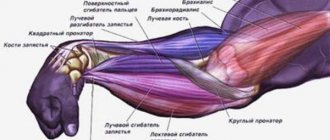
For every action there must be an equal and opposite reaction. This is true for muscles too. Perhaps the biggest misunderstanding about how skeletal muscle functions concerns its specific role. Most people think that muscles have one specific role and that they always perform only that specific role. This is wrong. Muscles must work together to produce different movements and the role of a particular muscle could change depending on the movement. Muscles are located in groups: agonists, antagonists and synergists, which produce and modulate movement.
Muscle Definition
Muscle
(lat.
muskulus
) - an organ of the human and animal body formed by muscle tissue.
Muscle tissue has a complex structure: myocyte cells and the membrane covering them, the endomysium, form separate muscle bundles, which, when joined together, form the muscle itself, dressed for protection in a cloak of connective tissue or fascia
.
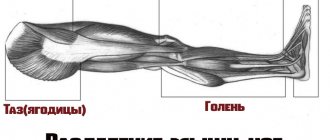
Muscles of the human body
can be divided into:
- skeletal
, - smooth
, - cardiac
.
As the name suggests, the skeletal type of muscle is attached to the bones of the skeleton. The second name is striated (
due to transverse striations), which is visible under microscopy. This group includes the muscles of the head, limbs and torso.
Their movements are voluntary, i.e. a person can control them. This group of human muscles
ensures movement in space; it is they that can be developed or “pumped up” with the help of training.
Smooth muscle is part of the internal organs - the intestines, bladder, vascular walls, and heart. Thanks to its contraction, blood pressure increases during stress or the food bolus moves through the gastrointestinal tract.
Cardiac - characteristic only of the heart, ensures continuous blood circulation in the body.
It is interesting to know that the first muscle contraction occurs already in the fourth week of the embryo’s life - this is the first heartbeat. From this moment until the death of a person, the heart does not stop for a minute. The only cause of cardiac arrest during life is open heart surgery, but then the CPB (heart-lung machine) works for this important organ.
Biology. Diversity of living organisms. 7th grade. Navigator textbook + CD
The navigator textbook is the main module of the innovative educational and methodological set “Navigator”. A simple and convenient navigation system connects the text of the textbook with the information field of the accompanying multimedia manual (disc): all terms and concepts found in the textbook are divided into main and additional material using a color indication. The methodological apparatus of the textbook consists of questions for self-testing, questions of an increased level of complexity (including those establishing interdisciplinary connections), as well as a system of tasks using other components of the teaching materials - both printed and electronic, which contributes to the effective assimilation of educational material.
Buy
Correction of age-related changes
With age, multifactorial processes occur that determine the aging process of the face. These processes affect the facial skeleton and integumentary tissues. After 30 years, the beginning changes in the face are already visually noticeable. Changes in all tissue layers lead to their displacement and downward movement. More pronounced processes occur in the middle third of the face. The decisive factor in the drooping of the integumentary tissues of the face is a change in the bone surface.
- Forehead
Flattening of the frontal bone, combined with constant tension of the frontal muscle, leads to drooping of the integumentary tissues of the upper area of the face and the formation of transverse grooves in the forehead. The sliding mass of soft tissues of the forehead forms excess tissue in the area of the upper eyelids, the tails of the eyebrows droop and a “heavy” look is formed.
- Middle face area
Atrophy of bone tissue and fat packets in the midface area, combined with weakening of the muscles, leads to contusion of the ligaments and grooves. Pronounced bags under the eyes and eye bags form.
- Neck
The framework that holds the tissues of the lower zone of the face is the platysma - the subcutaneous muscle of the neck. Atrophy of the jaw bone, prolapse of the submandibular salivary gland, together with weakening and divergence of the platysma fibers, form an obtuse cervical-mental angle and a “double chin.” Thus, with age we observe: a reduced lower jaw; a stretched space at the bottom of which fat has accumulated; atrophied neck muscles that can no longer hold soft tissue and sag under gravity; the resulting jowls.
Fig.1 Aging according to Mendelssohn
Rice. 2 Bone atrophy according to Mendelssohn
Rice. 3 Facial aging: pronounced folds, jowls, “fat packets”
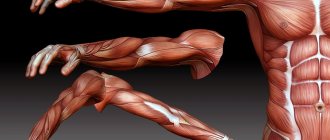
The structure of human muscles
The unit of structure of muscle tissue is the muscle fiber. Even a single muscle fiber can contract, indicating that a muscle fiber is not only a single cell, but also a functioning physiological unit capable of performing a specific action.
An individual muscle cell is covered by a sarcolemma.
– a strong elastic membrane provided by the proteins
collagen
and
elastin
. The elasticity of the sarcolemma allows the muscle fiber to stretch, and some people show miracles of flexibility - doing the splits and performing other tricks.
In the sarcolemma, like twigs in a broom, threads of myofibrils
, composed of individual sarcomeres. Thick myosin filaments and thin actin filaments form a multinucleated cell, and the diameter of the muscle fiber is not a strictly fixed value and can vary over a fairly wide range from 10 to 100 microns. Actin, which is part of the myocyte, is an integral part of the cytoskeleton structure and has the ability to contract. Actin consists of 375 amino acid residues, which makes up about 15% of the myocyte. The remaining 65% of muscle protein is myosin. Two polypeptide chains of 2000 amino acids form the myosin molecule. When actin and myosin interact, a protein complex is formed - actomyosin.
Description of human muscles
difficult, and for a visual representation you can refer to the textbook “Grade 8 Biology” edited by V.I. Sivoglazov, where on page 117 the illustration shows what a myocyte looks like under a microscope.
Botulinum therapy as one of the methods for treating hypertension and bruxism
Botulinum toxin type A, which is used in medicine and cosmetology, is able to relieve spasms and relax overstrained muscles, specifically reducing their activity or immobilizing them completely. But not forever, but only for a certain period of time - during this time the body adapts to new circumstances and stops overstraining a certain area. That is, the therapeutic effect for a diagnosis such as “bruxism” lasts for a long time, which is confirmed by numerous reviews from patients.
How it works?
Botulinum toxin type A is a neurotoxin produced by the bacteria Clostridium botulinum. It blocks nerve impulses from the central nervous system to muscle fibers. That is, in fact, the drug paralyzes a certain muscle without transmitting motor commands from the brain to it.
In medicine and cosmetology, it is used in ultra-small and highly purified forms - that is, it is not poisonous or toxic to the body!
The drug is injected into clearly defined points in order to affect only a specific muscle and not affect the work of others. The dosages are harmless, and the blocking is reversible. Over time, the drug is completely eliminated from the body - usually this takes from 5 to 7 months. Gradually, neuromuscular conduction in the area is restored, and mobility returns to the muscle - but since it has “rested,” the spasmodic fibers are smoothed out, and the body adapts and normalizes the load.
Botulinum toxin only relieves hypertonicity and allows the muscle to relax. This is the basis of its well-known cosmetic effect - smoothing out wrinkles by blocking the work of facial muscles. That is, it is wrong to think that you can “pump yourself up” with botulinum toxin preparations - they do not in any way increase the volume of soft tissues.
To relieve excess tension in the masticatory muscles, we use the drug Botulax for intramuscular injection with 99% active substance content, thereby increasing the speed of onset and duration of the therapeutic effect. And thanks to the high degree of purification of the drug, the risk of adverse reactions is minimized. The dosage and course are selected by the doctor strictly individually!
Name of human muscles
When anatomists in the Middle Ages began to dig up corpses on dark nights to study the structure of the human body, the question arose about the names of the muscles. After all, it was necessary to explain to the onlookers who had gathered in the anatomical theater what the scientist was currently cutting with a sharply sharpened knife.
Scientists have decided to name them either by the bones to which they are attached (for example, the sternocleidomastoid muscle), or by their appearance (for example, the latissimus dorsi or trapezius), or by the function they perform (extensor digitorum longus). Some muscles have historical names. For example, tailoring
so named because it drove the sewing machine pedal. By the way, this muscle is the longest in the human body.
What else should I read?
How are birds counted?
Cell theory in biology
What is photosynthesis? The history of the discovery of the process, the phases of photosynthesis and its significance.
Mathematics bees
Participation in sports[edit | edit code]
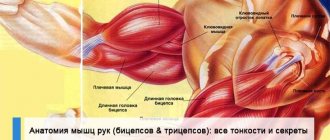
This muscle plays a major role in all sports that require flexion of the forearm.
- Fixed forearm - rock climbing, gymnastics (pull-ups), pole vaulting.
- Fixed shoulder - boxing, handball (forearm throw without hand return).
- Without a fixation point - weightlifting, rowing, kayaking, luge, archery, breaststroke or backstroke.
- Static work - sprinting in cycling.
As an instep support, this muscle is active during all types of wrestling (freestyle wrestling, judo), as well as during fencing and breaststroke. In breaststroke swimming, gymnastics and tennis, this muscle is involved in movements as a shoulder flexor, and in fencing - as an internal rotator of the shoulder. With external rotation of the shoulder, the long head abducts the shoulder (diving, rhythmic gymnastics), and the short head adducts the shoulder during breaststroke. In addition, the short head adducts the upper limb during discus throwing, shot put, and tennis exercises from lateral abduction.
| Kind of sport | Movement/hold | Function | Load | Types of abbreviations |
| Rock climbing | Pull-up and hang | Forearm flexion | Power endurance | Dynamic concentric and static |
| Gymnastics | Exercises on the bar (pull-ups) | Forearm flexion | Fast, strength endurance | Dynamic concentric |
| Exercises on rings: resting your arms to the sides (“cross”) | Shoulder flexion | Fast, strength endurance | Dynamic concentric and static | |
| Pole vaulting | Movement of the upper hand when jumping | Forearm flexion | Fast | Dynamic concentric |
| Weightlifting | Thrust phase | Forearm flexion | Fast, explosive, maximum | Dynamic concentric |
| Rowing | Thrust phase | Forearm flexion | Power endurance | Dynamic concentric |
| Kayaking | Pickup and transfer phases | Forearm flexion | Power endurance | Dynamic concentric |
| Archery | Bowstring tension | Forearm flexion | Power endurance | Dynamic concentric |
| Swimming | Breaststroke, pull-up phase | Forearm flexion | Power endurance | Dynamic concentric |
| Wrestling, judo | Capture | Supination of the forearm | Power endurance | Dynamic concentric and static |
| Tennis | Forehand | Shoulder flexion | Fast, explosive | Dynamic concentric |
| Forehand | Anteversion from a raised position | Fast, explosive | Dynamic concentric |
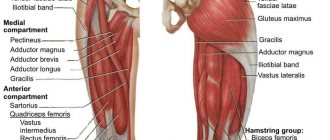
Muscle classification
There is no single classification, and muscles are classified according to various criteria.
By location:
- heads
; in turn are divided into: - – facial expressions
- – chewable
- neck
- torso
- belly
- limbs
By fiber direction:
- straight
- transverse
- circular
- oblique
- unipinnate
- bipinnate
- multipinnate
- semitendinosus
- semimembranosus
Muscles are attached to bones, extending over joints to produce movement. Depending on the number of joints through which the muscle is thrown:
- single-joint
- two-joint
- multi-joint
By type of movement performed:
- flexion-extension
- abduction, adduction
- supination, pronation ( supination
- outward rotation,
pronation
- inward rotation) - compression, relaxation
- raising, lowering
- straightening
To ensure body movement and movement from place to place, muscles work harmoniously and in groups. Moreover, according to their work they are divided into:
- agonists - take on the main load when performing a certain action (for example, biceps when bending the arm at the elbow)
- antagonists - work in different directions (the triceps muscle, involved in extending the limb at the elbow joint, will be an antagonist to the triceps); agonists and antagonists, depending on the action we want to perform, can change places
- synergists - assistants in performing actions, or stabilizers
Biology.Human. 8kl. Tutorial-navigator
This textbook is a multi-level textbook: sections marked with an asterisk are intended for students with a special interest in the subject. In addition, all terms and concepts found in the textbook are divided into basic and additional material using color indication. A simple and convenient navigation system links the text of the textbook with the information field of the accompanying multimedia manual (disc).
Buy
Read also[edit | edit code]
- Muscles - anatomy and functions
- Arm muscles
- Biceps - exercises and training features
- Biceps brachii muscle - training and exercises
- Brachialis muscle
- Triceps brachii
- Brachioradialis muscle
- Elbow muscle
- Arch support
- Pronator quadratus
- Pronator teres
- Extensor carpi radialis
- Extensor carpi ulnaris
- Flexor carpi radialis and palmaris longus muscles
- Flexor carpi ulnaris
Choosing a sleep guard for bruxism: types and price
Firstly, there are universal and individual options: finished products are produced in factories using standard templates, and custom-made mouth guards are made exactly to your measurements.
Also, as we mentioned, mouthguards are not only night guards. The vast majority of patients suffer from teeth grinding during sleep, but a number of people cannot control jaw clenching during the day - for such cases, there are options for daytime overlays that are more invisible and do not affect pronunciation.
A mouthguard for teeth against bruxism, especially a night guard, can be bought at a pharmacy (either in Moscow or in any other city). It costs about two to three times less than a custom-made one. The quality depends on the manufacturer, and universal options have limitations in size and shape, so they simply may not fit the dentition. But the most important limitation, which patients often forget about, is that a ready-made onlay should be purchased on the recommendation of a dentist, and not self-medicated. Alas, without diagnosing and searching for the causes of spasm of the masticatory muscles, a ready-made mouth guard will do more harm than good.
Therefore, it is better if the mouth guard is made individually - based on a cast of your jaws. Individual mouthguards for bruxism, made for sleep, take into account anatomical features to the smallest detail and do not overload the teeth. And if you need to wear the veneer during the day, then it should match the shape of the teeth so that it is truly invisible when communicating. You can order such a mouthguard for bruxism in dentistry by contacting your doctor about this problem.
The doctor will also give recommendations on how long a day it is best to wear a mouth guard, how to care for it, and when the product should be replaced.
Why is botulinum therapy not enough to eliminate hypertension?
You need to understand that Botox treatment in dentistry, like orthopedic treatment of bruxism (that is, the manufacture of special protective mouth guards for teeth during bruxism), is only an additional, and not an independent method. Botulinum therapy protects against the consequences of muscle strain - that is, visible relief will actually occur after administration of the drug. The spasm will go away, the muscles will relax, you will stop involuntarily clenching your jaw and thereby injuring your teeth. But as soon as the effect of botulinum toxin wears off, the problem may return, albeit to a lesser extent.
Of course, if it was just a formed habit based on nervousness, and the causes of bruxism are psychosomatic or neurological, then during treatment you have a good chance to completely get rid of it. But if the source lies in other pathologies and disorders, then you also need to address them: take care of your posture, solve bite problems, restore damaged teeth, replace low-quality dentures, etc. And botulinum therapy will become an effective comprehensive measure.
Prevention of bruxism: how to help yourself
By prevention we mean measures that prevent dental hypertonicity and bruxism in adults, because without finding the cause and monitoring a specialist, treating them at home is an unsafe activity, as with any disease. So if you notice alarming symptoms, your first step is to get diagnosed and get a plan to comprehensively eliminate this problem.
You may need the help of several specialists (neurologist, dentist, gastroenterologist, ENT doctor, psychotherapist), because bruxism occurs in different people for very different reasons. You may be prescribed courses of physiotherapy, taking certain medications (for example, magnesium supplements), but all this, of course, is very individual.
Self-help measures are helpful if you discuss them with your doctor. For example, you can do a light relaxing massage against bruxism in the area of the chin and temples. There are also a number of exercises that can help relieve muscle spasms; it is useful to repeat them regularly before bed. Relieve general stress: sleep enough hours, walk more in the fresh air, reduce the amount of coffee and strong tea, take relaxing baths with herbs, avoid anxious situations.
All this will help consolidate the results of complex professional treatment and forget about unpleasant symptoms.