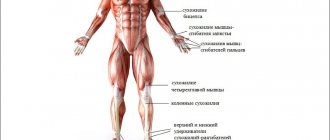
What vitamins are necessary for athletes
- B vitamins. Normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, stabilize metabolic processes. They have a positive effect on the nervous system and accelerate the growth of muscle mass.
- Vitamin A. Normal concentration of vitamin A is necessary for the production of collagen, glycogen synthesis, and acceleration of tissue regeneration. In addition, the element increases the body's endurance, accelerates muscle growth and the recovery period after exercise.
- Vitamin D. Improves the absorption of calcium and phosphorus. Increases bone density and strength.
- Vitamin E. Participates in activating the production of your own testosterone. Normalizes metabolic processes in the body, increases endurance, and adds energy.
- Vitamin C. Improves the absorption of iron and protein, activates the production of collagen and testosterone. Accelerates the recovery process after training and strengthens the immune system.
What are the benefits of women's sports vitamins?
Vitamins for women are very important not only for general well-being, health and functioning of all internal organs, but also for beauty, youth and longevity. And when we are talking about athletes, in this case the consumption of special vitamin complexes is simply necessary so as not to deplete the body with grueling loads.
What are the benefits of taking special vitamin complexes for female athletes? First of all, such complexes help to increase energy and performance, thereby improving the effect of training, and it does not matter whether it is aimed at gaining mass, losing weight, or increasing athletic performance. Otherwise, complexes of women’s vitamins for athletes contribute to:
- Strengthening the immune system.
- Acceleration of metabolic processes.
- Hormone synthesis.
- Optimization of oxidative processes.
- Destruction of fat cells.
- Providing energy both during training and throughout the day.
- Tissue regeneration.
- Strengthening the nervous system.
- Strengthening the cardiovascular system.
Muscle Pharm Armor-V
Muscle Pharm Armor-V is a representative of the group of natural dietary supplements for athletes. The plant complex includes:
- vitamin A;
- B vitamins;
- vitamin K;
- vitamin E;
- vitamin C;
- vitamin D;
- Omega acids.
Muscle Pharm Armor-V helps remove toxic substances from the body, increases endurance, accelerates the body's recovery after training, and improves immunity. In addition, the dietary supplement increases libido and has a positive effect on the condition of the skin. Among the disadvantages of the complex is the high cost. Depending on the region of residence, the price varies from 3,000 to 4,000 rubles.
Vitamins for women under 30 years old
The body needs vitamin support at any age. But each stage of life requires certain nutrients and in different quantities. Their list changes depending on social and physical activity, health status and a number of other factors.
Most girls after 20 years old begin to build families, give birth to children, and get a job. Therefore, vitamins for girls under 30 should help strengthen the immune system, supply the body with energy, and help fight stress. It is best to choose vitamin complexes. They contain all the necessary substances in the right proportions and help solve several problems at once.
The best vitamins for girls:
- Duovit - recommended for physical and mental stress, unbalanced diet, heavy menstruation, increased sweating. All components of the drug are balanced with each other.
- Lady's formula Antistress - American-made vitamins for girls. Relieves irritability, improves sleep and appetite. Pregnancy and lactation are contraindications for use.
Family, travel, relationships, sports - everything requires strength and vitamins from the body.
After 25 years, there are no fewer things to do, and even vice versa - their number is only growing, and life is in full swing. Many people at this age begin to pay special attention to caring for their appearance.
Vitamins for women under 30 years old:
- Woman's formula - complex contains the best vitamins for hair and skin. It also contains trace elements and plant extracts. Does not cause side effects.
- Alphabet Cosmetic - ensures rapid skin restoration and improves hair growth. Contains flavonoids and trace elements. Do not use if you have hyperthyroidism.
No matter how life “kicks”, it can be easily pacified if you have enough strength.
Vita Jym
Vita Jym is a natural dietary supplement for athletes. Used when you need to quickly get into shape. The complex contains vitamins B, A, K, E, chromium, and biopyrene. Vita Jym has the following effects:
- increases the body's protective functions;
- accelerates muscle growth;
- increases overall tone;
- stabilizes metabolic processes.
The duration of the course of taking the dietary supplement is determined individually. Vita Jum is available in tablet form. The disadvantage of the complex is the high price. The average cost of the supplement is 1500-1600 rubles for 60 tablets.
Top best vitamins for women for sports and fitness in sports nutrition
- Optimum Nutrition, Opti-Women.
- Rainbow Light, Multivitamin. Energy boosting vitamins for women.
- California Gold Nutrition Women's Multivitamin.
- Nature's Way Alive Women's Multivitamin.
- Solgar Female Multiple. Multivitamin complex.
- Biotech USA Multivitamin for Women 60 tablets.
- Myprotein Active WOMEN 120 tablets.
- NOW Eve Women's Multi, 120 tablets.
Vimicin
Vimicin is a vitamin and mineral complex suitable for use in athletes. Indications for taking the dietary supplement are severe fatigue, decreased performance, irritability, and immunodeficiency. Among the components of the bioactive additive are:
- vitamin A;
- vitamin E;
- vitamin C;
- vitamin D;
- manganese;
- silicon;
- zinc;
- copper;
- magnesium;
- iron;
- chromium;
- selenium;
- iodine.
Vimicin contains extracts of horsetail, barley, spirulina, acerola fruit, fucus, and rose hips. The dietary supplement increases endurance, stabilizes metabolic processes in the body, and increases protective functions. Thanks to its natural composition, it is suitable for all athletes. In addition, the dietary supplement can be taken for a long time due to its safety. Vimicin is available in tablet form. Take 1 tablet 2 times a day. Sold at an affordable price.
Olfactory impairment in COVID-19: review of drug treatment options
How to restore the sense of smell in patients with COVID-19? The effectiveness of the methods used in world practice. Overview of the prevalence of olfactory impairment in COVID-19. Medicinal and non-medicinal methods in medical practice that restore the sense of smell.
With COVID-19, in addition to general symptoms (cough, fever and fatigue), all countries are reporting an increase in the number of patients with loss of smell and taste. Changes in odor perception were previously noted in other viral infections (parainfluenza, rhinovirus, SARS, etc.), but with a much lower frequency than in those infected with SARS-CoV-2. The pathophysiology of post-infectious loss of smell is currently being considered in numerous domestic and foreign reviews.
The question of how to restore the sense of smell is quite acute, since throughout the world the number of people with coronavirus infection COVID-19, and therefore with this symptom, is increasing every day. The fact is that olfactory dysfunction affects the quality of life. People with loss of smell face problems when preparing food and determining its freshness. Eating behavior often changes - there is a decrease in appetite up to indifference to food. Olfactory dysfunction is associated with multiple comorbidities, including depression, cognitive impairment, and poor nutrition. Restoring the sense of smell is also necessary to warn about dangers in everyday life: the smells of gas, smoke, burning, acids, alkalis and alcohols are often the first signal that allows a person to save life and health. [1-3]
Terminology applicable to changes in smell:
- Normosmia – normal sense of smell.
- Hyposmia (or microsmia) is a decrease in the sensitivity of smell.
- Anosmia is a complete loss of smell.
- Hyperosmia is increased sensitivity to ordinary odors.
Identity disorders (dysosmia):
- Parosmia is a substitution of odor identification (perceived as the odor of another object).
- Phantosmia is the perception of smell in the absence of actual smell (olfactory hallucination).
- Cacosmia is a feeling of absent unpleasant odor (a special case of parosmia/phantosmia) or increased sensitivity to a certain unpleasant odor (selective hyperosmia).
Prevalence of smell impairment in COVID-19
On November 20, 2022, Jeyasakthy Saniasiaya and Md Asiful Islam published a meta-analysis of 27,492 patients, “Prevalence of olfactory dysfunction in coronavirus disease 2022 (COVID? 19).”
Overall, the prevalence of this symptom in patients with COVID-19 was 47.85%. From subgroup analysis, olfactory dysfunction was identified in 54.40% of European, 51.11% of North American, 31.39% of Asian and 10.71% of Australian patients with COVID-19. Additionally, anosmia, hyposmia, and dysosmia were observed in 35.39%, 36.15%, and 2.53% of COVID-19 patients, respectively. Interestingly, olfactory dysfunction was higher in non-severe patients compared to severe COVID-19 patients (47.48% vs 9.02%).[4]
Review of treatment options with recommendations
In August 2022, Hura N, Xie DX, Choby GW published a scientifically based review with recommendations “Treatment of post-viral olfactory dysfunction” [5], summarizing the data on the advisability of using various means that restore the sense of smell. Recommendation grades included cumulative grade of evidence (A to D). The purpose of the recommendations was to weigh the quality of the study against the potential balance of benefits and harms of smell loss.
Systemic steroids (prednisolone, methylprednisolone, betamethasone)
Six studies have been conducted to restore the sense of smell using systemic steroids. The duration of observation, olfactory testing, and systemic steroid dosing varied widely. Overall, 4 studies showed modest benefit from systemic steroids [6-9], while the design of other studies did not allow definitive conclusions about the ability to restore smell with this category of drugs. [10,11]
Summary:
- Cumulative evidence: C.
- Benefit: Objective improvement in the sense of smell based on several psychophysical tests.
- Harm: Possible side effects associated with systemic corticosteroids.
- Cost: low.
- Assessing benefits and harms: balance of benefits and harms
- Evaluative Opinion: The physician should consider the risk of systemic corticosteroids in the presence of comorbidities in patients.
- Recommendation level: possible. In the absence of additional risk factors, it may be possible to suggest a short course of systemic therapy to restore the sense of smell, after careful consideration of the potential benefits and risks associated with treatment.
Topical steroids
Four studies assessed the effect of topical corticosteroids, including fluticasone propionate, beclomethasone spray, and dexamethasone or betamethasone injections, as olfactory restorers. [12-15]
- Cumulative evidence: C
- Benefit: Improved TDI scores (odor threshold (T), discrimination (D), and identification (I) test scores)
- Harm: Minimal treatment-related side effects (eg, local irritation, possible nosebleeds).
- Cost : low.
- Assessing benefits and harms: balance of benefits and harms
- Opinion: Inhomogeneous studies make it difficult to make recommendations based on the minimum likely benefit combined with the minimum harm.
- Recommendation level: possible. Low-risk therapy with potential improvement in sense of smell but low potential benefit. It can be offered to patients in order to restore their sense of smell, but if there is no improvement effect at the start of therapy, it is rather inappropriate for long-term use.
Non-steroidal local drugs
Three studies examined intranasal sodium citrate for loss of smell. Additionally, one identified study compared intranasal insulin with saline placebo. [16-18] But since this is a single pilot study, there is not enough evidence to include it in a valid summary.
Intranasal sodium citrate
- Cumulative evidence: B
- Benefit: Short-term and temporary improvement in objective olfactory sensations after treatment.
- Harm: Minimal, including transient rhinorrhea, sore throat and nasal congestion.
- Cost: minimal
- Assessing benefits and harms: balance of benefits and harms
- Opinion: The level of evidence from these studies shows promise for intranasal sodium citrate in patients seeking olfactory restoration, but the variable nature and short-term follow-up make it difficult to determine the effectiveness of long-term clinical use of sodium citrate.
- Recommendation level: possible. A low-risk therapy with demonstrated temporary improvement in the sense of smell, but the long-term effectiveness of sodium citrate as a smell-restoring agent is unclear.
Non-steroidal oral drugs
Oral agents have also been studied as drugs that restore the sense of smell: antibiotics, vitamin A, alpha-lipoic acid. This group is characterized by low quality of clinical studies. Zinc sulfate has 3 studies with the best design - it has a separate conclusion, although it did not find significant effectiveness in restoring the sense of smell in patients receiving zinc sulfate in different regimens. [19-21]
Antibiotics. Two studies assessed the ability of different antibiotics to restore the sense of smell. In the first, there was no difference in TDI between the minocycline group and the placebo group. The second found no overall improvement in odor identification scores after treatment, but patients with smell loss improved odor detection thresholds after treatment. [22-23]
Vitamin A has also not shown consistent results when used to restore the sense of smell. Duncan et al. in 1962 reported improvement in subjective olfactory function. In a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study, Reden et al. compared the effectiveness of 10,000 IU vitamin A per day for 3 months with placebo. While TDI scores increased significantly in all patients, there was no significant difference between the placebo and vitamin A groups.[24,25]
Alpha lipoic acid, commonly used to treat diabetic neuropathy, was studied by Hummel et al. as a means of restoring the sense of smell. TDI improved after 4.5 months of alpha lipoic acid 600 mg/day but did not reach the minimal clinically important difference.[26]
Oral antibiotics, vitamin A, alpha lipoic acid.
- Cumulative evidence: D
- Benefit: Improved TDI scores, subjective assessments.
- Harm: Minimal drug side effects have been reported, but they were not strictly assessed in all studies.
- Cost: minimal to moderate.
- Assessing benefits and harms: balance of benefits and harms
- Evaluative opinion: a set of studies of different drugs performed to varying degrees of quality
- Level of recommendation: not recommended for use to restore the sense of smell.
Oral zinc sulfate
- Cumulative evidence: B
- Benefit: There are no studies demonstrating restoration of the sense of smell as a result of use
- Harm: There are no risks associated with therapy, although zinc toxicity is possible.
- Cost: moderate.
- Benefit-harm assessment: the preponderance of harm over benefit.
- Rating opinion: no
- Level of recommendation: not recommended as a means of restoring the sense of smell.
Olfactory training
Olfactory training refers to methods that allow you to restore your sense of smell without additional drug load on the patient’s body. Only ten studies assessed the effectiveness of olfactory training. [26-35]. Most studies used a protocol involving exposure to four odors twice daily for at least 12 weeks.
In 4 studies comparing olfactory training to no treatment, olfactory training was found to produce statistically better results and return of smell. [27,29,32,33]. The researchers also concluded that long-term training was superior to short-term training, with a significantly higher average TDI score after 56 weeks, although both groups showed the greatest improvement in their sense of smell during the first 16 weeks. [33] Interestingly, the shorter the duration of smell loss before treatment, the greater the effect of smell-restoring procedures. Damm et al. demonstrated a greater effect of olfactory training with high-concentration odors compared with low-concentration odors in patients with a duration of VOPD less than 12 months. [thirty]
Poletti et al. conducted a prospective pseudo-randomized study in which patients were trained using low molecular weight (<150 g/mol) or high molecular weight (>150 g/mol) odorants to regain their sense of smell. In this study, they concluded that high molecular weight odorants exceed threshold values compared to low molecular weight odorants in patients with smell loss.
Practical issues of olfactory training
For use in olfactory training, essential oils are the simplest and most effective. Essential oils have a high molecular weight and a complex chemical composition: they contain two or three main components, mainly terpenes, terpenoids and phenylpropanoids.
When choosing an essential oil to use to restore your sense of smell, it is important to pay attention to the quality of the product. There are a large number of surrogate essential oils on sale, which are vegetable oils with a small percentage of essential oil (the condition of high odor concentration is violated) or an artificial flavor with a low molecular weight, which will not be sufficiently effective and will not help restore the sense of smell.
The issue of training compliance is also open - loss of smell and other disturbances in the perception of smells during COVID-19 continue after the end of isolation of patients, and training with the use of 4 odors in some patients, due to employment and lifestyle, often causes difficulties, despite the desire to regain the sense of smell.
An alternative solution that can be easily implemented on the road or at work is to use one mixture of essential oils. In Russia, “Breathe Oil” is presented (JSC Akvion), which consists 100% only of essential oils. The dominant aromas in the composition are mint and eucalyptus, which allows you to concentrate on identifying these two aromas in turn during training sessions that restore your sense of smell, when it is impossible to conduct a full-fledged training session with 4 oils.
A distinctive feature of “Breathe Oil” is a high standard of quality and safety: the product is used for the prevention in complex therapy of respiratory infections and rhinitis in children; more than 11 clinical studies have been conducted on it (more details: https://clck.ru/SZWdc), which confirmed the high safety profile and effectiveness. The supplier of raw materials is the German company Freu&Lau with a European level of quality control. To increase compliance, there is a form in the form of a patch on clothes, a bracelet on the arm, a spray and oil with a dispenser. https://clck.ru/SUpek
Olfactory training
- Cumulative evidence: B
- Benefit: Improved performance on objective tests (UPSIT, Sniffin' Sticks).
- Harm: minimal, inconvenience of daily training.
- Cost: minimal.
- Assessment of benefits and harms: the preponderance of benefits over harm.
- Opinion: Given that it is a low-cost option with minimal to no harm and proven benefit, the value of this olfactory-restoring method is high.
- Recommendation Level: Recommended! Initiate olfactory training as soon as the patient is diagnosed with loss of smell or other olfactory dysfunction.
Overall, olfactory training was found to improve olfactory function in all 10 studies. It has been found that higher concentrations and molecular weights of odors, longer durations of olfactory training, and different odors used for them help restore the sense of smell more effectively. The shorter the time interval between the onset of smell disturbances and the start of training, the better the results of the procedures. As an alternative, if patients with loss of smell are refusing comprehensive training, you can consider using Breathe Oil. In addition to olfactory training, health care providers may suggest a course of systemic or topical steroids to restore the sense of smell after assessing the risks.
- Temmel AF, Quint C, Schickinger-Fischer B, Klimek L, Stoller E, Hummel T. Characteristics of olfactory disorders in relation to major causes of olfactory loss. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2002;128(6):635-41.
- Kollndorfer K, Reichert JL, Bruckler B, Hinterleitner V, Schopf V. Self-esteem as an important factor in quality of life and depressive symptoms in anosmia: A pilot study. Clin Otolaryngol. 2017;42(6): 1229-34.
- Boesveldt S, Postma EM, Boak D, Welge-Luessen A, Schopf V, Mainland JD, et al. Anosmia-A Clinical Review. Chem Senses. 2017;42(7):513-23.
- Saniasiaya J, Islam MA, Abdullah B. Prevalence of Olfactory Dysfunction in Coronavirus Disease 2022 (COVID-19): A Meta-analysis of 27,492 Patients. Laryngoscope. 2022 Nov 20.
- Hura N, Xie DX, Choby GW, et al. Treatment of post-viral olfactory dysfunction: an evidence-based review with recommendations. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2020;10(9):1065-1086.
- Seo BS, Lee HJ, Mo JH, et al. Treatment of postviral olfactory loss with glucocorticoids, Ginkgo biloba, and mometasone nasal spray. Arch Otolaryngol? Head Neck Surg. 2009;135(10):1000-1004.
- Kim DH, Kim SW, Hwang SH, et al. Prognosis of olfactory dysfunction according to etiology and timing of treatment. Otolaryngol? Head Neck Surg (United States). 2017;156(2):371-377.
- Schriever VA, Merkonidis C, Gupta N, et al. Treatment of smell loss with systemic methylprednisolone. Rhinology. 2012;50(3):284-289.
- Heilmann S, Huettenbrink KB, Hummel T. Local and systemic administration of corticosteroids in the treatment of olfactory loss. Am J Rhinol. 2004;18(1):29-33.
- Stenner M, Vent J, Hüttenbrink KB, et al. Topical therapy in anosmia: relevance of steroid-responsiveness. Laryngoscope. 2008;118(9):1681-1686.
- Ikeda K, Sakurada T, Suzaki Y, Takasaka T. Efficacy of systemic corticosteroid treatment for anosmia with nasal and paranasal sinus disease. Rhinology. 1995;33(3):162-165.
- Mori J, Aiba T, Sugiura M, et al. Clinical study of olfactory disturbance. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1998;538:197?201.
- Blomqvist EH, Lundblad L, Bergstedt H, Stjarne P. Placebo-controlled, randomized, double-blind study evaluating the efficacy of fluticasone propionate nasal spray for the treatment of patients with hyposmia/anosmia. Acta Otolaryngol. 2003;123(7):862-868.
- Fukazawa K. A local steroid injection method for olfactory loss due to upper respiratory infection. Chem Senses. 2005;30(suppl 1):212-213.
- Fleiner F, Goktas O. Topical beclomethasone in the therapy of smelling disorders—a new application technique. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011;63(1):5-9.
- Philpott CM, Erskine SE, Clark A, et al. A randomized controlled trial of sodium citrate spray for non-conductive olfactory disorders. Clin Otolaryngol. 2017;42(6):1295-1302.
- Whitcroft KL, Merkonidis C, Cuevas M, et al. Intranasal sodium citrate solution improves olfaction in post-viral hyposmia. Rhinology. 2016;54(4):368-374.
- Whitcroft KL, Ezzat M, Cuevas M, et al. The effect of intranasal sodium citrate on olfaction in post-infectious loss: results from a prospective, placebo-controlled trial in 49 patients. Clin Otolaryngol. 2017;42(3):557-563.
- Henkin RI, Schecter PJ, Friedewald WT, et al. A double blind study of the effects of zinc sulfate on taste and smell dysfunction. Am J Med Sci. 1976;272(3):285-299.
- Aiba T, Sugiura M, Mori J, et al. Effect of zinc sulfate on sensorineural olfactory disorder. Acta Otolaryngol. 1998;118(538):202-204.
- Quint C, Temmel AFP, Hummel T, Ehrenberger K. The quinoxaline derivative caroverine in the treatment of sensorineural smell disorders: a proof-of-concept study. Acta Otolaryngol. 2002;122(8):877-881.
- Reden J, Herting B, Lill K, et al. Treatment of postinfectious olfactory disorders with minocycline: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Laryngoscope. 2011;121(3):679-682.
- Wang JJ, Chen J, Doty RL. Impact of antibiotics on smell dysfunction. World J Otorhinolaryngol? Head Neck Surg. 2018;4(1):33-38.
- Duncan RB, Briggs M. Treatment of uncomplicated anosmia by vitamin A. Arch Otolaryngol. 1962;75(2):116-124.
- Reden J, Lill K, Zahnert T, et al. Olfactory function in patients with postinfectious and posttraumatic smell before disorders and after treatment with vitamin A: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. Laryngoscope. 2012;122(9):1906-1909.
- Hummel T, Heilmann S, Hüttenbriuk KB. Lipoic acid in the treatment of smell dysfunction following viral infection of the upper respiratory tract. Laryngoscope. 2002;112(11):2076-2080.
- Hummel T, Rissom K, Reden J, et al. Effects of olfactory training in patients with olfactory loss. Laryngoscope. 2009;119(3):496-499.
- Fleiner F, Lau L, Ö Göktas. Active olfactory training for the treatment of smelling disorders. Ear Nose Throat J 2012;91(5):198-215.
- Konstantinidis I, Tsakiropoulou E, Bekiaridou P, et al. Use of olfactory training in post-traumatic and postinfectious olfactory dysfunction. Laryngoscope. 2013;123(12):85-90.
- Damm M, Pikart LK, Reimann H, et al. Olfactory training is helpful in postinfectious olfactory loss: a randomized, controlled, multicenter study. Laryngoscope. 2014;124(4):826-831.
- Geißler K, Reimann H, Gudziol H, et al. Olfactory training for patients with olfactory loss after upper respiratory tract infections. Eur Arch Oto-Rhino-Laryngology. 2014;271(6):1557-1562.
- Altundag A, Cayonu M, Kayabasoglu G, et al. Modified olfactory training in patients with postinfectious olfactory loss. Laryngoscope. 2015;125(8):1763-1766.
- Konstantinidis I, Tsakiropoulou E, Constantinidis J. Long term effects of olfactory training in patients with post-infectious olfactory loss. Rhinology. 2016;54(2):170-175.
- Poletti SC, Michel E, Hummel T. Olfactory training using heavy and light weight molecule odors. Perception. 2017;46(3?4):343-351.
- Nguyen TP, Patel ZM. Budesonide irrigation with olfactory training improves outcomes compared with olfactory training alone in patients with olfactory loss. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2018;8(9):977-981.
Controlled Labs Orange Trade
Controlled Labs Orange Traid is a natural complex for maintaining the health of athletes. The effect of the supplement is to strengthen articular-cartilaginous tissue, increase the overall endurance of the body, restore protective functions, and increase tissue elasticity. Among the active components of the complex are:
- vitamin A;
- vitamin D;
- vitamin E;
- vitamin B;
- vitamin C;
- vitamin K;
- selenium;
- iodine;
- magnesium;
- calcium;
- phosphorus;
- manganese.
The disadvantage of Controlled Labs Orange Traid is considered to be high levels of vitamin C, which can lead to an overabundance of the element in the body. In addition, the average cost of a dietary supplement is 2500-3500 rubles, depending on the region of residence.
Why are vitamins needed for the male body?
Hundreds of major scientific publications prove that vitamin deficiency leads to a large number of negative consequences and worsens overall health. This affects not only physical and mental performance, but also metabolic processes, decreased immune reactions, and adaptation mechanisms. Despite the fact that a strong excess of substances has its negative consequences, a deficiency is considered much more destructive. Therefore, to prevent deficiency, strengthen the body, and increase mental and physical performance, dosages are used that significantly exceed the daily norm.
The main task of vitamin and mineral supplements is to compensate for dietary deficiencies and obtain the full norm of micronutrients. This affects all processes, the effects of stress, progression in sports, protection from diseases, etc. The quality of products and deficiencies in the diet no longer allow us to obtain the required amount of nutrients from food, this applies even to the most developed countries of the world. That's why multivitamins are the best way for men to maintain health and performance.
9 main reasons why men are better off buying vitamins in supplement form rather than trying to get the same amount of nutrients by eating huge amounts of food:
- Protecting muscles from destruction, improving muscle growth;
- Acceleration of fat burning processes, reducing the rate of accumulation of subcutaneous fat;
- Preventing slowdown of metabolic processes;
- Support the hormonal system for the normal production of important hormones;
- Minimizing the impact of stress on all organs, systems and tissues;
- Increased energy and endurance;
- Improving mood and well-being;
- Improving health and overall improving quality of life;
- Saving money.
Often, men begin to take a large number of supplements, medications and other drugs that are aimed at increasing physical performance. However, most often the main reason for the decline in performance is a lack of micronutrients and a poor diet. In this case, it is best for men to choose complex vitamins. In most cases, this will be an effective solution to solve health problems that are caused by a poor diet.
MuscleTech Platinum Multivitamin
MuscleTech Platinum Multivitamin is one of the vitamin and mineral complexes for athletes. The natural composition includes the following components:
- B vitamins;
- vitamin A;
- vitamin D;
- vitamin E;
- zinc;
- copper;
- potassium;
- boron;
- manganese.
In addition, among the elements of the bioactive supplement there are extracts of ginseng, green tea, turmeric, and wheat germ. MuscleTech Platinum Multivitamin has a tonic effect, accelerates the growth of muscle mass, stabilizes metabolic processes, and increases the body's protective functions. The dietary supplement is available in the form of tablets. Due to their large size, they are considered inconvenient to use.
How safe are high dosages in sports supplements?
The best vitamins for men from top manufacturers contain high dosages of all components. They can be either 300-500% of the daily value or 2000-8000%. You should not be afraid of this; manufacturers initially take into account all the features when developing the supplement formula. For example, the absorption of some substances will be reduced in combination with other components of the complex that suppress each other. All remaining excess is excreted in the urine, therefore multiple excesses of the norm, which are indicated on the packaging, cannot harm the body.
For example, the dose of vitamin C and E can easily be exceeded 10 times if a person leads an active lifestyle and regularly plays sports. B vitamins can be exceeded 20-30 times.
ADAM
ADAM is a vitamin and mineral complex for athletes. Available in tablet form. Among the components of the bioactive additive are:
- B vitamins;
- carotenoids;
- ginseng extract;
- saw palmetto extract;
- beta-carotene;
- Coenzyme Q10.
ADAM helps normalize metabolic processes in the body, strengthens the nervous system, increases the body's protective functions, and reduces the severity of inflammatory processes. An additional effect of the vitamin-mineral complex is to increase libido. Among the disadvantages of ADAM is that the complex is suitable exclusively for men.
Selecting vitamins and minerals for athletes is a responsible step. Therefore, before purchasing complexes, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
MULTIVITAMINS
And the first place among the ranking of the best vitamins for women, of course, is occupied by multivitamins, which contain a whole complex of vitamins and minerals that our body needs, without which it would be extremely difficult to actively train, lose weight or build muscle mass and at the same time be full of energy and energy for other matters related to household chores and work. Multivitamins are good because their daily dose (in one or several capsules) already contains all the necessary substances that we require, and there is no need to drink a bunch of different tablets and carry a million cans of different vitamins in your purse. It’s very convenient: you take a couple of capsules and replenish all the necessary vitamin reserves for the whole day.
Today, in pharmacies and sports nutrition stores there are a huge number of different companies and brands of multivatamines. And sometimes this wide selection does not simplify, but rather complicates the task when it comes to buying the right vitamins. For those who are reading this article, I can simplify this task a little by advising you which vitamins are better , based on my own experience and on reviews of my clients when taking certain medications.
The Best Vitamins for Teen Athletes
It is no secret that the consumption of minerals and vitamins in children involved in any sport significantly exceeds the same figure in ordinary schoolchildren. When choosing the best dietary supplements for teenagers, you must adhere to the main rule - uncontrolled use of any drugs can lead to unpredictable results and cause irreversible consequences in a fragile body. Young athletes are allowed to take only proven pharmaceutical multicomplexes strictly under the supervision of a specialist.
Vitamin intake standards
The following factors influence the daily norm:
- individual characteristics of the body;
- quantity and duration of physical activity;
- stress;
- external factors: climate, etc.
It is impossible to determine the dosage yourself. This can only be done by a specialist after taking a blood test. In unfavorable climates (when the temperature rises above +40° or falls below -40°), the daily norm increases two to three times. With high physical activity and, as a consequence, a large amount of required protein (2.5-5 g per kg of body weight), increased doses are also needed. Since at this moment the body is experiencing severe stress and there are not enough vitamins supplied with food.
© elenabs — depositphotos.com. Food Sources of Vitamins
Contraindications and side effects
The only contraindication is individual intolerance to the active and auxiliary substances.
During use, the athlete may experience side effects. This process is accompanied by:
- indigestion - constipation or diarrhea;
- deterioration of general health;
- fatigue, lethargy and apathy;
- sleep disturbance;
- dizziness and headaches;
- nausea.
If adverse reactions occur, you should stop using vitamin complexes.
Symptoms of vitamin deficiency in the body
A balanced diet covers almost all the body's needs for nutrients. We get most of the B vitamins, as well as K, E, A, C, PP and others from food.
Diets, lack of regimen and special dietary rules (vegetarianism, intolerance to certain substances) lead to a deficiency of vitamins and minerals. Let's look at the most popular symptoms of a lack of nutrients in the body:
- Fatigue and fatigue;
- Frequent infectious and colds;
- Problems with sleep, increased anxiety, nervous excitability;
- Weak nails and hair, dental problems;
- Apathy, depression;
- Muscle weakness, cramps;
- Dry skin, etc.
1-2 symptoms from the list do not indicate a vitamin deficiency, but a number of coincidences indicate that you should be checked by a specialist. By the way, only a laboratory analysis will show a deficiency of a certain substance, so you should not self-medicate and act on a whim.
When should you take vitamins?
The need to take vitamin complexes appears in the off-season, when the immune system is weakened by a lack of sunlight and fresh vegetables. But athletes benefit from taking supplements at any time of the year, especially during an intense training regimen.
Indications for taking vitamins are:
- Strength training 5-6 times a week;
- Walking at least 1.5-2 hours a day;
- Intense cardio 5-6 times a week;
- Heavy physical labor 5-6 times a week.
If you exercise in light mode 3-4 times a week, then vitamins should be taken as needed, just like people leading a sedentary lifestyle.
Residents of the middle zone, regardless of lifestyle, often have a deficiency of vitamin D, which is produced in the body under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. This vitamin is necessary for normal calcium absorption, healthy metabolism and strong immunity. In autumn and winter, it is necessary to take vitamin D supplements to avoid problems with joints, bones and teeth, which are most susceptible to a lack of this substance. In turn, athletes also need vitamin D, since it is responsible for the absorption of calcium, which is intensively consumed during physical activity.
In addition to vitamin D, in the off-season it is useful to take ascorbic acid (vitamin C) to strengthen the immune system and antioxidant defense of the body.