Aspartic acid (D-Aspartic Acid, abbreviated as DAA) is a non-essential amino acid that is genetically encoded in the human body. Other names: aspartate, or aminosuccinic acid. It can be found in all living organisms, both as part of protein compounds and in free form. Nutritional supplements with this substance are necessary for the normal functioning of several organ systems. Aspartic acid plays the role of a neurotransmitter in the central nervous system and also stimulates the production of a group of important hormones.
Aspartic acid: synthesis, formation
The process of synthesis of aspartic acid by a living organism occurs by converting the essential amino acid threonine into an isomer of another amino acid - homoserine with further oxidative reactions.
The substance was first discovered at the beginning of the 19th century. Scientists Etienne Ossiana Henry and Auguste-Arthur Plisson obtained the acid as a result of the reaction of the substance asparagine with water in the presence of strong mineral acids. Previously, asparagine was isolated from asparagus juice by boiling. A few years later, aspartic acid was recognized as the most important component of proteins.
In modern production, the amino acid is obtained by condensation of several esters (acetaminomalonic acid and chloroacetic acid). The carboxyl group is removed from the resulting products, followed by hydrolysis.
To compensate for the lack of aspartic acid in the body, you can eat certain foods: meat, cane, asparagus, oatmeal, avocado, soybeans. This food contains too little amino acid, so only dietary supplements with a high concentration of the substance are suitable for medicinal purposes.
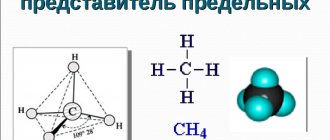
Aspartic acid: formula
The formula for aspartic acid was discovered in 1833 by the scientist J. Liebig. It has the form C4 H7 NO4.
The structural formula of the acid is as follows. You need to know that aspartic acid has several forms that differ in structure: L and D forms. The first is found in the human body in large quantities, and the second is found only in adults.
Despite its general functions, L-aspartic acid is responsible for protein synthesis and removal of toxic substances, and the D form normalizes brain function and stimulates hormone production. Such differentiation is not particularly important, because when the L-form enters the body, it is transformed into the D-amino acid isomer.
Characteristic
The chemical formula of aspartic acid is transparent crystals. The substance has other names - aminosuccinic acid, aspartate, aminobutanedioic acid.
Aspartic acid reaches its maximum concentration in brain cells. Thanks to the stimulating effect on cells, the central nervous system improves the ability to assimilate information.
By interacting with phenylalanine, aspartate forms a new compound used as a food sweetener - aspartame. It is an irritant to the nervous system, therefore supplements containing it are not recommended for use in children whose nervous system is not fully formed.
Aspartic acid: composition
The composition of dietary supplements with aspartic acid is quite simple: they contain only one component that affects hormone levels and other indicators. The high concentration of acid allows you to achieve maximum effect in a short period of time.
Depending on the type of production, the preparations may contain additional ingredients - residual products. For example, wheat, milk, peanuts, herbs and more. They are harmless to the body and are contained in very small quantities, which does not affect the properties of the supplement in any way.
Aspartic acid: properties
The properties of aspartic acid are widely known to various categories of people: athletes, men and women with sexual problems or impaired cognitive functions.
The positive properties of aspartic amino acid include:
- is a component of proteins that serve as material for building cells;
- normalizes the functioning of the endocrine system through interaction with the hypothalamus;
- promotes the production of somatropin (growth hormone) and the main sex hormones of men and women (testosterone, progesterone);
- plays the role of a neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, improves brain function;
- has antibactericidal properties;
- necessary for the formation of other amino acids, such as lysine, methionine, arginine;
- promotes the movement of mineral compounds that support the normal functioning of RNA and DNA;
- enhances the protective function of the immune system;
- prevents the proliferation of microorganisms and neutralizes their toxic effects by increasing the production of antibodies;
- rids the body of nitrogen metabolism products, including ammonia;
- protects nerve cells from pathogenic effects;
- fights mental disorders, depressed mood;
- increases muscle mass.
It is worth noting that aspartic acid undergoes an oxidation stage in mitochondria, forming the energy necessary for the body. This amino acid is not only a source of energy, but also the most important energy stimulator of the brain.
Aspartic acid: application
Aspartic acid is used in several completely different cases, such as:
- depression (you can also get rid of it with fish oil, ademetionine, phosphatidylserine);
- cognitive disorders (impaired thinking, memory impairment);
- erectile dysfunction and decreased sexual activity;
- for the purpose of building muscles for athletes;
- hormonal imbalance (hormone deficiency);
- CNS disorders;
- for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases;
- visual impairment (myopia, nyctalopia);
- toxic liver contamination;
- chronic fatigue syndrome;
- postoperative period or recovery after a serious illness.
It is important that with an insufficient amount of amino acid in the body, patients experience memory impairment, a depressed state and a reluctance to engage in vigorous activity. However, with an increased amount of the substance in the body, a person feels nervous and aggressive, and is unable to control emotions. There are even changes in blood density, which often causes blood clots in the blood vessels.
Typically, the use of aspartic acid is necessary for all people after 40 years of age. At this age, even in a healthy person, its level begins to decrease. Therefore, in order to prevent possible diseases, it is advisable to take acid without a good reason.
Food Sources of Acid
Despite the fact that the body produces the amino acid independently during normal functioning, during intense training the need for its concentration increases. You can get it by eating legumes, avocados, nuts, unsweetened fruit juices, beef and poultry.
© nipadahong — stock.adobe.com
Aspartic acid: testosterone
Scientists have proven that aspartic acid regulates the synthesis of testosterone, the main male sex hormone. This biologically active substance affects not only the production of sperm, but also the development of muscles and bones, and is capable of establishing an emotional background.
The increase in this hormone was first studied in studies on rats. A few years later, the effectiveness of aspartic acid was confirmed once again, but in this case the substance was taken by people. Thus, after 12 days of consuming the daily norm of aspartate , the level of the male hormone increased by almost half, which became a landmark discovery in the world of medicine.
The amino acid can also increase the production of its own gonadotropin. This hormone is produced in the body of a pregnant woman, as well as in the anterior pituitary gland in all people. It has a stimulating effect on the synthesis of male reproductive cells and is necessary for the normal development of the organs of the reproductive system.
For male hormones, it is beneficial to take bee pollen and pregnenolone. For elevated testosterone levels, inositol is prescribed.
Mechanism of action
Unsaturated fatty acids of the omega-3 family (eicosapentaenoic acid-era, docosahexaenoic acid-dha, alpha-linolenic acid-ala) (venous blood) in the istra
The perceived sweetness of aspartame (and other sweet substances such as acesulfame K) in humans is due to its binding to a heterodimeric G protein-coupled receptor formed by the TAS1R2 and TAS1R3 proteins. Aspartame is not recognized by rodents due to differences in taste buds.
Metabolites
Aspartame is rapidly hydrolyzed in the small intestine. Even when taking very high doses of aspartame (more than 200 mg/kg), aspartame is not detectable in the blood due to rapid breakdown. When ingested, aspartame breaks down into residual components including aspartic acid, phenylalanine, methanol, and other breakdown products including formaldehyde and formic acid. Human studies show that formic acid is eliminated from the body faster than it is produced after taking aspartame. In some fruit juices, higher
concentrations of methanol can be found than the amount produced from aspartame in drinks.
The main degradation products of aspartame are its cyclic dipeptide (in the form of 2,5-diketopiperazine or DKP), the non-esterified dipeptide (aspartylphenylalanine) and its constituent components, phenylalanine, aspartic acid and methanol. At 180 °C, aspartame decomposes to form the diketopiperazine derivative.
Aspartate
Aspartic acid (aspartate) is one of the most abundant amino acids in a typical diet. As with methanol and phenylalanine, aspartic acid intake from aspartame is less than would be expected from other food sources. At the 90th percentile of intake, aspartame provides only 1% to 2% of the daily value of aspartic acid. It has been suggested that aspartame, when combined with other amino acids such as glutamate, may cause excitotoxicity, causing damage to the brain and nerve cells. However, clinical studies have shown no evidence of neurotoxicity, and metabolic studies indicate that it is not possible to ingest enough aspartic acid and glutamate in food and drink to levels expected to be toxic.
Methanol
Methanol produced by metabolism of aspartame is absorbed and quickly converted to formaldehyde and then completely oxidized to formic acid. Methanol from aspartame is unlikely to pose a safety risk for several reasons. Fruit juices and citrus fruits contain methanol, and there are other dietary sources of methanol, such as fermented drinks, and the amount of methanol produced from aspartame-sweetened foods and drinks is likely to be less than from these and other sources already found in humans. diets. As for formaldehyde, it is quickly converted in the body, and the amount of formaldehyde resulting from the metabolism of aspartame is negligible compared to the amounts normally produced by the human body and other foods and drugs. At the highest expected levels of human aspartame consumption, there are no elevated levels of methanol or formic acid in the blood, and taking aspartame at the 90th percentile of intake would produce 25 times less methanol than what is considered toxic.
Complete course of biochemistry
| Reagent | Metabolite | Percentage of reagent metabolized | Half life | Mechanism |
| Aspartame | Phenylethylamine | 50% | "Swift" | |
| Aspartame | Aspartic acid (aspartate) | 40% | "Swift" | |
| Aspartame | Methanol | 10% | "Swift" | |
| Methanol | Formaldehyde | 100% | 142 min. | Alcohol dehydrogenase |
| Formaldehyde | Formic acid | 100% | 1 minute | Catalase-peroxide system, mixed cytochrome P450 oxidase system, alcohol dehydrogenase |
| Phenylethylamine | Phenylalanine | 100% | — | Decarboxylation of phenylalanine |
| Phenylalanine | Phenylpyruvate (PPA) | |||
| Phenylpyruvate | Phenyl lactate (PLA) | |||
| Phenylpyruvate | Phenylacetate (PAA) | Decarboxylation via the Ehrlich pathway | ||
| Phenylalanine | Acetoacetic acid | 50% | ||
| Phenylalanine | Fumaric acid | 50% | ||
| Phenyl lactate (PLA) | Phenyllactic acid | Lactate dehydrogenase | ||
| Phenylalanine | Tyrosine | Phenylalanine hydroxylase |
Aspartic acid: libido, erection
To restore libido and normalize erection, you need aspartic acid . This is due to the fact that it increases the natural production of sex hormones, which significantly affect sexual function.
Decreased libido, as well as enlarged breasts in men and prostate disease occur due to increased estrogen levels. This happens extremely rarely, but it significantly disrupts sex life. Aspartic acid will help combat this . Both men and women can take the substance. Over time, sexual desire will resume and the previous quality of life will be restored.
Acetyl L-carnitine, pycnogenol, curcumin, Tongkat Ali and yohimbe are also suitable for restoring male erection.
Side effects
Features of flaxseed flour: benefits and harms, side effects. product use: how to take flaxseed meal to your advantage
When taking the drug in a dosage of no more than 3 g per day, no side effects were observed. When studying electrolytes, liver enzymes, glucose, urea, creatinine, all indicators were within the physiological norm.
Recently, a study published in the Annals of Pharmacotherapy found the opposite. Researchers at the University of Texas at Galveston conducted an eight-year study of 420 men over 66 years of age who were treated with testosterone. During the study period, their medical development was compared with that of a control group of participants of the same age, ethnicity, and health data. In contrast, men who were more likely to have cardiovascular problems due to other factors had lower rates of heart problems.
Meanwhile, undesirable reactions are possible, and they are associated with the main effect of the drug: an increase in the synthesis of sex hormones and their associated imbalance.
An increase in dihydrotestosterone can lead to hair loss and acne.
An increase in general excitability up to uncontrolled aggression is possible.
We must wait for further research
It's important to emphasize that we still have little research with them, and the answers vary. There are patients who show improvement and others who do not.
However, it is a less risky way to mimic testosterone, especially in patients who do not have a proven laboratory deficiency and who want to have better training performance. Improves libido and erection. Increases endurance and muscle mass. Improving spermatogenesis and regulating ovulation.
Natural Asia. Its roots resemble the human form, which made the ancients think that this plant would cure all diseases. The Chinese see him as the king of plants, who brings longevity, strength and joy. Actions are postulated, but few studies fail to try. Reduces alcohol toxicity: reduces gastric absorption, increases dehydrogenase activity, increases excretion. Improved respiratory function: in patients with chronic respiratory disease. Reduces cholesterol: activates lipase, reduces cholesterol and triglycerides.
Hormonal imbalance can lead to an increase in the production of progesterone, which increases cortisol, which leads to the active formation of fat tissue at the expense of muscle tissue.
An increase in estrogen levels can lead to phenomena such as prostate disease, gynecomastia (female breast enlargement in men) and decreased libido.
Increased Fertility: Increases gamete resistance, sperm count, sperm motility and sperm count. Improved erectile function: endothelial relaxation factor, improved neuromuscular response. Improvement of menopausal symptoms: reduces fatigue, bad mood, depression. Hypoglycemic: Reduces glucose levels in type 2 diabetes by increasing insulin secretion and increasing cellular insulin receptors, increasing glucose metabolism. Presentation: Dry extract standardized to 3.0% ginsenosides Side effects: Rare cases of mild and transient gastrointestinal reactions and insomnia, possibly related to ginseng, have been reported.
An increase in prolactin levels is possible, which is extremely undesirable for men, because libido decreases and gynecomastia occurs.
Aspartic acid: bodybuilding
Aspartic acid is often used in bodybuilding by professional athletes to quickly build muscle mass. With its help, they regulate the functioning of the endocrine system, namely the production of growth hormone and testosterone, a hormonal factor for muscle growth. Athletes often take the more well-known herbal dietary supplement Tribulus.
Aspartic acid is necessary not only for those who want to have a sculpted, pumped up body. Its regular use will help achieve high results in powerlifting, where the main role is played by the athlete’s strength indicators. During preparation for competitions or active training, this substance must be taken. The first positive changes will appear in the loss of excess weight and increased endurance during active physical activity.
Casein, glycine and alpha-lipoic acid are used as fat burners and also for muscle building. Citrulline is especially important, increasing the duration of training and restoring muscles.
Aspartic acid: preparations
1). There are many drugs containing D-aspartic acid . The leading position among them is D-Aspartic Acid (100 g, 0.22 lb) from AI Sports Nutrition . This is a natural dietary supplement that can increase blood testosterone levels by 42% in less than 2 weeks.
Recommendations for use of the additive:
- permissible dose – 3 g;
- take once in the morning after waking up;
- prohibited for children under 18 years of age, pregnant women or during lactation;
- be sure to consult a doctor if you have additional diseases or if your relatives have them;
- an excessive dosage can provoke myocardial infarction or stroke, as well as other serious health problems;
- If negative symptoms appear (headache, dizziness, rapid heart rate), go to the hospital.
Interactions with hormones
Pituitary hormones
The accumulation of D-aspartic acid in the adenohypophysis (anterior pituitary gland) causes an increase in the rate of secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone, growth hormone and prolactin releasing factors, which cause the production of luteinizing hormone, follicle stimulating hormone, growth hormone and prolactin, respectively.
Pineal gland hormones
In the pineal gland, where D-aspartate reaches its highest concentrations, it acts as a regulator of melatonin secretion. The study initially incubated 10 µM norepinephrine with pinealocytes, which confirmed that melatonin is synthesized in response to norepinephrine, and that this synthesis is reduced by D-aspartate incubation (down to 20% of control values at 0.2 mM). L-aspartate also has the ability to inhibit melatonin synthesis, but at the same concentrations it is slightly weaker. D-aspartate can be synthesized in the pineal gland (which expresses aspartate racemase but more likely acts as a D-aspartate sequester outside the cell) and then secreted out of the cell via the sodium-dependent glutamate/aspartate transporter present on pinealocytes, which react to D-aspartate; it then acts on receptors coupled to inhibitory Gi receptors and inhibits melatonin synthesis. D-aspartate can then pass through GLT-1 back into pinelocytes, preventing excessive signaling - thus acting as a regulator of melatonin synthesis. It is currently unknown whether D-aspartic acid supplementation affects these processes. D-aspartic acid is involved in the circadian rhythm of melatonin, stored in the pineal gland and released when necessary to suppress melatonin synthesis. The practical relevance of D-AA is currently unknown.
Testosterone
D-aspartic acid causes an increase in testosterone synthesis through increased activity of mRNA that produces a compound called StAR (Steroidogenic acute regulatory protein). StAR regulates androgen synthesis in Leydig cells. Secretion of hypothalamic LH (from excess active N-methyl-D-aspartate neurons) also induces testosterone synthesis in Leydig cells, and may be a mechanism by which D-aspartic acid influences testosterone synthesis. D-aspartic acid may directly increase testosterone synthesis by increasing the activity of the StAR enzyme, and indirectly by stimulating the release of luteinizing hormone in the hypothalamus. A study conducted over 12 days found that D-aspartic acid supplementation (brand DADAVIT) increased testosterone levels by 15% after six days and 42% after twelve days relative to baseline levels (initial levels dropped to 22% after three days). discontinuation of use). This study was replicated again - a dose of 2.66 g of D-aspartic acid (DADAVIT) was able to increase testosterone levels in infertile men by 30-60% after 90 days. Another study of athletes taking D-aspartic acid supplements at 3 grams per day for 28 days found no increase in testosterone levels when measured at day 28. This study noted a statistically significant induction of serum D-aspartate oxidase, which is responsible for the breakdown of D-aspartate; this suggests that a form of negative feedback may be possible, and aromatase (which can also be induced by D-aspartic acid) does not make significant changes since estrogens remain unchanged. Short-term use of D-aspartic acid increases testosterone levels, but long-term use is associated with both an increase and a maintenance of the same level. Induction (increase) of the enzyme that breaks down D-aspartic acid indicates a negative effect; it is likely that this downregulation occurs in athletes (with normal to high testosterone levels) and is not observed in infertile men (with low testosterone levels), since the second group shows a long-term increase in testosterone levels.
Estrogen
Taking a 3g D-aspartic acid supplement in trained athletes, along with strength training, for 28 days does not significantly change circulating estrogen levels. No significant changes were found in circulating estrogen levels in otherwise healthy men.
Aspartic acid: Primaforce
2). Primaforce is a dietary supplement containing D-Aspartic Acid (DAA, D-Aspartic Acid) (100 g). As a result of testing, this product has proven its effectiveness and ability to increase testosterone levels, as well as speed up recovery after illness and surgery.
Recommendations for use: take 3 g (1 scoop) with your first meal. You need to know that the preparation may contain residues of some products: wheat, milk, soybeans, herbs, eggs, seafood, peanuts.
Aspartic acid: in the pharmacy
Pharmacy products are not always of high quality and original. This is the situation with aspartic acid : it is difficult to buy in a pharmacy. There is a chance to purchase an expensive remedy from domestic manufacturers, but this medicine will not help solve existing problems due to the low concentration of the amino acid itself.
The only option is to turn to online pharmacies, where official representatives of world pharmaceutical companies present a natural product. A link to such a site is given below.
Aspartic acid: instructions
There is nothing complicated in the instructions for using aspartic acid
- should be stored in a dark place, avoiding direct sunlight;
- keep away from children;
- follow the indicated dosage;
- Before use, be sure to consult a doctor.
Aspartic acid: how to take
The dose safe for the body is 3 g (1 false measure) of aspartic acid . The dose can be divided into several times: in the morning immediately after sleep, before lunch and before the last meal.
drink aspartic acid for 2-3 weeks, then take a week break. This cyclic scheme is the most effective for obtaining the desired effect.
The doctor may also prescribe an increased dose depending on the purpose of taking the amino acid. An increased dosage is necessary for people with severe nervous disorders, depression, abnormalities in brain function, and poor memory. Regular use of the drug can solve these problems.
Culture media for parenteral nutrition
Amino acids (protein nutrition)
Currently, amino acid mixtures are used for parenteral nutrition.
Solutions of protein hydrolysates, blood, native blood, plasma albumin are not currently used for parenteral nutrition, because The breakdown of protein molecules into amino acids occurs very slowly, for example, the half-life of albumin is 20 days. Amino acids
| Essential amino acids | Nonessential amino acids |
| Valin | Alanin |
| Leucine | Glycine |
| Isoleucine | Histidine |
| Phenylalanine | Arginine |
| Threonine | Aspartic acid |
| Lysine | Cystine |
| Tryptophan | Cysteine |
| Methionine | Glutamic acid |
| Proline | |
| Serin | |
| Tyrosine |
Amino acid solutions for parenteral nutrition can be divided into several groups.
- General solutions
- Solutions used for liver diseases
- Solutions used for kidney disease General solutions include both essential and essential amino acids in various proportions and with different concentrations of total nitrogen. Solutions with concentrations from 3 – 5% to 8 – 10% are used. These include vamine, aminosteril, infezol, aminosol, aminoplasmal.
Characteristics of some general amino acid solutions (see table)
For kidney diseases in animals that occur with renal failure, when limiting the amount of protein is required, the most effective is the use of amino acid solutions of 8 essential amino acids and histidine - aminosteril Nefro.
Characteristics of some amino acid solutions for patients with kidney pathology (see table)
Research by a number of authors has shown that in sick animals with liver disease, protein metabolic products, aromatic amino acids, methyl mercoptans, serotann, and ammonium contribute to the development of hepatic encephalopathy. The risk of encephalopathy can be reduced by reducing the amount of protein infused or by using special formulas enriched with branched chain amino acids - aminosteril Hepa.
Characteristics of some amino acid solutions for patients with liver diseases (see table)
Carbohydrates
For the full use of protein for plastic purposes, it is necessary that each gram of introduced nitrogen is provided with 150 calories of energy (4). These calories must be provided by non-protein sources of energy - calories from fats and carbohydrates. When choosing carbohydrates for parenteral nutrition, preference is given to glucose, not only because of its low price and availability, but also because it is an indispensable metabolite for the nervous system and other glucose-dependent tissues.
Fats
They are the main energy carrier of the body. Parenteral administration of fats is possible only in the form of a special emulsion.
Advantages of fat emulsions in parenteral nutrition
- High energy value
- No overload of the circulatory system with excess fluid
- Providing the body with essential fatty acids, especially linoleic and linolenic acids, which support the functional ability of cell membranes and stimulate wound healing.
Fat emulsions for parenteral nutrition – lipofundin and intralipid 10% and 20%.
Composition of fat emulsions (see table).
Water and electrolytes
Water is a natural part of all parenteral nutrition preparations and accounting for the volume of fluid administered is an important component. (4) Up to 30–40 ml should be administered per 1 kilogram of animal body weight per day plus visible losses (vomiting, diarrhea). Liquid volumes should be administered in the form of electrolyte solutions - Ringer, Hartmann.
Vitamins
When implementing a parenteral nutrition program, you should remember to include vitamins in its composition, most of which are stimulants of protein biosynthesis and enter the body only from the external environment.
A cat's vitamin needs per body weight per day (see table).
The MJ metabolic energy requirements of growing dogs and cats as determined by the National Research Council (NRC). (see table).
In our clinic, when providing intensive care to cats after massive surgical interventions, polytraumas, or severe infectious diseases, nutritional support in the form of parenteral nutrition is always used.
Aspartic acid: contraindications
Aspartic acid is contraindicated:
- minors, especially children, whose nervous system is too susceptible to such dietary supplements (also in childhood there is a risk of addiction to the drug);
- pregnant women and during breastfeeding (may provoke autistic disorder in the fetus);
- hypersensitivity to the components of the supplement.
The need to take an amino acid is also reduced when:
- hormonal disorders characterized by excessive production of substances;
- atherosclerosis and pathology of blood vessels;
- high blood pressure.
With excessive dosage or improper use of the drug, an allergic rash, skin irritation, insomnia, and headache may occur. To avoid side effects, you should consult a doctor before use or use only natural products with aspartic acid that are not addictive.
Aspartic acid: price
Prices for aspartic acid are quite high, but in online stores you can buy dietary supplements 1.5-3 times cheaper. At the same time, the product is of high quality and corresponds to customer reviews. They sell original nutritional supplements, vitamins, drugs, such as coenzyme Q10, rutin, choline, manuka honey, silymarin and much more. Quality guaranteed.
Asparagine synthesis
Aspartic acid is a source of asparagine, acquiring an additional amine group NH2. It would seem simpler: take ammonia, which is always abundant and which simply needs to be neutralized, add it to aspartic acid - and here it is, asparagine.
Such a reaction really exists. It occurs with the participation of ATP under the action of the enzyme Ammonia-Dependent Asparagine Synthetase in many bacteria. Regarding humans, the opinions of luminaries differ: some believe that this reaction is not characteristic of higher animals, others argue the opposite. One thing is certain: direct synthesis of asparagine from aspartic acid and ammonia is not leading in humans. In humans, a predominantly different reaction occurs: see below.
Glutamine acts as a donor of the amine group for the synthesis of asparagine in human cells. With the participation of the enzyme Glutamine-Dependent Asparagine Synthetase, it donates one amine head to aspartic acid, and itself is converted into glutamic acid. The reaction occurs with the participation of ATP, from which two phosphoric acid residues are split off, and ATP is converted into AMP. Asparagine synthesis is an energy-intensive process that requires chemical energy stored in the phosphorus bonds of ATP.