A
Anaerobic threshold
The anaerobic threshold is also called PANO, the threshold of anaerobic metabolism. This is the level of exercise intensity at which the concentration of lactate in the blood increases sharply, since the rate of its formation becomes higher than the rate of utilization.
Above this level, lactic acid begins to accumulate in the muscles, resulting in more fatigue. To develop PANO, it is effective to run tempo and interval training.
Aerobic threshold
An indicator of the heart rate at which muscles work on energy obtained with the participation of oxygen. It is generally accepted that the aerobic threshold does not exceed 80% of a runner's maximum heart rate.
Ironman
The word comes from the English Ironman, literally meaning “iron man.” This is the name given to the finisher of a full (“iron”) distance in a triathlon, consisting of three stages: swimming – 3.86 km, cycling – 180.25 km and running 42.195 km.
Jan Frodeno is an Olympic champion and multiple world champion in triathlon. Source: Instagram Yana
Formally, Ironman is a brand of a series of long-distance triathlon competitions conducted by the World Triathlon Corporation (WTC).
Read on the topic: Triathlon: what kind of sport is it and what are the distances?
Achilles (Achilles tendon)
The largest and strongest tendon in the human body. When running, it takes on a lot of stress, which can lead to a common running injury: Achilles tendinitis. Most often, runners who increase the intensity or mileage of training too early suffer from Achilles inflammation.
Sprinting technique
Victory in a sprint race can be achieved within a few seconds. Therefore, an effective system with refined movements is needed. Otherwise, due to an annoying oversight, time will be lost.
According to the sprint technique, it is necessary:
- Tilt the body 10-15 degrees to the vertical.
- Pull your shoulders back a little.
- Place your feet almost in line.
- Move the support from the front of the foot, slightly short of the heel.
- Copy the pose of a kangaroo before jumping.
- During short sprint runs, the runner is required to fully utilize the physical and psycho-emotional reserves of the body.
This sport has its own characteristics:
- mobilization of all available resources;
- development of movement coordination;
- training endurance and maximum speed in a short period of time.
During a sprint race, dormant energy sources are activated in the body. The human body works at its limit. If you exclude people from risk groups, such loads bring exceptional benefits.
Body changes during training:
- improving the body's endurance;
- development of dexterity, reaction and coordination of movements;
- increased lung volume;
- improved blood circulation;
- waste products and metabolic products are intensively removed;
- the heart is subjected to a payload;
- the cardiovascular system is trained during acceleration;
- muscle tone increases;
- burning excess fat deposits.
The history of the development of sprint running technology continues. It's too early to call it a day. Initially, at the very beginning of the victorious procession of sprint, at the dawn of the Olympic Games, training was carried out 2-3 times a week. The main attention was paid to the indicators of the psyche and physiology inherent in nature. Only on their basis were running records achieved.
And with the advent of the “fastest fallow deer in Europe” E. Sechenova, the number of training sessions increased to five per week. For the first time, 2 training sessions were conducted per day. During the preparatory training, jogging was carried out at a speed close to the maximum. The improvement of the methodological part of training initially followed the path of increasing training volumes and the use of various special preparation means.
Phases, running tactics and key mistakes in sprint distances
B
Hurdling
Hurdling is a set of sprint athletics disciplines where athletes need to overcome barriers as they move. Despite the fact that the length of the distance in this sport ranges from 50 to 400 m, hurdle running requires a lot of preparation. Each athlete must not only combine strength, speed, coordination, but also be able to correctly calculate the required number of steps to clear an obstacle.
Jogging
It is also called jogging from the English jog - “jogging”. Jogging is a slow run at a speed of 7-9 km/h. For beginning runners, this type of running can be the foundation of a workout, while more experienced athletes typically use it as a rest period between speed intervals or as part of a cool-down.
marathon and half marathon training plans and start training today!
Charity race
A charity race is a competition in which the entry fee for participation goes to a charitable foundation or as help to a specific person.
Speed running. Training programs
Your program to improve your speed running results will look like this:
Sprint running. Program No. 1
Monday. Speed running + muscle development
| Exercise | Weight | Approaches | Repetitions | Rest minutes between sets | Rest minutes between exercises |
| Acceleration at 100 meters | — | 2 | — | 2 | 4 |
| Shuttle run 10 by 10 | — | 2 | — | 2 | 4 |
| Squats | 35 | 3 | 15 | 2 | 4 |
| Jumping | — | 2 | 20 | 2 | 4 |
| Jumping rope | 2 | 1 minute | 2 | 4 | |
| Lunges with a barbell | 20 | 3 | 12 | 2 | 4 |
| Acceleration at 200 meters | — | 2 | — | 2 | 4 |
| Jogging at an easy pace | — | 1 | 10 minutes | — | — |
Wednesday. Running workout
| Exercise | Weight | Approaches | Repetitions | Rest minutes between sets | Rest minutes between exercises |
| Acceleration at 100 meters | — | 2 | — | 2 | 4 |
| Acceleration at 50 meters with weights | 2 to 1.5 | 2 | — | 2 | 4 |
| Running up the stairs one step at a time | — | 2 | No more than 2 minutes | 2 | 4 |
| Acceleration at 200 meters | — | 2 | — | 2 | 4 |
| Acceleration at 400 meters | — | 2 | — | 2 | 4 |
| Running uphill | — | 2 | 1.5 minutes | 2 | 4 |
| Jogging at an easy pace | — | 1 | 10 minutes | — | — |
Thursday. Recovery training
| Exercise | Duration in minutes |
| Jogging at an easy pace | 15 |
Friday. Gym workout + sprinting
| Exercise | Weight | Approaches | Repetitions | Rest minutes between sets | Rest minutes between exercises |
| Lunges with a barbell | 20 | 3 | 12 | 2 | 4 |
| Jumping | — | 2 | 15 | 2 | 4 |
| 100 meter sprint | — | 2 | — | 2 | 4 |
| Acceleration with weights for 100 meters | — | 2 | — | 2 | 4 |
| 200 meter sprint | — | 2 | — | 2 | 4 |
| Shuttle run 10 to 10 | — | 2 | — | 2 | 4 |
| Acceleration uphill | — | 2 | — | 2 | — |
Do the stretching when it is comfortable for you.
Sprint running. Program No. 2 . We follow the principle of progression of loads and increase the number of approaches.
Monday. Speed running + muscle development
| Exercise | Weight | Approaches | Repetitions | Rest minutes between sets | Rest minutes between exercises |
| Acceleration at 100 meters | — | 3 | — | 2 | 4 |
| Shuttle run 10 by 10 | — | 3 | — | 2 | 4 |
| Squats | 35 | 4 | 15 | 2 | 4 |
| Jumping | — | 3 | 20 | 2 | 4 |
| Jumping rope | 3 | 1 minute | 2 | 4 | |
| Lunges with a barbell | 20 | 4 | 12 | 2 | 4 |
| Acceleration at 200 meters | — | 3 | — | 2 | 4 |
| Jogging at an easy pace | — | 1 | 12 minutes | — | — |
Wednesday. Running workout
| Exercise | Weight | Approaches | Repetitions | Rest minutes between sets | Rest minutes between exercises |
| Acceleration at 100 meters | — | 3 | — | 2 | 4 |
| Acceleration at 50 meters with weights | 2 to 1.5 | 3 | — | 2 | 4 |
| Running up the stairs one step at a time | — | 3 | No more than 2 minutes | 2 | 4 |
| Acceleration at 200 meters | — | 3 | — | 2 | 4 |
| Acceleration at 400 meters | — | 3 | — | 2 | 4 |
| Running uphill | — | 4 | 1.5 minutes | 2 | 4 |
| Jogging at an easy pace | — | 1 | 12 minutes | — | — |
Thursday. Recovery training
| Exercise | Duration in minutes |
| Jogging at an easy pace | 17 |
Friday. Gym workout + sprinting
| Exercise | Weight | Approaches | Repetitions | Rest minutes between sets | Rest minutes between exercises |
| Lunges with a barbell | 20 | 4 | 12 | 2 | 4 |
| Jumping | — | 3 | 15 | 2 | 4 |
| 100 meter sprint | — | 3 | — | 2 | 4 |
| Acceleration with weights for 100 meters | — | 3 | — | 2 | 4 |
| 200 meter sprint | — | 3 | — | 2 | 4 |
| Shuttle run 10 to 10 | — | 3 | — | 2 | 4 |
| Acceleration uphill | — | 3 | — | 2 | — |
Sprint running. Program No. 3 . We follow the principle of progression of loads and increase the number of approaches.
Monday. Speed running + muscle development
| Exercise | Weight | Approaches | Repetitions | Rest minutes between sets | Rest minutes between exercises |
| Acceleration at 100 meters | — | 4 | — | 2 | 4 |
| Shuttle run 10 by 10 | — | 4 | — | 2 | 4 |
| Squats | 35 | 5 | 15 | 2 | 4 |
| Jumping | — | 4 | 20 | 2 | 4 |
| Jumping rope | 4 | 1 minute | 2 | 4 | |
| Lunges with a barbell | 20 | 5 | 12 | 2 | 4 |
| Acceleration at 200 meters | — | 4 | — | 2 | 4 |
| Jogging at an easy pace | — | 1 | 15 minutes | — | — |
Wednesday. Running workout
| Exercise | Weight | Approaches | Repetitions | Rest minutes between sets | Rest minutes between exercises |
| Acceleration at 100 meters | — | 4 | — | 2 | 4 |
| Acceleration at 50 meters with weights | 2 to 1.5 | 4 | — | 2 | 4 |
| Running up the stairs one step at a time | — | 4 | No more than 2 minutes | 2 | 4 |
| Acceleration at 200 meters | — | 4 | — | 2 | 4 |
| Acceleration at 400 meters | — | 4 | — | 2 | 4 |
| Running uphill | — | 4 | 1.5 minutes | 2 | 4 |
| Jogging at an easy pace | — | 1 | 15 minutes | — | — |
Thursday. Recovery training
| Exercise | Duration in minutes |
| Jogging at an easy pace | 20 |
Friday. Gym workout + sprinting
| Exercise | Weight | Approaches | Repetitions | Rest minutes between sets | Rest minutes between exercises |
| Lunges with a barbell | 20 | 5 | 12 | 2 | 4 |
| Jumping | — | 4 | 15 | 2 | 4 |
| 100 meter sprint | — | 4 | — | 2 | 4 |
| Acceleration with weights for 100 meters | — | 4 | — | 2 | 4 |
| 200 meter sprint | — | 4 | — | 2 | 4 |
| Shuttle run 10 to 10 | — | 4 | — | 2 | 4 |
| Acceleration uphill | — | 4 | — | 2 | — |
Sprint running. Program No. 4 . We follow the principle of load progression: increase the weight in exercises with a barbell, the duration of the approaches, and reduce the rest between exercises.
Monday. Speed running + muscle development
| Exercise | Weight | Approaches | Repetitions | Rest minutes between sets | Rest minutes between exercises |
| Acceleration at 100 meters | — | 4 | — | 1,5 | 4 |
| Shuttle run 10 by 10 | — | 4 | — | 1,5 | 4 |
| Squats | 40 | 3 | 15 | 2 | 4 |
| Jumping | — | 3 | 25 | 2 | 4 |
| Jumping rope | 3 | 2 minutes | 2 | 4 | |
| Lunges with a barbell | 25 | 3 | 12 | 2 | 4 |
| Acceleration at 200 meters | — | 4 | — | 1,5 | 4 |
| Jogging at an easy pace | — | 1 | 15 minutes | — | — |
Wednesday. Running workout
| Exercise | Weight | Approaches | Repetitions | Rest minutes between sets | Rest minutes between exercises |
| Acceleration at 100 meters | — | 4 | — | 1,5 | 4 |
| Acceleration at 50 meters with weights | 2 to 1.5 | 4 | — | 1,5 | 4 |
| Running up the stairs one step at a time | — | 4 | No more than 2 minutes | 1,5 | 4 |
| Acceleration at 200 meters | — | 4 | — | 1,5 | 4 |
| Acceleration at 400 meters | — | 4 | — | 1,5 | 4 |
| Running uphill | — | 4 | 1.5 minutes | 1,5 | 4 |
| Jogging at an easy pace | — | 1 | 15 minutes | — | — |
Thursday. Recovery training
| Exercise | Duration in minutes |
| Jogging at an easy pace | 25 |
Friday. Gym workout + sprinting
| Exercise | Weight | Approaches | Repetitions | Rest minutes between sets | Rest minutes between exercises |
| Lunges with a barbell | 25 | 3 | 12 | 2 | 4 |
| Jumping | — | 4 | 15 | 1 | 4 |
| 100 meter sprint | — | 4 | — | 1,5 | 4 |
| Acceleration with weights for 100 meters | — | 4 | — | 1,5 | 4 |
| 200 meter sprint | — | 4 | — | 1,5 | 4 |
| Shuttle run 10 to 10 | — | 4 | — | 1,5 | 4 |
| Acceleration uphill | — | 4 | — | 1,5 | — |
Sprint running. Program No. 5 . We follow the principle of progression of loads: increase the number of approaches in strength exercises, reduce rest between approaches.
Monday. Speed running + muscle development
| Exercise | Weight | Approaches | Repetitions | Rest minutes between sets | Rest minutes between exercises |
| Acceleration at 100 meters | — | 4 | — | 1 | 4 |
| Shuttle run 10 by 10 | — | 4 | — | 1 | 4 |
| Squats | 40 | 4 | 15 | 2 | 4 |
| Jumping | — | 4 | 25 | 2 | 4 |
| Jumping rope | 4 | 2 minutes | 2 | 4 | |
| Lunges with a barbell | 25 | 4 | 12 | 2 | 4 |
| Acceleration at 200 meters | — | 4 | — | 1 | 4 |
| Jogging at an easy pace | — | 1 | 15 minutes | — | — |
Wednesday. Running workout
| Exercise | Weight | Approaches | Repetitions | Rest minutes between sets | Rest minutes between exercises |
| Acceleration at 100 meters | — | 4 | — | 1 | 4 |
| Acceleration at 50 meters with weights | 2 to 1.5 | 4 | — | 1 | 4 |
| Running up the stairs one step at a time | — | 4 | No more than 2 minutes | 1 | 4 |
| Acceleration at 200 meters | — | 4 | — | 1 | 4 |
| Acceleration at 400 meters | — | 4 | — | 1 | 4 |
| Running uphill | — | 4 | 1.5 minutes | 1 | 4 |
| Jogging at an easy pace | — | 1 | 17 minutes | — | — |
Thursday. Recovery training
| Exercise | Duration in minutes |
| Jogging at an easy pace | 28 |
Friday. Gym workout + sprinting
| Exercise | Weight | Approaches | Repetitions | Rest minutes between sets | Rest minutes between exercises |
| Lunges with a barbell | 25 | 4 | 12 | 2 | 4 |
| Jumping | — | 4 | 15 | 1 | 4 |
| 100 meter sprint | — | 4 | — | 1 | 4 |
| Acceleration with weights for 100 meters | — | 4 | — | 1 | 4 |
| 200 meter sprint | — | 4 | — | 1 | 4 |
| Shuttle run 10 to 10 | — | 4 | — | 1 | 4 |
| Acceleration uphill | — | 4 | — | 1 | — |
Sprint running. Program No. 6 . We follow the principle of progression of loads and increase the number of approaches.
Monday. Speed running + muscle development
| Exercise | Weight | Approaches | Repetitions | Rest minutes between sets | Rest minutes between exercises |
| Acceleration at 100 meters | — | 5 | — | 1 | 4 |
| Shuttle run 10 by 10 | — | 5 | — | 1 | 4 |
| Squats | 40 | 5 | 15 | 2 | 4 |
| Jumping | — | 5 | 25 | 2 | 4 |
| Jumping rope | 5 | 2 minutes | 2 | 4 | |
| Lunges with a barbell | 25 | 5 | 12 | 2 | 4 |
| Acceleration at 200 meters | — | 5 | — | 1 | 4 |
| Jogging at an easy pace | — | 1 | 17 minutes | — | — |
Wednesday. Running workout
| Exercise | Weight | Approaches | Repetitions | Rest minutes between sets | Rest minutes between exercises |
| Acceleration at 100 meters | — | 5 | — | 1 | 4 |
| Acceleration at 50 meters with weights | 2 to 1.5 | 5 | — | 1 | 4 |
| Running up the stairs one step at a time | — | 5 | No more than 2 minutes | 1 | 4 |
| Acceleration at 200 meters | — | 5 | — | 1 | 4 |
| Acceleration at 400 meters | — | 5 | — | 1 | 4 |
| Running uphill | — | 5 | 1.5 minutes | 1 | 4 |
| Jogging at an easy pace | — | 1 | 20 minutes | — | — |
Thursday. Recovery training
| Exercise | Duration in minutes |
| Jogging at an easy pace | 30 |
Friday. Gym workout + sprinting
| Exercise | Weight | Approaches | Repetitions | Rest minutes between sets | Rest minutes between exercises |
| Lunges with a barbell | 25 | 5 | 12 | 2 | 4 |
| Jumping | — | 5 | 15 | 1 | 4 |
| 100 meter sprint | — | 5 | — | 1 | 4 |
| Acceleration with weights for 100 meters | — | 5 | — | 1 | 4 |
| 200 meter sprint | — | 5 | — | 1 | 4 |
| Shuttle run 10 to 10 | — | 5 | — | 1 | 4 |
| Acceleration uphill | — | 5 | — | 1 | — |
Sprint running. Program No. 7 . We follow the principle of progression of loads: increase the weight and duration of exercises.
Monday. Speed running + muscle development
| Exercise | Weight | Approaches | Repetitions | Rest minutes between sets | Rest minutes between exercises |
| Acceleration at 100 meters | — | 5 | — | 1 | 4 |
| Shuttle run 10 by 10 | — | 5 | — | 1 | 4 |
| Squats | 45 | 3 | 15 | 2 | 4 |
| Jumping | — | 5 | 30 | 2 | 4 |
| Jumping rope | 5 | 2.5 minutes | 2 | 4 | |
| Lunges with a barbell | 30 | 3 | 12 | 2 | 4 |
| Acceleration at 200 meters | — | 5 | — | 1 | 4 |
| Jogging at an easy pace | — | 1 | 17 minutes | — | — |
Wednesday. Running workout
| Exercise | Weight | Approaches | Repetitions | Rest minutes between sets | Rest minutes between exercises |
| Acceleration at 100 meters | — | 5 | — | 1 | 4 |
| Acceleration at 50 meters with weights | 2 to 1.5 | 5 | — | 1 | 4 |
| Running up the stairs one step at a time | — | 5 | No more than 2 minutes | 1 | 4 |
| Acceleration at 200 meters | — | 5 | — | 1 | 4 |
| Acceleration at 400 meters | — | 5 | — | 1 | 4 |
| Running uphill | — | 5 | 2 minutes | 1 | 4 |
| Jogging at an easy pace | — | 1 | 20 minutes | — | — |
Thursday. Recovery training
| Exercise | Duration in minutes |
| Jogging at an easy pace | 35 |
Friday. Gym workout + sprinting
| Exercise | Weight | Approaches | Repetitions | Rest minutes between sets | Rest minutes between exercises |
| Lunges with a barbell | 30 | 3 | 12 | 2 | 4 |
| Jumping | — | 5 | 20 | 1 | 4 |
| 100 meter sprint | — | 5 | — | 1 | 4 |
| Acceleration with weights for 100 meters | — | 5 | — | 1 | 4 |
| 200 meter sprint | — | 5 | — | 1 | 4 |
| Shuttle run 10 to 10 | — | 5 | — | 1 | 4 |
| Acceleration uphill | — | 5 | — | 1 | — |
Comments on the programs:
- We continue to increase the load in this way until we reach our goal.
- In speed exercises, focus on the ability to show results, and not on the number of approaches or rest duration . Such schemes exist in order to show maximum results in the first approach, and then put the body under greater stress, stimulating it to develop. Pay attention to the speed in the first approach. The results of other approaches can also be recorded. Rest within these schemes does not begin from the moment the approach is completed, but after returning to the starting position.
- Adapt the programs to suit you . If you don't have a lift or treadmill that you can run up for 2 minutes, replace this exercise with another.
IN
Volunteer
An assistant who participates in organizing the race on a voluntary basis. Most often, volunteers work at registration at the start town, help distribute food and drinks at food stations, orient runners along the course and meet finishers with medals.
Source: westend61.de
Read on the topic: If I don’t run, I’ll help: how to become a volunteer at a race
G
Handicap
In simple terms, it is a head start that stronger runners give to weaker ones so that everyone has an equal chance of winning. The handicap can be carried out by gender, and then women start the race, followed by men - or by age, when more mature runners go first to the distance.
Read more in the article: Handicap in running: what is it, how is it calculated, at what starts is it used
Gun time
Translated from English, this word means “shot time.” Gun time is the time from the starting shot until the runner crosses the finish line. This indicator is always greater than the chip time or equal to it if the athlete starts from the elite cluster.
Hydration pack
A water container in the form of a plastic flexible bag, which is located inside the running backpack and has a hose so that the athlete can drink water on the go.
Features of the distance-overcoming technique
Speed over a distance is the maximum possible frequency of the widest steps. For professional athletes, the width of the step is equal to their height plus 30-40 cm. The foot is placed on the ground very quickly, but springily, in order to immediately push off.
The body should be tilted forward. The optimal angle of inclination is so that the inclination helps to move forward inertia, but there are no difficulties with the extension of the leading leg.
Elbows bent at 90 degrees, vigorous arm work will help increase momentum. Hands are kept as close to the body as possible, directed forward in movement to reduce air resistance.
Each athlete's speed running technique is individual. But you can always increase your own speed limit.
D
Long run
Long run – continuous running for an extended duration. In most cases, a long-term workout is considered to last more than 1.5 hours. The goal of such running is to increase lipid power, that is, the ability to perform a workout at a given intensity on depleted glycogen.
DNF
The DNF or Did not finish marker in the finishing protocol means that the athlete started but did not finish, that is, left the race and did not cross the finish line. You can fail to finish for various reasons: from physiological to technical (equipment breakdown), but more often they leave the race due to unsatisfactory health.
DNS
The DNS or Did not start marker in the finish protocol means that the athlete did not start. That is, the participant purchased a slot, registered for the competition, but then changed his mind and did not participate in the race.
D.S.Q.
The DSQ or Disqualified marker on the finish sheet means that the athlete is disqualified and removed from the race. Usually, along with such a note, a link is given to the rule that the participant violated. This may include unsportsmanlike conduct, intentional harm to other participants, or use of cheerleader assistance where prohibited.
Read on the topic: What is DNS, DNS, DSQ in running and triathlon
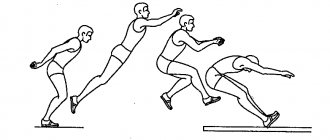
Execution technique
One of the most important moments of the race is the start. At the moment of start, almost all muscle groups should be involved: muscles of the arms, legs, back and abs.
After lifting your hands off the track and your feet off the blocks, the most important thing is not to fall, but to accelerate successfully. To do this, you need sufficient torso tilt.
In sprinting, the most important role is given to the arms. Using your hands, you set the rhythm and frequency of running.
Each hand movement is aimed at accelerating and maintaining speed.
A good acceleration duration is considered to be 25-30 m. Acceleration that is too large and too small will not allow you to develop a good speed in the future.
When accelerating, the body should tilt forward and gradually straighten. The steps should not be too long or too short. The most acceptable cadence (steps per minute) is 180 steps per minute.
When running short distances, the main task is to develop and maintain the speed gained. In short-distance running, it is necessary to move the shin forward of the knee, performing raking movements, and active work of the arms.
A successful finish requires composure and resistance to stress. The main thing is to try to successfully lunge, but not earlier than required.
4 phases of running technique
Start
The start of the race starts from a low start.
This is a special, separately developed technique. Your hands should be shoulder-width apart and your strong leg should be in front. At the “ Attention ” command, the center of gravity is moved forward, and at the “ March ” command, repulsion from the surface occurs with the help of the hands.
Arms and legs should work in the same rhythm.
Overclocking
Athletes usually accelerate at a distance of 30 m. At this moment, runners need to gain maximum speed, which will remain until the end of the race.
When started correctly, the speed is gained within 6 seconds.
To increase speed, you need to increase the frequency and length of your stride.
Distance running
When running a short distance, you need to maintain the speed that was gained during acceleration.
Finish
It is advisable to approach the finish line with maximum acceleration, without jumping.
Jumping often results in losing seconds of time. Ready for your first workout?
Not really.
AND
Isotonic
Isotonic is a drink that maintains the water-salt balance in the body during sports. Isotonic drinks are quickly absorbed, so they quench thirst more effectively than regular water.
Intervals
Intervals are short sections of a distance, usually ranging from 200 to 1600 m.
Interval training is running with alternating fast and slow segments in the anaerobic and aerobic zones, respectively. They develop endurance and strength and help improve speed performance.
Source: runnersworld.com
Intervals can be measured in different ways: periods (minutes) or distances (meters).
TO
Cadence
Cadence is the number of steps a runner takes in one minute. Cadence affects the efficiency and injury rate of running. The optimal rate for running is considered to be between 170 and 185 steps per minute.
Qualification
This is the name given to a certain sporting level that is required to participate in major competitions. That is, not everyone will be able to get to the start, but only those who confirm their compliance with the level of this start.
This may be due to the large number of entries for the race or the complexity of the course.
Cluster
Place in the starting corridor, which depends on the expected finish time and pace: the slower you run, the more distant the cluster you will be at the start. Typically, clusters are designated by Latin letters: A, B, C and so on. At the same time, runners from cluster A are closest to the starting line.
"Runner's Knee"
“Runner's knee” is a common sports injury that is characterized by the development of chondromalacia of the patella (softening and deformation of the cartilage tissue of the patella) or inflammation of the iliotibial tract. Although it's not just runners who suffer from knee injuries, the term has stuck because there are especially many victims of such injuries among runners.
Long-distance runners are most susceptible to the syndrome.
Compression clothing
Compression clothing is a type of clothing used to speed up the recovery period, improve an athlete's performance characteristics and increase comfort levels. The most popular are compression gaiters, knee socks and socks.
Krepatura
This is the same condition when the next day after intense or unusual physical activity the whole body or some individual muscles hurt. Another name for sore throat is delayed muscle pain syndrome.
There is nothing terrible in this condition itself; it only means that the load has increased, and the muscles have not had time to adapt to it. But it is important not to confuse soreness with injury or other unpleasant sensations. It occurs several hours after exercise and is characterized by a dull, rather than sharp, pain.
Cross
Cross – running over rough terrain, including grass, dirt and hills. Unlike trail races, classic cross-country running takes place on circular routes with less elevation change. The total length of the distance is also shorter and rarely exceeds 12 km.
Source: phillymag.com
History of development
People knew about the benefits of running back in ancient times. With its help, they hunted and ran away from enemies and predators. The speed of the infantry determined the speed of movement of the army as a whole.
The first official running competitions were the old Olympic Games, which took place in 776 BC. Then there was one distance - 192 m. Over the next 50 years, 24 more running distances were created and used at the Games. Even then there were special exercises for running in Greece. And the favorites of the races were the state heroes.
With the end of antiquity, the Olympic competitions ended. Running as a sport continued its development in the eighteenth century. In particular, it spread to Great Britain, where races often took place. The first obstacle race took place in 1837, and long-distance competitions were opened in 1845.
In 1886, the first Olympic Games were held in Athens. They were also represented in the following distances: 100, 400, 800, 1500, 110 meter hurdle and marathon.
In Russia, running was noted as a sporting discipline in 1888 with the emergence of an amateur club near St. Petersburg under the leadership of Pyotr Moskvin. A year later, the first official competitions took place. And in 1901, in Sweden, members of the circle performed at international competitions.
In 1912, Russian athletes made their debut at the Olympic Games.
During the Soviet era, running was of a general nature. Successful Russian athletes participated in the Olympic Games.
The sport of running continues to develop today. New ways to increase endurance and improve technology are being developed. It has gained immense popularity among amateur runners. In all countries of the world, people run in parks, stadiums and even in the streets. Those who wish can compete in general races.
L
Lactate
Lactate is a component of lactic acid. Lactic acid itself is the result of the breakdown of glucose, which is the main source of energy for muscles during physical activity.
Lactic acid is constantly produced in human muscles, but this does not lead to discomfort. The characteristic muscle pain after exercise indicates an excess of acid, which appears at the moment when the breakdown products enter much more than what the body is able to remove.
Personal
An athlete’s personal record at any distance, that is, the best time in which he covers this distance.
Profit
- It is quite obvious that this is primarily physical health. Systematic training forces the body to work in the mode for which it was, in fact, created. Metabolism accelerates, general tone and immunity increase, and the head begins to work better. (Here is a good article examining the relationship between immunity and physical activity.)
- The improvement in mental health is not so obvious. I don’t have any workouts shorter than an hour now. An hour of running is a unique opportunity to be alone with yourself, disconnect from all annoying things, establish an internal dialogue, understand problems, make decisions, think through ideas. Most of this article, for example, came to me during training in preparation for the Moscow marathon.
- Another not-so-obvious point: testing one’s strengths and expanding the boundaries of what is possible. I can run for thirteen hours straight, with minor breaks for meals and bio-pauses. I can run all night and then walk with my wife in the scorching sun and wind until lunch. And I feel that this is not the limit. What does this give me in life? The concept of your performance. I can dig potatoes in the garden all day and run a half marathon in the evening. Mushroom picking, walks in the forest? Walk for hours and kilometers without feeling tired. Tourist trips? I can walk around, sightseeing, all day long with a tour. in a group, then return to the hotel, put on a running shoe and walk ten kilometers along the streets you especially like, and at night go with rested friends to look at the city at night. The fear of distances disappears: “Pfft, it’s only 7 km away: I’ll get there in 40 minutes without straining!” I also understand more clearly how much time and with what efficiency I can do my work - in case of emergency or unforeseen situations.
- The next moment is new emotions and new achievements. In running there is the concept of “personal record” (personal record). You can constantly improve, running faster and further each time, and this progress, as the result of work well done, is a separate value in itself.
It's nice to see such an inscription on the display of your fitness tracker after the next race. Strava is especially zealous in this regard, which likes to celebrate achievements of the type “Third fastest time at a distance of 1 km” and draw medals of the corresponding color. - Besides, running achievements are objectively impressive. Try telling someone that you have run ten kilometers, a half marathon, a marathon, or even to the ultra-average person for whom the distance from home to the bus stop on foot seems “long”... and get ready to “catch the lulz.” It’s also flattering to feel that you are capable of things that 99% of the world’s population cannot repeat (even if they haven’t tried). And these are quite serious, applied things, and not nonsense in the spirit of the “Guinness Book of Records”, when a certain part of the body is used in an original way.
- And from the comments to the article we can conclude that many simply like to “live with a feeling of strength.”
Other benefits
I can’t help but say a word about age-related crises.
Psychologists distinguish the first type of midlife crisis - this is when “gray hair in the beard, a devil in the rib.” Men begin to look younger, buy expensive cars, motorcycles, begin to pursue women half their age, disappear into bars, indulge in all sorts of bad things... And the second type of midlife crisis, when a man wants to be sure that with age he becomes better than before. In European countries, for example, there is the term MAMIL (Middle Aged Man In Lycra). Look for meaning for interest. My running coincided with the onset of a midlife crisis and helped me overcome it safely: it works - I confirm! I also want to say about the options for accompanying activities when running. I used to read a lot and had an arrogant disdain for audiobooks. Over time, opportunities for reading became fewer and fewer, until this activity was completely replaced by viewing social media feeds. Running actually gave me that ability back. And yes, audiobooks are great. Everything, of course, greatly depends on the quality of the reading, but over time I have developed a top list of authors whose works often resemble audio plays, with their own unique atmosphere, and are quite tempting to co-author.
I can personally recommend this book about running from the most famous running writer in the world. By the way, his series “Air Cocoon”, read by Igor Knyazev and the Abuki Theater, also works exceptionally well for running. Especially during long workouts.
Music while running is also good, but it often disrupts my step, breathing, pulse, pace, so during training I listen to it occasionally and depending on my mood.
In the comments to the first part of the article there were also people who listen to educational audio courses and podcasts while running, which is too boring “just sitting.”
Running and remote work
I started this article by stating that running is the best choice for a remote worker. Some called him pretentious. I’ll try to explain why I emphasized the word remote worker:
- Being in your home office, you don’t waste time commuting to work: finding time for training is much easier, which, coupled with their high availability (go out and run), makes training much easier.
- When working remotely, the schedule is usually flexible. Because of this, there is a great temptation to sit too long and mix work and personal life. Running serves as a wonderful “watershed” between work and personal life
. Once you have a goal and a workout plan, just set your alarm for the right time and always stop to go for a run (unless you're working on a "die-or-do" task, of course). The end of the workout, coupled with the mental release during running, helps to shift focus to family and personal life. The training time can be selected in such a way that it ends exactly when the children do their homework and the wife finishes her chores. Or even the other way around: wait until everyone is finished and take the family with you on a bike ride. After all, the pace of an average runner is quite within the capabilities of a child on a bicycle. My family loves to accompany me on their bikes while jogging. - Motivation and discipline. I think it’s quite obvious that the level of motivation and self-control of a remote worker should be higher than that of an office worker
. In terms of motivation, running has much more opportunities than any other sport (I talked in detail about setting and achieving goals, with examples, in the first part). It's the same with discipline. Running is a unique tool for developing it. The training plan will need to be followed - otherwise you will not be able to achieve your goal. You will have to build and follow a daily routine - to recover from increased physical activity, you need high-quality, full-fledged sleep. When you manage to build a daily routine, it will become clear that “night owls and larks” are just a convenient myth for those who do not want to go to bed on time...
However, everything is learned through comparison. The first part of the article already talked about rugby, kickboxing, cycling and the difficulties that arose with it after switching to remote training. I consider these problems to be fairly typical.
M
"Marathon Wall"
The “marathon wall” is a state of extreme fatigue caused by fatigue during the final kilometers of a race. The main reason is hypoglycemia, that is, a decrease in glycogen reserves in the body. The “wall” most often occurs after 30 km, but can happen earlier or later depending on the level of preparedness and the chosen pace along the distance.
Manege
An enclosed space intended for running and athletics competitions. In a track and field arena, the length of the track is traditionally 200 m, and in a football and track and field arena (one where there is a football field in the middle) – 400 m.
Useful material: Rules for running in the arena
Major marathons
World Marathon Majors, the “big six”, are a series of the largest and most prestigious road marathons in the world. These include three starts in America, two in Europe and one in Asia: New York, Boston, Chicago, Berlin, London and Tokyo.
Maximum oxygen consumption (VO2)
MOC or VO2max is an indicator of how much oxygen from inhaled air the body can consume and process at critical, maximum speed or power. The MOC of the average healthy trained person can reach 60-65 ml/kg/min.
But it is believed that this indicator is a value given to a specific person by nature, although it can still be developed to a certain level.
Effects of training
If after reading these schemes you have the question “What will this give me?”, read on:
- You will become an athlete physically and psychologically . The appearance will significantly improve, which will be based on the psychology of the athlete. Discipline in training transfers to all areas of life. If earlier you could not force yourself to be entrepreneurial, open your own business, or achieve a promotion, then in the process of training this skill will begin to appear.
- The effectiveness of the worldview increases . Thanks to changes in the hormonal system, the athlete begins to see more opportunities than before starting training. You do not lose the ability to adequately assess reality. The efficiency of actions in this reality increases.
- With the help of training, you can find a company of like-minded people and friends . Many athletes find a soul mate based on common interests. Sport is not only strength, health, speed and beauty, but also an opportunity for socialization. You don't have to do it alone. Thanks to these trainings, you will be able to join the mass events that take place in the city.
- Running training can be the beginning of a sports path that will bring you everything you desire . There are many sports exercises to achieve any goal. Improve your health, appearance, live 15 years longer, completely change your life, turning from a loser into a champion - this is something that everyone can do if they start working on themselves. Running is the cheapest and safest way to start a new life.
- The motivation to work on oneself increases, the desire to live increases . Example: an average man who works an average job and lives an ordinary boring life suddenly makes his first independent decision: to go in for sports, start running according to the schemes given above. At this moment his worldview changes. He made the first independent decision in his life, and from that moment on he no longer flounders in the flow of life, but can choose his own path. After several months of training, he understands: “The whole previous life was like a dream. Only now have I begun to live.” It’s not only about improving the functioning of the hormonal system, but also about a sharp jump in the level of consciousness. A sharp change in priorities, constant overcoming of weaknesses.
- You can join sports recreation, team sports, diving and other active entertainment . It's scary to just start. After overcoming this fear, a world of new opportunities opens up before a person. This is why athletes who have trained for at least 2-3 months are so fanatical in their passion. They realize that this has breathed life into their previous existence.
ABOUT
Deer running
It is also called multi-jump. This exercise is similar to a mix of jumping and running. When performing, trainers recommend imagining an obstacle in front of you, for example, a wide puddle, and you need to jump over it with one leg, while bending the knee. The second leg remains straight.
Source: irunning.com.ua
Orthopedic insoles
Custom-fitted shoe insoles that help correct anatomical foot imperfections, relieve foot, leg and back pain, and even prevent injury.
Negative (negative) split
Tactics during a race when an athlete runs the second half of the distance faster than the first. Negative splits can be performed by experienced amateur or professional runners. For beginners, it usually happens the opposite: from the start they run as fast as possible, but by the middle of the race they lose strength and inevitably slow down.
A negative split helps you set a personal best, distribute your strength correctly over the distance, and reduce the time you spend on the track.
General physical training (GPP)
General physical training is exercises aimed at developing the musculoskeletal system. When performing such exercises, the performance of joints, ligaments and tendons improves, and muscles are activated and developed.
Competition rules
If some criteria are not suitable for amateur runners, then in professional competitions the organizers must adhere to special standards for the quality of the surface and marking of running tracks.
Running space requirements
The radial area of the stadium should be divided into 6-8 separate lanes. The width of the marking in this case is 5 centimeters, and the width of any stripe is 1.25 meters. For a convenient and safe start and finish, the stadium provides at least 10 meters at the beginning and 15 at the end.
The initial and final routes differ in the width of the markings with the numbering of the treads. For sprint events, blocks are used at the start of the track, taking into account the radius of the track in order to equalize the chances of all runners.
The materials used to cover competition tracks are layered to create a good tread surface, and the surface is made of a rubberized polymer to improve traction.
Indications and contraindications for athletes
Amateur running has virtually no restrictions and is used to strengthen the body, as well as for the rapid recovery of athletes after injuries.
Professional running is prohibited in case of acute diseases of the cardiovascular system or serious injuries to the musculoskeletal system. These restrictions were introduced in order to protect athletes, since overload increases the risk of developing irreversible consequences in the activity of the heart and blood vessels, as well as degenerative processes in the musculoskeletal system, leading to disability.
Important! Anthropomorphic properties, and in particular a person’s propensity for aerobic and anaerobic exercise, are taken into account when choosing the disciplines in which the athlete is most active.
Features of sportswear and shoes
Professional athletes compete in special shoes - sneakers with spikes (5-7 pieces in front of the sole).
This gives better traction. For long distances, sneakers with shock-absorbing soles are used.
Runners' clothing should fit snugly to the body, reducing friction with the air. Otherwise, the uniform should be comfortable and appropriate for the time of year.
Regulations
In modern sports there are strict rules for racing. One of the most common violations is a false start - crossing the starting line before the signal. In official competitions, the athlete is eliminated from the race after the second false start.
Important! It is prohibited to cross road markings over short distances; this will result in disqualification.
It is unacceptable to interfere with the movement of other athletes when running long distances and unsportsmanlike behavior.
Today, runners' finish line is recorded using ultra-sensitive cameras, and the favorite is determined by a "photo finish" system, a version of moments where the finish is determined in a split second.
Athletes in controversial situations have the right to call the organizers to check the results. The victory is recorded by a mechanical and electric stopwatch. Their choice depends on the level of the competition and the requirements of the organizers.
P
Pasta party
The term comes from the English pasta party, which means “pasta party”. This is a free portion of pasta from the race organizers for everyone who decides to cover a long distance. An invitation in the form of a voucher is usually issued along with the starter package.
Pasta is easily digestible and contains complex carbohydrates, which is why pasta is considered the most popular pre-race dinner.
Read on topic: Pasta-party: 10 delicious pasta recipes for runners
Pacemaker
A pacemaker (from the English pace - “tempo”), also known as a pacer, also known as a hare, is a specially hired athlete whose task is to run a distance at a given pace. Pacemakers help other athletes finish at the right time by leading them at a certain speed.
Source: marathon.md
The most popular time for an amateur marathon is 3 hours 59 minutes, and for a half marathon it is 1:59 minutes. This time always gathers large groups of amateur runners around pacemakers.
Overtraining
Weakened immunity, decreased performance and athletic performance, sleep disorders, mood disorders. A condition occurs when the volume and intensity of the training program exceeds the body’s ability to restore resources.
Eyeliner
It is also sometimes called a taper. This is the period of time immediately before the competition. The volume of the load at this time is reduced so that the athlete reaches peak form immediately before the start.
"Half"
This refers to the half marathon distance - 21.1 km. Exactly half of a full marathon.
Pronation
Pronation is the way the foot is positioned when walking or running. If the dorsum of the foot turns inward and the sole turns outward, this is overpronation, that is, overpronation. Underpronation is called hypopronation. Both features affect running technique, which must be taken into account when choosing running shoes.
Heart rate monitor
A device that allows you to monitor your heart function while jogging. Heart rate monitors are distinguished by the type of attachment to the body: wrist, chest, headphones, fixed on the finger, forearm or ear.
Food point
A food and drink area where participants can refresh themselves during the long run. Usually you can find easily digestible food here: bananas, dried fruits, cookies. Professional athletes have the opportunity to put their own food on a separate table.
R
Alignment of forces
When they say that an athlete “ran well over the distance,” this means that he was able to correctly calculate his own strength and maintain an even pace throughout the entire race.
Rogaine
Rogaining is a team sport similar to orienteering. Participants move around the area with a compass and a map of the training ground in their hands and look for control points marked by the organizers on the map.
Types of running training
The very name sports running is in contrast to jogging that takes place in the format of health training, which can often be observed in a park or forest, since it can be carried out if you have certain skills.
In particular, the athlete is required to have strength, endurance, and reaction. Therefore, if you are a beginner and are out jogging for the first time, it is worth knowing how this or that training is carried out.
Jogging or jogging
The word jogging itself has English roots and comes from the medical term – jogging. And there is no difference in this type of running; these are traditionally amateur runs, which are often used as part of recovery and rehabilitation programs.
Fartlek
So, at its core, fartlek is interval training, which in the program involves alternating different running paces. As an example, the first 1,000 meters can be covered in 5, the second in 4.5, and the third in 4 minutes.
This type of running does not involve easy jogging and requires considerable willpower from the runner. As a result, this type of running is not inherently easy, requiring a lot of effort.
Rogaine
Rogaining is a team sport. In essence, it involves the athlete passing a control point along the distance. For the most part, it resembles orienteering, but with slightly different tasks and goals.
Cross running
The most popular and sought after type of running among amateurs and professional athletes, carried out on rough terrain.
The route can pass through forests, sand dunes, shallow ponds and other natural obstacles.
This variety involves a combination in the program of overcoming obstacles over several types of terrain. Much depends on the level of training of the athlete himself and the distance of the race.
Marathon running
Marathon running is a race whose distance does not exceed 40 kilometers. And although not all countries hold it, the whole world follows it, since a marathon runner must have good training and endurance, and a desire to win.
It is these qualities that are called the most basic in marathon running - many athletes do not classify it as a sport.
Sports running is not just jogging as part of a sports program. This is taking care of your health and playing for championship, training your mind and body, which will ultimately make your body fit, your spirit strong, and your passion healthy. But the main thing in every sports competition is not so much the victory itself, as a healthy, athletic competition between athletes.
WITH
Special running exercises (SBU)
SBU is a set of running exercises aimed at developing strength, power and coordination of all leg muscles involved in running. Specific running exercises will help increase the physical and technical fitness required for running. Each of these exercises is a separate accented element of running.
Skyrunning
Skyrunning is a race in the mountains at an altitude of up to 7200 meters, where the degree of difficulty is not higher than category 2 (according to the mountaineering classification) and the slope does not exceed 40%. The elevation gain is at least 1000 meters, and the asphalt surface is no more than 15% of the entire distance.
Kilian Jornet is the world leader in skyrunning. Source: Kilian's Instagram
Skyrunning is a mountaineering discipline.
Slot
“Ticket” to participate in the race.
Starter pack
A set that a race participant receives on the eve of the competition. Includes a bib number with a chip and items marked with that number, such as clothes check-in stickers and a coupon for a pasta party. The rest of the content depends on the race sponsors and can be quite varied: sports nutrition, cosmetics samples, discount booklets, running accessories, etc.
Often a T-shirt is included in the package, but at some races it is offered to be purchased separately.
Exercises to practice technique
To teach short-distance running techniques, a whole arsenal of running, jumping and strength training tools is used.
1.Running work
Practicing low and high starts, starting from different positions, running short distances at maximum speed, practicing arm movements while standing still, bringing your hips together as often as possible while standing still or in support.
Jumping work
Standing long jumps, multi-jumps, jumps on every second step, skipping, jumping from a full squat and jumping onto a high stand, jumping alternately on one and the other leg, SBU.
Strength work
A variety of general physical training exercises designed to increase leg strength, performed both with weights and with your own weight: squats, lunges, pistols, stepping onto a high surface, step-ups, etc.
T
Tights
Tights are tight-fitting sports leggings made from high-tech fabrics. These clothes do not restrict movement and are well suited for running.
Tape (kinesio tape)
An elastic tape with an adhesive backing, similar to a colored plaster. Taping involves applying tape along muscle lines to reduce pain and inflammation, to relax overstrained and tired muscles, and to support muscles and ligaments.
Running pace
Running pace is the amount of time it takes a runner to cover one kilometer (or mile in non-metric units). Tempo is the reciprocal of speed. If it shows how much time you spent covering a certain distance, then speed is how much distance you cover per unit time.
Tempo (threshold) training in the plan involves running for a certain time on the border of the anaerobic threshold.
Trail running
The term trail running comes from the English trail - “path, path”. This is trail running. Everything that is not asphalt or tiles is a trail: soil, stones, water, dirt, sand, etc. The International Trail Running Association defines the discipline as “a running/walking event open to all, in a natural environment, with a minimum of 20% paved roads, on a marked course.”
Such competitions are often held in conditions of full or partial autonomy of the participants, that is, each athlete takes a supply of food and drink with him to the distance.
Running as a sport
Sport is a type of physical activity that involves constant physical activity and participation in competitions that involve covering set distances in a certain time. Running sports are included in the Olympic athletics program. In addition, running is necessary in various games and sports disciplines, such as triathlon, long/high jump, football, basketball, etc.
Professional running differs from recreational running in that it involves constant exercise to improve speed and endurance characteristics.
In addition, all movements in sports running are performed using a certain technique. The running process includes two alternative phases: support and flight.
Support. This phase is a process of abandoning the supporting leg with the release of the knee of the forefoot. The flight phase is the simultaneous release of both feet from the ground, which is the hallmark of running.
Short distance sprint
Sprint is a run that involves an athlete covering impressive distances. Spectators enjoy watching this process. Completing the sprint course requires a small amount of time, but at the same time, the fate of the first three runners can change at the last moment.
Usain Bolt, Justin Gatlin and Yohan Blake are all sprinters. Among them, Usain Bolt is a multiple winner of various Olympics and a world record holder. But his opponents came very close to the record he set. The traditional distance for short distances is:
- 100 meters;
- 200 meters;
- 400 meters.
There are also 30 m (school standards), 60 m (indoor competitions) and 300 m.
Middle distance running
Middle distances are considered easier than the sprint, but the 100 meters before the finish line always intrigues the viewer. Judges often use a photo finish to determine the favorite.
Main distances in the average run:
- 800 m;
- 1500 m;
- 3000 m (with obstacles).
In addition, middle-distance athletes participate in 600-, 1000-mile (1610 m) and 2000-meter races. Middle distance running is a difficult type of running because it has a long distance. On the one hand, the distance is small, on the other hand, not everyone can maintain the sprint pace. As a result, the speed of passing the distance tends to high speed indicators.
Athletes who exceed middle distances often compete over 400 (sprint) or 5,000 meters (long distance). From time to time, middle distance runners make it to the finals, where they don't always win.
The best runners in this discipline are from Ethiopia and Kenya. A popular 800-meter athlete is Kenyan David Rudisha. Algerian runner Tawfik Makhloufi, who successfully completed the 800 meters and won numerous prizes, won the 1500 meters race.
Long distance running (stayers)
Distances from 3000 meters are considered long (an alternative name is stayer distances). Long-distance running competitions take place in a stadium or along a highway. From 3,000 to 10,000 meters - in a stadium located along a motorway, longer than 10,000 meters, which is measured in kilometers, excluding marathons.
Olympic distances:
- 5000 meters;
- 10000 meters;
- 42 km 195 meters.
Long distance running competitions have no boundaries in terms of space and time. Such races may be adjusted according to distance or time. Preferred limited time races include a one-day race. Stayer races also include ultramarathons (100 km or more).
A popular marathon runner is Kenyan athlete Dennis Kimetto, who managed to cover a distance of 42 kilometers 195 meters in 2 hours 2 minutes and 57 seconds. It is worth noting that among women the fastest runner in the marathon is Paula Radcliffe (Great Britain) with a result of 15 minutes 25 seconds.
Obstacle course (steeplechase)
An obstacle course is a narrower type of running that includes only two distances: 2000 m in an arena and 3000 m in an outdoor stadium.
The essence of such a race is to overcome a distance at which there are 5 obstacles, in the center of which there is a pool of water. You can create groups that are 10 meters apart from each other.
From time to time, the favorite in the obstacle course moves away from his pursuers by a semicircle equal to 200 meters.
Qatari runner Saif Saeed Shaheen has set a men's world record. He completed the distance in 7:53.63 minutes. The Russian record was set by Russian Gulnara Galkina-Samitova, who completed the 3000 meters with obstacles in 8:58.81 minutes.
Hurdling
The hurdle race has a distance that can be classified as a sprint event. The difference between the types of running is that there are additional obstacles that athletes must overcome.
The Olympic program includes the following distances:
- women - 100 m;
- men - 110 m 400 meters.
The number of barriers, regardless of the distance and gender of the participants, remains constant - 10 pieces. You can only change the distance between barriers and the height of the obstacle.
Record holders: (among men) - Aris Merritt - 110 m in 12.80 s., (among women) 100 m - Yordanka Donkova - 12.21 s.
Relay race
The team's discipline is the relay race, which takes place over two distances at the Olympic Games. Relay means passing the baton to your partner after covering a certain distance.
The relay has distances of 4 × 100 meters and 4 × 400 meters. World records are also set at various distances.
There are also mixed and combined relay races: 800+400+200+100 meters and 4 × 100 hurdles.
The world record in the 4x100 is held by Jamaica thanks to Usain Bolt. The men's team finished in 36.84 seconds. The American women have a record of 40.82 seconds.
U
Carbohydrate loading
Carbohydrate loading – consuming foods rich in complex carbohydrates the day before the race. Can be part of a marathon diet, during which carbohydrate days are preceded by protein days. The point of this approach is to first reduce glycogen reserves to a certain limit, and then force the body to accumulate it for future use.
Carbohydrate window
The carbohydrate window is a short (30-45 minutes) period of time after a workout or race during which the body is most sensitive to the absorption of nutrients, primarily proteins and carbohydrates. During this period, the athlete especially urgently needs to replenish expended resources.
Let's run!
So, theoretically savvy and equipped, we got to the training. And here I again want to repeat the mantra about the correctness of the loads and their gradual increase
. Don't try to achieve everything at once: this will lead to discomfort, injury and disappointment. Train gradually and learn to listen to body signals.
At the first stage, you just need to prepare the body for new loads. We set the threshold on the heart rate monitor to 148 beats per minute and try to run slowly and very easily, without exceeding this threshold. At first, you shouldn’t run for too long - 3..5 km is quite enough. You may just have to walk quickly at first. We don’t forget about running technique: we try to at least avoid the main mistakes (leg overshoot and “sticking in”). During this period, muscle pain in the most unpredictable parts of the body and some kind of discomfort are possible.
When the discomfort passes, you will need to start working on your aerobic base and improving your running technique and economy: continue running slowly, at a low heart rate, gradually increasing the distance covered (in general, it is recommended to increase volumes by no more than 10% per week), introduce elements SBU. At this stage, you need to clearly understand that an insufficiently trained heart will be your main limiting and slowing factor.
Once the body has fully adapted to the new loads, you can think about intervals, fartlek, strength, maintenance and recovery training and work in the anaerobic zone. But the main thing is not to forget that running should be fun.
. This is the key condition.
All of the above is presented in a very simplified manner and is based on my own experience. It is worth understanding that each person is individual, there is no universal approach. A good practice is to contact a professional trainer.
who will be able to properly structure your training and set up the technique.
I would also like to focus on warming up before running and stretching after.
. Many beginners neglect this - and in vain! A short warm-up before running - joint exercises and several dynamic exercises (the key word is “dynamic”: stretching relaxes the muscles and is contraindicated before training!) will help warm up the body before starting intense exercise. This will reduce the risk of injury.
The next mandatory item is stretching
. At the beginning of the article I mentioned runner's knee injury. More correctly, iliotibial tract friction syndrome (most of the runners I knew had this injury). The essence of the injury: the muscle strengthens from high load and, becoming less elastic, rubs against the bone. The pain is localized in the area of the knee joint and feels like joint pain, not muscle pain. You can avoid (or cure) this problem only by regularly stretching after each workout. I recommend the video on this subject - thanks to the advice from it, I got rid of pain caused by insufficient stretching of the soleus muscle.
Lately I have also been practicing myofascial release (self-massage - rolling out muscles on a massage roller and similar massagers, here is an introductory video). I highly recommend this practice to all athletes and representatives of sedentary professions (search for information using the keywords “trigger point”).
And the last absolutely necessary step: communicate.
. Give high fives to runners you meet on runs, make running connections, install Strava and add new people as friends, go to parkruns, join a running club, meet people at races, share your achievements and support the successes of others.
F
Fan run
An amateur race over a short distance for fun, not results. The English word fun means “fun”, run means “running”. Often such races are costumed or timed to coincide with some event.
Fartlek
The word "fartlek" comes from the Swedish fartlek, which means "fast play." This is a type of interval training with a random set of tempo and recovery sections, when within one run the athlete mixes different types of running - from anaerobic sprinting to jogging.
Read also[edit | edit code]
- Running at the Olympics
- History of athletics
- Focus on running training
- Building a running workout
- Running training program
- Types of Running Workouts
- How to start running
- Running technique
- Proper breathing when running
- Health running: programs and techniques
- Training to develop running speed
- Athletics in pre-revolutionary Russia and the USSR
- Athletics at the Olympics
- History of the Olympic Athletics Movement
H
Chip time
Sometimes called "clean time". The time it took a runner to cover the distance from the starting line to the finish line. If he starts not from the elite, but from a more distant cluster, he will inevitably spend some time getting from the starting point to the immediate start.
The athlete’s net time is recorded using a special chip attached to the start number.
Heart rate (HR)
One of the most essential concepts for a runner if he wants to track his performance. Heart rate is the number of heart beats per minute. By paying attention to your heart rate during exercise, you can control its frequency, intensity and your own well-being.
Read on the topic: How to calculate maximum heart rate (MHR)
Basic rules of running competitions
Different types of running disciplines have different competition rules. At a distance of up to 110 meters, running is carried out on a straight track; if the distance is greater, circular tracks are used, with athletes moving counterclockwise. If the distances are short (less than or equal to 400 m), each athlete moves along a strictly allocated lane. For longer distances (600-1000 m), athletes are required to run along a designated track, starting from the start line until the end of the very first turn, i.e. to the place where the runners transition to the common track.
In some cases, the rules provide for the race to be held from a common start - this happens in competitions at distances of 400-1000 m. At other distances, the participants run along one common track. If the race is carried out on separate tracks, according to the rules, the number of participants must correspond to the number of tracks, while in races over distances of 200 meters or more, the maximum number of participants must be eight people.
The main goal of a running competition is to determine the fastest runner. The winner of the competition will be the athlete who crossed the finish line (ribbon) first. If the number of participants is large and the distance is long, several stages of the competition are held, each of which ends on a specific lap.
Different competition stages have their own competition rules. The race consists of 4 main stages - the start, running along the distance, which can be regular, hurdle or relay, and the finish.
Start
If the distance is less than 400 meters, according to the rules, 3 teams are given. The first is “To the start”, in which participants must take their starting position. After the second command (“Attention”), athletes need to concentrate as much as possible on the upcoming jerk. The last command (“March”) is given when all participants show their readiness for the race.
A participant who takes off without the appropriate command receives a warning. At the same time, he must raise his hand up to confirm that he has heard the warning. If the same participant receives a 2nd warning, it means he is breaking the rules and is removed from the race. In cross-country events, participants are removed only after the third warning.
Movement along the main distance
When a race takes place on separate tracks, the rules provide for participants to run exclusively on their own tracks. An athlete may accidentally move to an adjacent lane, but only if he immediately returns to his own. The main thing is that his short-term transition does not interfere with the running of another participant.
When turning, a participant is not allowed to cross into an adjacent lane. If an athlete on a bend takes two or more steps on someone else's track to the left or along the left boundary line, he will be disqualified, since this will mean that he has shortened the distance. If a participant moves several steps onto the path on the right and quickly returns back, without interfering with another participant, such an action will not be considered an error.
Finish
The participant who has crossed the finish line (usually an imaginary line set by the judges) with any part of the body other than the neck, head, legs or arms will be considered to have completed the distance. If an athlete falls after touching the finish line, his arrival time is counted on the condition that he crosses the finish line on his own.
The simultaneous finishing of several runners in the final stages requires the judge to decide on the race of these participants, or to approve the results so that both participants are considered winners. This applies only to those athletes who showed the best results in the final races. The remaining runners with the same results are automatically awarded first place.
At competitions where results are measured using stopwatches, the time is determined rounded to one tenth of a second. For example, if the reading is 12.24 s, the time will be rounded to 12.3 s. Separate stopwatches are used for each competitor, with the time of the leading athlete calculated using three stopwatches.
E
Ekiden
A sports competition in road running, which is a relay race over a marathon distance. The distance of 42,195 meters is run in 6 stages, which are distributed in the following order: 5 km, 10 km, 5 km, 10 km, 5 km, 7.195 km.
Read on the topic: What is ekiden and why is it so popular in Japan
Expo
A sports fair that opens on the eve of the start. This is where participants are registered and starter packs and numbers are issued. At the Expo, runners can purchase sporting goods, food, chat, take pictures in photo zones, or take part in sweepstakes from the organizers and partners of the race.
Source: runfitexpo.co.uk
Electrolytes
Minerals found in fluids in the human body. They are responsible for regulating water balance, blood PH levels, and also create electrical impulses necessary for any physical activity. If an athlete loses a lot of salts through sweat, and their content in the blood plasma drops, this can lead to fatigue, cramps, and in severe cases, hyponatremia.
Energy gels
Energy gels are specialized sports nutrition that allows you to replenish carbohydrate reserves during intense physical activity. Unlike regular high-calorie foods (bananas, dried fruits, nuts), gels are quickly absorbed by the body, do not require chewing and may contain various additives: caffeine, guarana, BCAA, sodium.
Of course, if you try to collect all the running terms, you will get not a dictionary, but a multi-volume encyclopedia. But you’ve already become familiar with the basic terms, so you can safely go to training or a race and put your new knowledge into practice.
Read next: How to start running: a complete guide to running for beginners