower"
To complete this complex there is another “retro movement”. Imagine that you have a scythe in your hands and swing this tool. The torso should be motionless. The exercise can be performed either standing still or while moving. I’ll add on my own that when I had the opportunity to work with a real scythe, the next day I learned that I had many muscles that I didn’t even know existed. Working with a scythe is a very challenging and useful exercise that allows you to work the deep muscles of the spine.
And finally – about pleasant things.
The exercise section of the “Book of Health” is not limited to these six numbers. This means there are new old exercises ahead. Tags:
- Story
- Exercises
Exercise "sawyer"
The next exercise is also unusual for a modern person. Nowadays, few people use wood for heating, and in those years there was even a special profession - a wood cutter. Let's get started. We bend the torso forward, one arm is pulled up to the armpit, the other is straightened forward and down. We change the position of our hands: with one hand we seem to be pulling something towards ourselves, with the other we are pushing away. During this exercise, all the muscles of the arms, shoulders and back work comprehensively.
Diagnostics
The first suspicion appears upon detailed questioning and visual inspection. The most painful point during palpation is localized just between the lunate and the head of the ulna; pain intensifies when the hand deviates to the ulnar side and attempts to pronate/supinate.
On an x-ray you may not see any destructive changes, but you can see the same anatomical feature - the long ulnar bone (positive ulnar variance).
The diagnosis can be accurately confirmed after performing an MRI - an area of local swelling on the lunate bone will be visible.
Here it is very important to distinguish limited bone swelling from the total one that we see with Kienböck’s disease. In the case of lunate-ulnar impingement, a so-called “kissing lesion” is noted. That is, there is a slight swelling on both the lunate and the head of the ulna.
Equipment
To perform extensions with a barbell, you will need a comfortable horizontal bench, a curved or straight bar, as well as weight discs. Instead of a barbell, you can use dumbbells. They will allow you to better develop your technique.
In some cases, athletes are advised to wrap elastic bandages around their wrists. This is especially true when working with very heavy weights, which can stretch ligaments and damage the joint. Also, those athletes who have had injuries in the past should not exercise without elastic bandages.
Physical therapy
The goal of any rehabilitation program is to provide a gradually increasing controlled stress that stimulates differential tendon gliding and controls early collagen deposition; helps to strengthen the site of the operation; avoid formation of adhesion, seam dehiscence or re-rupture. It has been shown in animal models that movement and tension ultimately increase strength. Specific programs have emerged that include a combination of passive and active exercises to restore range of motion.
Friends, Anna Ovsyannikova’s seminar “Rehabilitation of the hand after a fracture of the distal radius (fracture of the “radius in a typical place”) and fractures of the metacarpal bones” will take place very soon. Find out more...
Early physical therapy and splinting after flexor tendon repair are important for
- improving tendon healing;
- increasing tensile strength;
- reducing adhesion formation;
- Early restoration of function, reduction of stiffness and deformity.
Once recovery has been optimized, the team of therapists works with the surgeon to select a rehabilitation plan that protects the injured site while still helping to maintain tendon gliding. There are 3 types of rehabilitation programs designed for repaired flexor tendons: delayed mobilization, early passive mobilization, or early active mobilization. The first part of the process is to ensure that a thorough assessment has been carried out.
Physiotherapeutic protocols
- Immobilization: Indicated for children and non-compliant patients.
- Splints/splints are applied to the wrist and metacarpophalangeal joints in a flexion position, while the interphalangeal joints are in extension.
- Early passive movement: Duran protocol: low force and low excursion; active finger extension with passive finger flexion with patient assistance and a static splint.
- Kleinert protocol: low force and low excursion; active extension of the fingers with dynamic passive flexion of the fingers using a splint.
- Mayo synergic splint: low force and high tendon excursion; active wrist movement is added, which increases the mobility of the flexor tendon to the greatest extent.
- Early active movement: Moderate strength and potentially high excursion.
- Dorsal locking splint that limits wrist extension.
- Performing “place and hold” exercises with your fingers.
It is not necessary to follow all directives exactly. Many factors influence therapeutic decisions, depending on tendon healing, the presence of swelling, and tendon adhesion. These factors can help guide the repair process and promote functional range of motion, safely mobilize the repaired tendons, and prevent dehiscence, rupture, and or adhesions.